
Empathogens or entactogens are a class of psychoactive drugs that induce the production of experiences of emotional communion, oneness, relatedness, emotional openness—that is, empathy or sympathy—as particularly observed and reported for experiences with 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA). This class of drug is distinguished from the classes of hallucinogen or psychedelic, and amphetamine or stimulants. Major members of this class include MDMA, MDA, MDEA, MDOH, MBDB, 5-APB, 5-MAPB, 6-APB, 6-MAPB, methylone, mephedrone, GHB, αMT, and αET, MDAI among others. Most entactogens are phenethylamines and amphetamines, although several, such as αMT and αET, are tryptamines. When referring to MDMA and its counterparts, the term MDxx is often used. Entactogens are sometimes incorrectly referred to as hallucinogens or stimulants, although many entactogens such as ecstasy exhibit psychedelic or stimulant properties as well.

Indanorex (Dietor) is a stimulant drug which was developed in the 1970s. It has appetite suppressant effects and also has antihypoglycemia effects.

MEAI, also known as 5-methoxy-2-aminoindane (5-MeO-AI), is a monoamine releasing agent of the 2-aminoindane group. It specifically acts as a selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA). The drug is under development for the treatment of alcoholism, cocaine use disorder, metabolic syndrome, and obesity under the developmental code name CMND-100.

MDAI, also known as 5,6-methylenedioxy-2-aminoindane, is an entactogen drug of the 2-aminoindane group which is related to MDMA and produces similar subjective effects.

3-Methoxy-4-methylamphetamine (MMA) is an entactogen and psychedelic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine classes. It was first synthesized in 1970 and was encountered as a street drug in Italy in the same decade. MMA was largely forgotten until being reassayed by David E. Nichols as a non-neurotoxic MDMA analogue in 1991, and has subsequently been sold as a designer drug on the internet since the late 2000s.
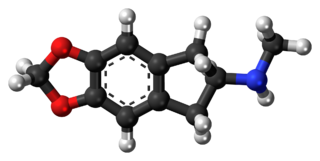
5,6-Methylenedioxy-N-methyl-2-aminoindane (MDMAI), is a drug of the 2-aminoindane group developed in the 1990s by a team led by David E. Nichols at Purdue University. It acts as a non-neurotoxic and highly selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) in animals and a putative entactogen in humans.

5-Iodo-2-aminoindane (5-IAI) is an entactogen drug of the 2-aminoindane group. Human anecdotal reports suggest that it is entactogenic but produces little euphoria or stimulation.

2-Aminoindane (2-AI) is an aminoindane and research chemical with applications in neurologic disorders and psychotherapy that has also been sold as a designer drug. It acts as a selective substrate for NET and DAT.

N-Ethyl-5-trifluoromethyl-2-aminoindane (ETAI) is a drug of the 2-aminoindane group with putative entactogenic effects. It functions as a selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA). ETAI is the aminoindane analogue of fenfluramine and is approximately 50% as neurotoxic in comparison.

5-Trifluoromethyl-2-aminoindane (TAI) is a drug of the 2-aminoindane group with putative entactogenic effects. It functions as a selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA). TAI is the aminoindane analogue of norfenfluramine and is approximately 50% as neurotoxic in comparison.

para-Iodoamphetamine (PIA), also known as 4-iodoamphetamine (4-IA), is a monoamine releasing agent (MRA) and serotonergic neurotoxin of the amphetamine family related to para-chloroamphetamine (PCA).

2-Amino-1,2-dihydronapthalene is a stimulant drug. It is a rigid analogue of phenylisobutylamine and substitutes for amphetamine in rat drug discrimination tests, although at approximately one-fourth the potency.

1-Aminomethyl-5-methoxyindane (AMMI), is a drug developed by a team led by David E. Nichols at Purdue University, which acts as a selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) and binds to the serotonin transporter with similar affinity relative to DFMDA.
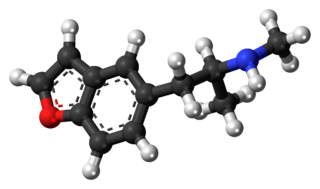
5-MAPB, also known as 5-(N-methyl-2-aminopropyl)benzofuran, is an entactogen and designer drug of the amphetamine family that is similar to MDMA in its structure and effects.

NM-2-AI, also known as N-methyl-2-aminoindane, is a drug of the 2-aminoindane group that has been sold online as a designer drug. It is a rigid analogue of methamphetamine. NM-2-AI acts as a selective norepinephrine releasing agent, but also has affinity for several monoamine receptors.
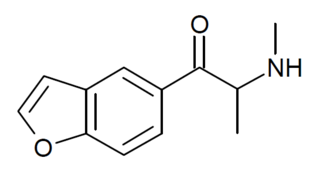
βk-5-MAPB, or BK-5-MAPB, is an entactogen of the benzofuran and cathinone groups which is related to both 5-MAPB and methylone. It was patented by Matthew Baggott and Tactogen and is under investigation by Tactogen for potential medical use.

BK-NM-AMT, or βk-NM-αMT, also known as β-keto-N-methyl-αMT or as α,N-dimethyl-β-ketotryptamine, is a serotonin–dopamine releasing agent (SDRA) and putative entactogen of the tryptamine, α-alkyltryptamine, and β-ketotryptamine families. Along with certain other tryptamines, such as α-ethyltryptamine (αET), 5-chloro-αMT and 5-fluoro-αET, it is one of the few SDRAs known.
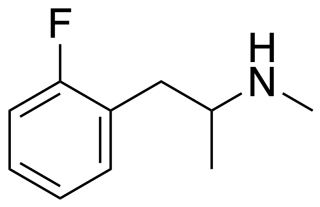
The Borax combo, also known by the informal brand names Blue Bliss and Pink Star, is a combination recreational and designer drug described as an MDMA-like entactogen.

6-MBPB, also known as 6-(2-methylaminobutyl)benzofuran (6-MABB), is a monoamine releasing agent (MRA) and entactogen-like drug of the amphetamine, phenylisobutylamine, and benzofuran families. It is a positional isomer of 5-MBPB (5-MABB).
Matthew John Baggott, PhD is an American neuroscientist who studies entactogens, hallucinogens, and other psychoactive drugs. He is one of the leading experts on MDMA and other entactogens per Hamilton Morris and is an important figure in the psychedelic medicine movement.




















