
Empathogens or entactogens are a class of psychoactive drugs that induce the production of experiences of emotional communion, oneness, relatedness, emotional openness—that is, empathy or sympathy—as particularly observed and reported for experiences with 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA). This class of drug is distinguished from the classes of hallucinogen or psychedelic, and amphetamine or stimulants. Major members of this class include MDMA, MDA, MDEA, MDOH, MBDB, 5-APB, 5-MAPB, 6-APB, 6-MAPB, methylone, mephedrone, GHB, αMT, and αET, MDAI among others. Most entactogens are phenethylamines and amphetamines, although several, such as αMT and αET, are tryptamines. When referring to MDMA and its counterparts, the term MDxx is often used. Entactogens are sometimes incorrectly referred to as hallucinogens or stimulants, although many entactogens such as ecstasy exhibit psychedelic or stimulant properties as well.

3,4-Methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA), sometimes referred to as sass, is an empathogen-entactogen, stimulant, and psychedelic drug of the amphetamine family that is encountered mainly as a recreational drug. In its pharmacology, MDA is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA). In most countries, the drug is a controlled substance and its possession and sale are illegal.
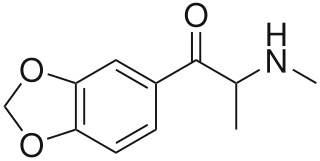
Methylone, also known as 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylcathinone (MDMC), is an entactogen and stimulant drug of the amphetamine, cathinone, and benzodioxole families related to 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine. It is the β-keto or cathinone analogue of MDMA. Methylone is usually taken orally, but is also used by other routes.

3,4-Ethylenedioxy-N-methylamphetamine (EDMA) is an entactogen drug of the methamphetamine class. It is an analogue of MDMA where the methylenedioxy ring has been replaced by an ethylenedioxy ring. EDMA was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the dosage is listed as 150–250 mg, and the duration listed as 3–5 hours. According to Shulgin, EDMA produces a bare threshold consisting of paresthesia, nystagmus, and hypnogogic imagery, with few to no other effects.

MDAI, also known as 5,6-methylenedioxy-2-aminoindane, is an entactogen drug of the 2-aminoindane group which is related to MDMA and produces similar subjective effects.

A monoamine releasing agent (MRA), or simply monoamine releaser, is a drug that induces the release of one or more monoamine neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron into the synapse, leading to an increase in the extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitters and hence enhanced signaling by those neurotransmitters. The monoamine neurotransmitters include serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine; MRAs can induce the release of one or more of these neurotransmitters.

5-Iodo-2-aminoindane (5-IAI) is an entactogen drug of the 2-aminoindane group. Human anecdotal reports suggest that it is entactogenic but produces little euphoria or stimulation.

A serotonin releasing agent (SRA) is a type of drug that induces the release of serotonin into the neuronal synaptic cleft. A selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) is an SRA with less significant or no efficacy in producing neurotransmitter efflux at other types of monoamine neurons, including dopamine and norepinephrine neurons.

A dopamine releasing agent (DRA) is a type of drug which induces the release of dopamine in the body and/or brain.
A serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA), also known as a triple releasing agent (TRA), is a type of drug which induces the release of serotonin, norepinephrine/epinephrine, and dopamine in the brain and body. SNDRAs produce euphoriant, entactogen, and psychostimulant effects, and are almost exclusively encountered as recreational drugs.
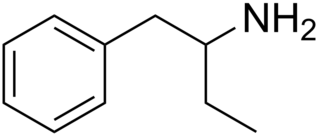
Phenylisobutylamine, also known as α-ethylphenethylamine (AEPEA) or as butanphenamine (B), is a stimulant drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine families. It is a higher homologue of amphetamine, differing from amphetamine's molecular structure only by the substitution of the methyl group at the alpha position of the side chain with an ethyl group.
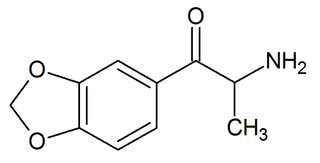
3,4-Methylenedioxycathinone, also known as β-keto-3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (βk-MDA), is an entactogen and stimulant drug of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and cathinone families. It is the β-keto analogue of MDA.
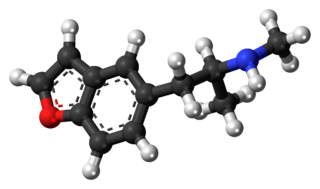
5-MAPB, also known as 5-(N-methyl-2-aminopropyl)benzofuran, is an entactogen and designer drug of the amphetamine family that is similar to MDMA in its structure and effects.

4-Hydroxy-3-methoxymethamphetamine (HMMA) is an active metabolite of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA). It is a slightly more potent stimulant than MDMA in rodents. The drug is substantially less potent than MDMA as a monoamine releasing agent in vitro. Nonetheless, HMMA has been found to induce the release of serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine with EC50Tooltip half-maximal effective concentration values of 589 nM, 625 nM, and 607–2884 nM, respectively, and hence acts as a lower-potency serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA). The predicted log P of HMMA is 1.2.

5-MBPB is an amphetamine and phenylisobutylamine derivative which is structurally related to MDMA and has been sold as a designer drug. It can be described as the benzofuran-5-yl analogue of MBDB or the butanamine homologue of 5-MAPB, and is also a structural isomer of 5-EAPB and 6-EAPB. Anecdotal reports suggest this compound has been sold as a designer drug in various European countries since early 2015, but the first definitive identification was made in December 2015 by a forensic laboratory in Slovenia.
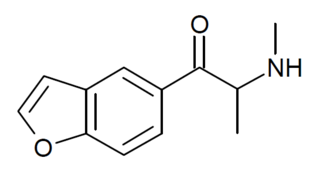
βk-5-MAPB, or BK-5-MAPB, is an entactogen of the benzofuran and cathinone groups which is related to both 5-MAPB and methylone. It was patented by Matthew Baggott and Tactogen and is under investigation by Tactogen for potential medical use.

(R)-3,4-Methylenedioxy-N-methylamphetamine ((R)-MDMA), also known as (R)-midomafetamine or as levo-MDMA, is the (R)- or levorotatory (l-) enantiomer of 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylamphetamine (MDMA; midomafetamine; "ecstasy"), a racemic mixture of (R)-MDMA and (S)-MDMA. Like MDMA, (R)-MDMA is an entactogen or empathogen. It is taken by mouth.
The Borax combo, also known by the informal brand names Blue Bliss and Pink Star, is a combination recreational and designer drug described as an MDMA-like entactogen.

4-Methylthiomethamphetamine, also known as N-methyl-4-methylthioamphetamine (NMMTA), is a monoamine releasing agent (MRA) of the amphetamine family related to 4-methylthioamphetamine (4-MTA) and N,N-dimethyl-4-methylthioamphetamine. Much less is known about 4-MTMA compared to 4-MTA.
Tactogen is a public benefit corporation and start-up pharmaceutical company based in Palo Alto, California that is developing novel MDMA-like entactogens and psychedelics as medicines. Its stated goal is to develop new MDMA-like drugs with improved effectiveness, tolerability, and safety, as well as gentleness and accessibility, for treatment of psychiatric disorders and other conditions. Tactogen was co-founded by neuroscientist Matthew J. Baggott and Luke Pustejovsky in 2020. Baggott is the chief executive officer (CEO) while Pustejovsky is the chief operating officer (COO).

















