
Empathogens or entactogens are a class of psychoactive drugs that induce the production of experiences of emotional communion, oneness, relatedness, emotional openness—that is, empathy or sympathy—as particularly observed and reported for experiences with 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA). This class of drug is distinguished from the classes of hallucinogen or psychedelic, and amphetamine or stimulants. Major members of this class include MDMA, MDA, MDEA, MDOH, MBDB, 5-APB, 5-MAPB, 6-APB, 6-MAPB, methylone, mephedrone, GHB, αMT, and αET, MDAI among others. Most entactogens are phenethylamines and amphetamines, although several, such as αMT and αET, are tryptamines. When referring to MDMA and its counterparts, the term MDxx is often used. Entactogens are sometimes incorrectly referred to as hallucinogens or stimulants, although many entactogens such as ecstasy exhibit psychedelic or stimulant properties as well.

3,4-Methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA), sometimes referred to as sass, is an empathogen-entactogen, stimulant, and psychedelic drug of the amphetamine family that is encountered mainly as a recreational drug. In its pharmacology, MDA is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA). In most countries, the drug is a controlled substance and its possession and sale are illegal.
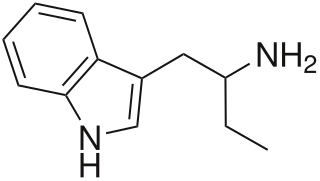
α-Ethyltryptamine, also known as etryptamine, is an entactogen and stimulant drug of the tryptamine family. It was originally developed and marketed as an antidepressant under the brand name Monase by Upjohn in the 1960s before being withdrawn due to toxicity.
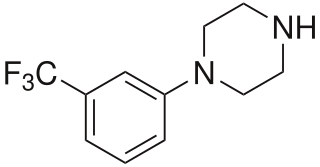
3-Trifluoromethylphenylpiperazine (TFMPP) is a recreational drug of the phenylpiperazine chemical class and is a substituted piperazine. Usually in combination with benzylpiperazine (BZP) and other analogues, it is sold as an alternative to the illicit drug MDMA ("Ecstasy").

(–)-Benzofuranylpropylaminopentane is an experimental drug related to selegiline which acts as a monoaminergic activity enhancer (MAE). It is orally active in animals.

para-Chloroamphetamine (PCA), also known as 4-chloroamphetamine (4-CA), is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA) and serotonergic neurotoxin of the amphetamine family. It is used in scientific research in the study of the serotonin system, as a serotonin releasing agent (SRA) at lower doses to produce serotonergic effects, and as a serotonergic neurotoxin at higher doses to produce long-lasting depletions of serotonin.

A serotonin releasing agent (SRA) is a type of drug that induces the release of serotonin into the neuronal synaptic cleft. A selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) is an SRA with less significant or no efficacy in producing neurotransmitter efflux at other types of monoamine neurons, including dopamine and norepinephrine neurons.

A serotonin–dopamine releasing agent (SDRA) is a type of drug which induces the release of serotonin and dopamine in the body and/or brain.

5-(2-Aminopropyl)indole is an indole and phenethylamine derivative with empathogenic effects. Its preparation was first reported by Albert Hofmann in 1962. It is a designer drug that has been openly sold as a recreational drug by online vendors since 2011.
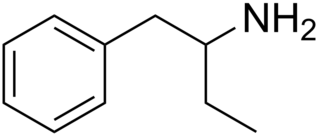
Phenylisobutylamine, also known as α-ethylphenethylamine (AEPEA) or as butanphenamine (B), is a stimulant drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine families. It is a higher homologue of amphetamine, differing from amphetamine's molecular structure only by the substitution of the methyl group at the alpha position of the side chain with an ethyl group.

6-(2-Aminopropyl)-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran is a stimulant and entactogen drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine classes. It is an analogue of MDA where the heterocyclic 4-position oxygen from the 3,4-methylenedioxy ring has been replaced with a methylene bridge. 5-APDB (3-Desoxy-MDA) is an analogue of 6-APDB where the 3-position oxygen has been replaced with a methylene instead. 6-APDB, along with 5-APDB, was first synthesized by David E. Nichols in the early 1990s while investigating non-neurotoxic MDMA analogues.
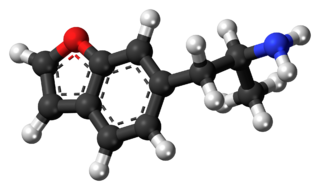
6-APB is an empathogenic psychoactive drug of the substituted benzofuran and substituted phenethylamine classes. 6-APB and other compounds are sometimes informally called "Benzofury" in newspaper reports. It is similar in structure to MDA, but differs in that the 3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl ring system has been replaced with a benzofuran ring. 6-APB is also the unsaturated benzofuran derivative of 6-APDB. It may appear as a tan grainy powder.

5-APB is an empathogenic psychoactive compound of the substituted benzofuran, substituted amphetamine and substituted phenethylamine classes. 5-APB and other compounds are sometimes informally called "Benzofury".
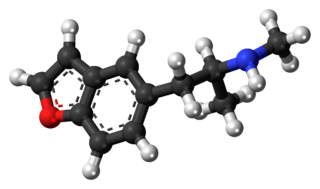
5-MAPB, also known as 5-(N-methyl-2-aminopropyl)benzofuran, is an entactogen and designer drug of the amphetamine family that is similar to MDMA in its structure and effects.

5-Chloro-α-methyltryptamine (5-Chloro-αMT), also known as PAL-542, is a tryptamine derivative related to α-methyltryptamine (αMT) and one of only a few known serotonin–dopamine releasing agents (SDRAs). It is also a potent serotonin 5-HT2A receptor agonist and hence may be a serotonergic psychedelic. The drug has been investigated in animals as a potential treatment for cocaine dependence.

Substituted phenylmorpholines, or substituted phenmetrazines alternatively, are chemical derivatives of 2-phenylmorpholine or of the psychostimulant drug phenmetrazine. Most such compounds act as releasers of monoamine neurotransmitters, and have stimulant effects. Some also act as agonists at serotonin receptors, and compounds with an N-propyl substitution act as dopamine receptor agonists. A number of derivatives from this class have been investigated for medical applications, such as for use as anorectics or medications for the treatment of ADHD. Some compounds have also become subject to illicit use as designer drugs.

The substituted benzofurans are a class of chemical compounds based on the heterocyclyc and polycyclic compound benzofuran. Many medicines use the benzofuran core as a scaffold, but most commonly the term is used to refer to the simpler compounds in this class which include numerous psychoactive drugs, including stimulants, psychedelics and empathogens. In general, these compounds have a benzofuran core to which a 2-aminoethyl group is attached, and combined with a range of other substituents. Some psychoactive derivatives from this family have been sold under the name Benzofury.
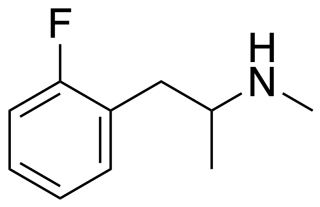
The Borax combo, also known by the informal brand names Blue Bliss and Pink Star, is a combination recreational and designer drug described as an MDMA-like entactogen.

6-MBPB, also known as 6-(2-methylaminobutyl)benzofuran (6-MABB), is a monoamine releasing agent (MRA) and entactogen-like drug of the amphetamine, phenylisobutylamine, and benzofuran families. It is a positional isomer of 5-MBPB (5-MABB).

The substituted benzothiophenes are a class of chemical compounds based on benzothiophene. They are closely related to the substituted benzofurans, substituted tryptamines, and to other chemical groups such as the substituted benzodioxoles.




















