
Benzylpiperazine (BZP) is a substance often used as a recreational drug and is known to have euphoriant and stimulant properties. Several studies conducted between 2000 and 2011 found that the effects of BZP are similar to amphetamine, although BZP's dosage is roughly 10 times higher by weight.
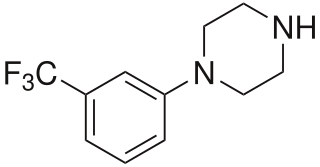
3-Trifluoromethylphenylpiperazine (TFMPP) is a recreational drug of the phenylpiperazine chemical class and is a substituted piperazine. Usually in combination with benzylpiperazine (BZP) and other analogues, it is sold as an alternative to the illicit drug MDMA ("Ecstasy").

Piperazine is an organic compound that consists of a six-membered ring containing two nitrogen atoms at opposite positions in the ring. Piperazine exists as small alkaline deliquescent crystals with a saline taste.

Trazodone, sold under many brand names, is an antidepressant medication, used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and insomnia. It is a phenylpiperazine compound of the serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor (SARI) class. The medication is taken orally.

Nefazodone, sold formerly under the brand names Serzone, Dutonin, and Nefadar among others, is an atypical antidepressant medication which is used in the treatment of depression and for other uses. Nefazodone is still available in the United States, but was withdrawn from other countries due to rare liver toxicity. The medication is taken by mouth.

Vanoxerine is an investigational drug which is being evaluated for the treatment of heart arrhythmias and cocaine dependence. Vanoxerine is a piperazine derivative which has multiple pharmacological activities including acting as an dopamine reuptake inhibitor, serotonin transporter inhibitor, and as a blocker of the cardiac hERG repolarizing potassium channel (IKr).

Etoperidone, associated with several brand names, is an atypical antidepressant which was developed in the 1970s and either is no longer marketed or was never marketed. It is a phenylpiperazine related to trazodone and nefazodone in chemical structure and is a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor (SARI) similarly to them.

meta-Chlorophenylpiperazine (mCPP) is a psychoactive drug of the phenylpiperazine class. It was initially developed in the late-1970s and used in scientific research before being sold as a designer drug in the mid-2000s. It has been detected in pills touted as legal alternatives to illicit stimulants in New Zealand and pills sold as "ecstasy" in Europe and the United States.

para-Methoxyphenylpiperazine is a piperazine derivative with stimulant effects which has been sold as an ingredient in "Party pills", initially in New Zealand and subsequently in other countries around the world.

para-Fluorophenylpiperazine is a piperazine derivative with mildly psychedelic and euphoriant effects. It has been sold as an ingredient in legal recreational drugs known as "Party pills", initially in New Zealand and subsequently in other countries around the world.

Niaprazine (INN) is a sedative-hypnotic drug of the phenylpiperazine group. It has been used in the treatment of sleep disturbances since the early 1970s in several European countries including France, Italy, and Luxembourg. It is commonly used with children and adolescents on account of its favorable safety and tolerability profile and lack of abuse potential.
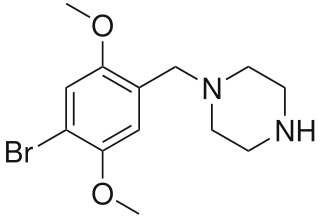
4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxy-1-benzylpiperazine (2C-B-BZP) is a psychoactive drug and research chemical of the piperazine chemical class which has been sold as a "designer drug". It produces stimulant effects similar to those of benzylpiperazine (BZP).

Midafotel is a potent, competitive antagonist at the NMDA receptor. It was originally designed as a potential therapy for excitotoxicity, epilepsy or neuropathic pain. It looked very promising in in vitro trials proving to be a potent competitive antagonist at the NMDA without affecting other receptors. Research continued through to in vivo cat studies where it proved to limit damage after occluding the middle cerebral artery, leading to ischaemia. It also blocked photosensitive epilepsies in baboons.

Fluprazine (DU-27,716) is a drug of the phenylpiperazine class. It is a so-called serenic or antiaggressive agent. It is closely related to several other piperazines, including eltoprazine and batoprazine, and TFMPP, as well as more distantly to the azapirones such as buspirone. The pharmacology of fluprazine is unknown, but it is likely to act as an agonist at the 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors like its sister compound eltoprazine.

Mepiprazole is an anxiolytic drug of the phenylpiperazine group with additional antidepressant properties that is marketed in Spain. It acts as a 5-HT2A and α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist and inhibits the reuptake and induces the release of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine to varying extents, and has been described as a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor (SARI). Controlled clinical trials of mepiprazole in patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) were also carried out and suggested some benefits of the drug in relieving symptoms of IBS in some patients. Similarly to other phenylpiperazines like trazodone, nefazodone, and etoperidone, mepiprazole produces mCPP as an active metabolite.

2,3-Dichlorophenylpiperazine (2,3-DCPP or DCPP) is a chemical compound from the phenylpiperazine family. It is both a precursor in the synthesis of aripiprazole and one of its metabolites. It is unclear whether 2,3-DCPP is pharmacologically active as a serotonin receptor agonist similar to its close analogue 3-chlorophenylpiperazine (mCPP), though it has been shown to act as a partial agonist of the dopamine D2 and D3 receptors.
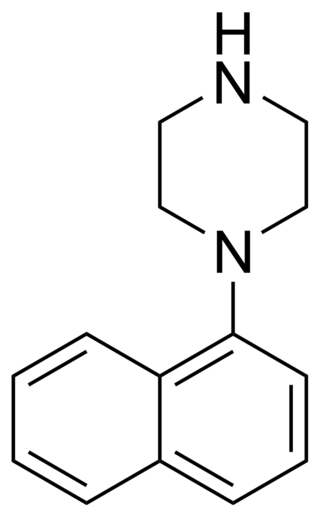
1-(1-Naphthyl)piperazine (1-NP) is a drug which is a phenylpiperazine derivative. It acts as a non-selective, mixed serotonergic agent, exerting partial agonism at the 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D, 5-HT1E, and 5-HT1F receptors, while antagonizing the 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C receptors. It has also been shown to possess high affinity for the 5-HT3, 5-HT5A, 5-HT6, and 5-HT7 receptors, and may bind to 5-HT4 and the SERT as well. In animals it produces effects including hyperphagia, hyperactivity, and anxiolysis, of which are all likely mediated predominantly or fully by blockade of the 5-HT2C receptor.

MT-45 (IC-6) is an opioid analgesic drug invented in the 1970s by Dainippon Pharmaceutical Co. It is chemically a 1-substituted-4-(1,2-diphenylethyl) piperazine derivative, which is structurally unrelated to most other opioid drugs. Racemic MT-45 has around 80% the potency of morphine, with almost all opioid activity residing in the (S) enantiomer. It has been used as a lead compound from which a large family of potent opioid drugs have been developed, including full agonists, partial agonists, and antagonists at the three main opioid receptor subtypes. Fluorinated derivatives of MT-45 such as 2F-MT-45 are significantly more potent as μ-opioid receptor agonists, and one of its main metabolites 1,2-diphenylethylpiperazine also blocks NMDA receptors.
5-HT2C receptor agonists are a class of drugs that activate 5-HT2C receptors. They have been investigated for the treatment of a number of conditions including obesity, psychiatric disorders, sexual dysfunction and urinary incontinence.
Substituted piperazines are a class of chemical compounds based on a piperazine core. Some are used as recreational drugs and some are used in scientific research.


















