
3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), commonly known as ecstasy, and molly, is an empathogen–entactogenic drug with stimulant and minor psychedelic properties. In studies, it has been used alongside psychotherapy in the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and social anxiety in autism spectrum disorder. The purported pharmacological effects that may be prosocial include altered sensations, increased energy, empathy, and pleasure. When taken by mouth, effects begin in 30 to 45 minutes and last three to six hours.

Methcathinone is a monoamine alkaloid and psychoactive stimulant, a substituted cathinone. It is used as a recreational drug due to its potent stimulant and euphoric effects and is considered to be addictive, with both physical and psychological withdrawal occurring if its use is discontinued after prolonged or high-dosage administration. It is usually snorted, but can be smoked, injected, or taken orally.

Cathine, also known as D-norpseudoephedrine or as (+)-norpseudoephedrine, is a psychoactive drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine groups which acts as a stimulant. Along with cathinone, it is found naturally in Catha edulis (khat), and contributes to the overall effects of the plant. Cathine has approximately 7 to 10% of the potency of amphetamine.
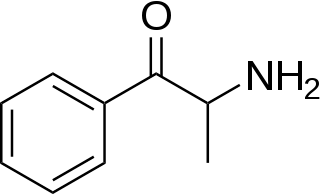
Cathinone is a monoamine alkaloid found in the shrub Catha edulis (khat) and is chemically similar to ephedrine, cathine, methcathinone and other amphetamines. It is probably the main contributor to the stimulant effect of Catha edulis, also known as khat. Cathinone differs from many other amphetamines in that it has a ketone functional group. Other phenethylamines that share this structure include the stimulants methcathinone, MDPV, mephedrone and the antidepressant bupropion.

3,4-Methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA), sometimes referred to as sass, is an empathogen-entactogen, stimulant, and psychedelic drug of the amphetamine family that is encountered mainly as a recreational drug. In its pharmacology, MDA is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA). In most countries, the drug is a controlled substance and its possession and sale are illegal.
Phentermine, sold under the brand name Adipex-P among others, is a medication used together with diet and exercise to treat obesity. It is available by itself or as the combination phentermine/topiramate. Phentermine is taken by mouth.
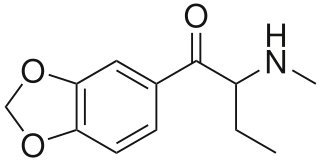
Butylone, also known as β-keto-N-methylbenzodioxolylbutanamine (βk-MBDB), is an entactogen, psychedelic, and stimulant psychoactive drug of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, phenylisobutylamine, and cathinone families. It is the β-keto analogue of MBDB and the substituted methylenedioxyphenethylamine analogue of buphedrone.

Etilamfetamine, also known as N-ethylamphetamine and formerly sold under the brand names Apetinil and Adiparthrol, is a stimulant drug of the amphetamine family. It was invented in the early 20th century and was subsequently used as an anorectic or appetite suppressant in the 1950s, but was not as commonly used as other amphetamines such as amphetamine, methamphetamine, and benzphetamine, and was largely discontinued once newer drugs such as phenmetrazine were introduced.

Propylamphetamine is a psychostimulant of the amphetamine family which was never marketed. It was first developed in the 1970s, mainly for research into the metabolism of, and as a comparison tool to, other amphetamines.

Norfenfluramine, or 3-trifluoromethylamphetamine, is a never-marketed drug of the amphetamine family and a major active metabolite of the appetite suppressants fenfluramine and benfluorex. The compound is a racemic mixture of two enantiomers with differing activities, dexnorfenfluramine and levonorfenfluramine.

Methedrone is a recreational drug of the cathinone chemical class. Chemically, methedrone is closely related to para-methoxymethamphetamine (PMMA), methylone and mephedrone. Methedrone received media attention in 2009 after the death of two young Swedish men. In both cases toxicology analysis showed methedrone was the only drug present in both men during the time of their overdose and subsequent deaths.

Mephedrone, also known as 4-methylmethcathinone, 4-MMC, and 4-methylephedrone, is a synthetic stimulant drug belonging to the amphetamine and cathinone classes. It is commonly referred to by slang names such as drone, M-CAT, White Magic, meow meow,and bubble. Chemically, it is similar to the cathinone compounds found in the Khat plant, native to eastern Africa.

MDAI, also known as 5,6-methylenedioxy-2-aminoindane, is an entactogen drug of the 2-aminoindane group which is related to MDMA and produces similar subjective effects.

A monoamine releasing agent (MRA), or simply monoamine releaser, is a drug that induces the release of one or more monoamine neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron into the synapse, leading to an increase in the extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitters and hence enhanced signaling by those neurotransmitters. The monoamine neurotransmitters include serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine; MRAs can induce the release of one or more of these neurotransmitters.

4-Methylamphetamine (4-MA), also known by the former proposed brand name Aptrol, is a stimulant and anorectic drug of the amphetamine family. It is structurally related to mephedrone (4-methylmethcathinone).

4-Methylmethamphetamine (4-MMA), also known as mephedrine, is a putative stimulant and entactogen drug of the amphetamine family. It acts as a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA). The drug is the β-deketo analogue of mephedrone and the N-methyl analogue of 4-methylamphetamine (4-MA).

Substituted cathinones, or simply cathinones, which include some stimulants and entactogens, are derivatives of cathinone. They feature a phenethylamine core with an alkyl group attached to the alpha carbon, and a ketone group attached to the beta carbon, along with additional substitutions. Cathinone occurs naturally in the plant khat whose leaves are chewed as a recreational drug.

4-Methylcathinone (4-MC), also known as normephedrone is a stimulant drug of the cathinone group. It is an active metabolite of the better known drug mephedrone.

3',4'-Methylenedioxy-4-methylaminorex (MDMAR) is a recreational designer drug from the substituted aminorex family, with monoamine-releasing effects. It is a potent serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA).

3-Methoxymethcathinone (3-MeOMC), also known as meta-methoxymethcathinone (m-MeOMC), is a designer drug of the substituted cathinone family described as a stimulant.






















