
APINACA (AKB48, N-(1-adamantyl)-1-pentyl-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide) is a drug that acts as a reasonably potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors. It is a full agonist at CB1 with an EC50 of 142 nM and Ki of 3.24 nM (compared to the Ki of Δ9-THC at 28.35 nM and JWH-018 at 9.62 nM), while at CB2 it acts as a partial agonist with an EC50 of 141 nM and Ki of 1.68 nM (compared to the Ki of Δ9-THC at 37.82 nM and JWH-018 at 8.55 nM). Its pharmacological characterization has also been reported in a discontinued patent application. It had never previously been reported in the scientific or patent literature, and was first identified by laboratories in Japan in March 2012 as an ingredient in synthetic cannabis smoking blends, along with a related compound APICA. Structurally, it closely resembles cannabinoid compounds from a University of Connecticut patent, but with a simple pentyl chain on the indazole 1-position, and APINACA falls within the claims of this patent despite not being disclosed as an example.

AB-PINACA is a compound that was first identified as a component of synthetic cannabis products in Japan in 2012.

ADBICA (also known as ADB-PICA) is a designer drug identified in synthetic cannabis blends in Japan in 2013. ADBICA had not previously been reported in the scientific literature prior to its sale as a component of synthetic cannabis blends. ADBICA features a carboxamide group at the 3-indole position, like SDB-001 and STS-135. The stereochemistry of the tert-butyl side-chain in the product is unresolved, though in a large series of indazole derivatives structurally similar to ADBICA that are disclosed in Pfizer patent WO 2009/106980, activity resides exclusively in the (S) enantiomers. ADBICA is a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor and CB2 receptor with an EC50 value of 0.69 nM and 1.8 nM respectively.

ADB-FUBINACA (ADMB-FUBINACA) is a designer drug identified in synthetic cannabis blends in Japan in 2013. In 2018, it was the third-most common synthetic cannabinoid identified in drugs seized by the Drug Enforcement Administration.

AB-CHMINACA is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid. It is a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor (Ki = 0.78 nM) and CB2 receptor (Ki = 0.45 nM) and fully substitutes for Δ9-THC in rat discrimination studies, while being 16x more potent. Continuing the trend seen in other cannabinoids of this generation, such as AB-FUBINACA and AB-PINACA, it contains a valine amino acid amide residue as part of its structure, where older cannabinoids contained a naphthyl or adamantane residue.
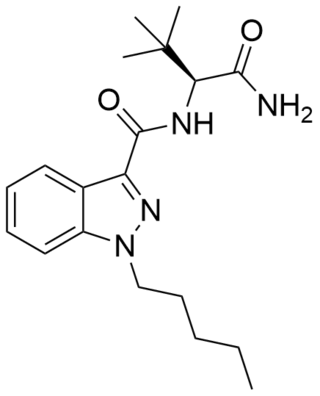
ADB-PINACA is a cannabinoid designer drug that is an ingredient in some synthetic cannabis products. It is a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor and CB2 receptor with EC50 values of 0.52 nM and 0.88 nM respectively. Like MDMB-FUBINACA, this compound incorporates the unnatural amino acid tert-leucine.

5F-ADB (also known as MDMB-5F-PINACA and 5F-MDMB-PINACA) is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid from the indazole-3-carboxamide family, which has been used as an active ingredient in synthetic cannabis products and has been sold online as a designer drug. 5F-ADB is a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor, though it is unclear whether it is selective for this target. 5F-ADB was first identified in November 2014 from post-mortem samples taken from an individual who had died after using a product containing this substance. Subsequent testing identified 5F-ADB to have been present in a total of ten people who had died from unexplained drug overdoses in Japan between September 2014 and December 2014. 5F-ADB is believed to be extremely potent based on the very low levels detected in tissue samples, and appears to be significantly more toxic than earlier synthetic cannabinoid drugs that had previously been sold.
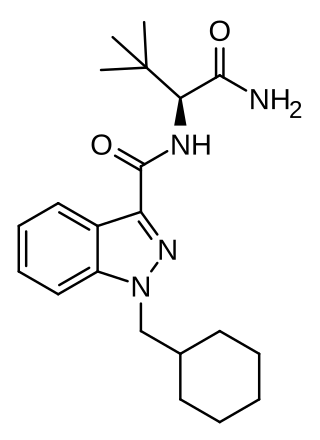
ADB-CHMINACA (also known as ADMB-CHMINACA and MAB-CHMINACA) is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid. It is a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor with a binding affinity of Ki = 0.289 nM and was originally developed by Pfizer in 2009 as an analgesic medication. It was identified in cannabinoid blends in Japan in early 2015.

5F-APINACA is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid that has been sold online as a designer drug. Structurally it closely resembles cannabinoid compounds from patent WO 2003/035005 but with a 5-fluoropentyl chain on the indazole 1-position, and 5F-APINACA falls within the claims of this patent, as despite not being disclosed as an example, it is very similar to the corresponding pentanenitrile and 4-chlorobutyl compounds which are claimed as examples 3 and 4.

5F-CUMYL-PINACA (also known as SGT-25 and sometimes sold in e-cigarette form as C-Liquid) is an indazole-3-carboxamide based synthetic cannabinoid. 5F-CUMYL-PINACA acts as a potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors, with the original patent claiming approximately 4x selectivity for CB1, having an EC50 of <0.1 nM for human CB1 receptors and 0.37 nM for human CB2 receptors. In more recent assays using different techniques, 5F-CUMYL-PINACA was variously found to have an EC50 of 0.43 nM at CB1 and 11.3 nM at CB2, suggesting a somewhat higher CB1 selectivity of 26 times, or alternatively 15.1 nM at CB1 and 34.8 nM at CB2 with only 2.3 times selectivity, however these figures cannot be directly compared due to the different assay techniques used in each case.
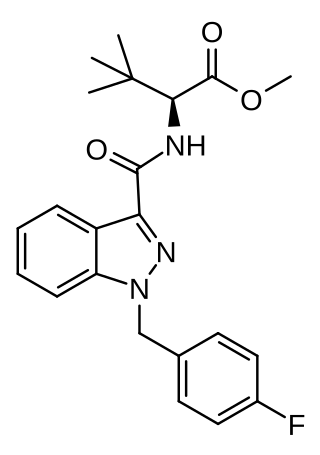
MDMB-FUBINACA (also known as MDMB(N)-Bz-F and FUB-MDMB) is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid that is a potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors, with Ki values of 1.14 nM at CB1 and 0.1228 nM at CB2 and EC50 values of 0.2668 nM at CB1 and 0.1411 nM at CB2, and has been sold online as a designer drug. Its benzyl analogue (instead of 4-fluorobenzyl) has been reported to be a potent agonist for the CB1 receptor (Ki = 0.14 nM, EC50 = 2.42 nM). The structure of MDMB-FUBINACA contains the amino acid, 3-methylvaline or tert-leucine methyl ester.
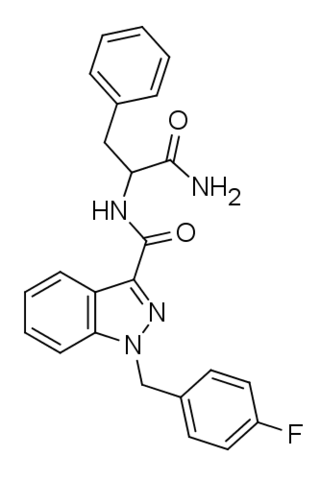
APP-FUBINACA is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid that has been sold online as a designer drug. Pharmacological testing showed APP-FUBINACA to have only moderate affinity for the CB1 receptor, with a Ki of 708 nM, while its EC50 was not tested. It contains a phenylalanine amino acid residue in its structure.

5F-ADB-PINACA is a cannabinoid designer drug that is an ingredient in some synthetic cannabis products. It is a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor and CB2 receptor with EC50 values of 0.24 nM and 2.1 nM respectively.

AMB-FUBINACA (also known as FUB-AMB and MMB-FUBINACA) is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid that is a potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors, with Ki values of 10.04 nM at CB1 and 0.786 nM at CB2 and EC50 values of 0.5433 nM at CB1 and 0.1278 nM at CB2, and has been sold online as a designer drug. It was originally developed by Pfizer which described the compound in a patent in 2009, but was later abandoned and never tested on humans. AMB-FUBINACA was the most common synthetic cannabinoid identified in drug seizures by the Drug Enforcement Administration in 2017 and the first half of 2018.

AMB-CHMINACA or MMB-CHMINACA (also known as MA-CHMINACA) is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid that is a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor and has been sold online as a designer drug.

FUB-144 (also known as FUB-UR-144) is an indole-based synthetic cannabinoid that is presumed to be a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor and has been sold online as a designer drug. It is an analogue of UR-144 and XLR-11 where the pentyl chain has been replaced with fluorobenzyl.
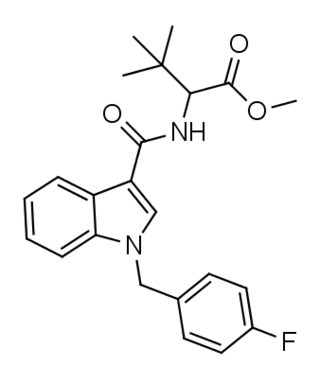
MDMB-FUBICA is an indole-based synthetic cannabinoid that is presumed to be a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor and has been sold online as a designer drug.

5F-MDMB-PICA (MDMB-5F-PICA) is a designer drug and synthetic cannabinoid. In 2018, it was the fifth-most common synthetic cannabinoid identified in drugs seized by the Drug Enforcement Administration.

5F-EDMB-PINACA is a designer drug and synthetic cannabinoid. In 2018, it was the fourth-most common synthetic cannabinoid identified in drugs seized by the Drug Enforcement Administration.

4F-MDMB-BINACA (also known as MDMB-4F-BINACA, 4F-MDMB-BUTINACA or 4F-ADB) is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid from the indazole-3-carboxamide family. It should not be confused with the amantadine analogue 4F-ABINACA. It has been used as an active ingredient in synthetic cannabis products and sold as a designer drug since late 2018. 4F-MDMB-BINACA is an agonist of the CB1 receptor (EC50 = 7.39 nM), though it is unclear whether it is selective for this target. In December 2019, the UNODC announced scheduling recommendations placing 4F-MDMB-BINACA into Schedule II throughout the world.




















