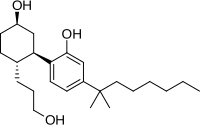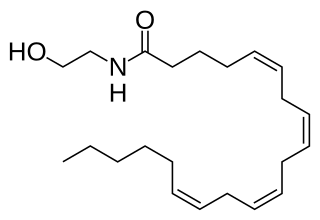
Anandamide (ANA), also referred to as N-arachidonoylethanolamine (AEA) is a fatty acid neurotransmitter belonging to the fatty acid derivative group known as N-acylethanolamine (NAE). Anandamide takes its name from the Sanskrit word ananda, meaning "joy, bliss, delight," plus amide. Anandamide, the first discovered endocannabinoid, engages with the body's endocannabinoid system by binding to the same cannabinoid receptors that THC found in cannabis acts on. Anandamide can be found within tissues in a wide range of animals. It has also been found in plants, such as the cacao tree.

Cannabinoids are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is also a major constituent of temperate cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 100 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea.

Cannabinoid receptors, located throughout the body, are part of the endocannabinoid system of vertebrates– a class of cell membrane receptors in the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. As is typical of G protein-coupled receptors, the cannabinoid receptors contain seven transmembrane spanning domains. Cannabinoid receptors are activated by three major groups of ligands:

WIN 55,212-2 is a chemical described as an aminoalkylindole derivative, which produces effects similar to those of cannabinoids such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) but has an entirely different chemical structure.

The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a biological system composed of endocannabinoids, which are neurotransmitters that bind to cannabinoid receptors, and cannabinoid receptor proteins that are expressed throughout the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. The endocannabinoid system is still not fully understood, but may be involved in regulating physiological and cognitive processes, including fertility, pregnancy, pre- and postnatal development, various activity of immune system, appetite, pain-sensation, mood, and memory, and in mediating the pharmacological effects of cannabis. The ECS plays an important role in multiple aspects of neural functions, including the control of movement and motor coordination, learning and memory, emotion and motivation, addictive-like behavior and pain modulation, among others.

Levonantradol (CP 50,556-1) is a synthetic cannabinoid analog of dronabinol (Marinol) developed by Pfizer in the 1980s. It is around 30 times more potent than THC, and exhibits antiemetic and analgesic effects via activation of CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors. Levonantradol is not currently used in medicine as dronabinol or nabilone are felt to be more useful for most conditions, however it is widely used in research into the potential therapeutic applications of cannabinoids.

2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) is an endocannabinoid, an endogenous agonist of the CB1 receptor and the primary endogenous ligand for the CB2 receptor. It is an ester formed from the omega-6 fatty acid arachidonic acid and glycerol. It is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system, with cannabinoid neuromodulatory effects. It has been found in maternal bovine and human milk. The chemical was first described in 1994–1995, although it had been discovered some time before that. The activities of phospholipase C (PLC) and diacylglycerol lipase (DAGL) mediate its formation. 2-AG is synthesized from arachidonic acid-containing diacylglycerol (DAG).

2-Arachidonyl glyceryl ether is a putative endocannabinoid discovered by Lumír Hanuš and colleagues at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel. It is an ether formed from the alcohol analog of arachidonic acid and glycerol. Its isolation from porcine brain and its structural elucidation and synthesis were described in 2001.

N-Arachidonyl glycine receptor, also known as G protein-coupled receptor 18 (GPR18), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR18 gene. Along with the other previously orphan receptors GPR55 and GPR119, GPR18 has been found to be a receptor for endogenous lipid neurotransmitters, several of which also bind to cannabinoid receptors. It has been found to be involved in the regulation of intraocular pressure.

G protein-coupled receptor 55 also known as GPR55 is a G protein-coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the GPR55 gene.

Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1), is a G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptor that in humans is encoded by the CNR1 gene. And discovered, by determination and characterization in 1988, and cloned in 1990 for the first time. The human CB1 receptor is expressed in the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system. It is activated by endogenous cannabinoids called endocannabinoids, a group of retrograde neurotransmitters that include lipids, such as anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol; plant phytocannabinoids, such as docosatetraenoylethanolamide found in wild daga, the compound tetrahydrocannabinol which is an active constituent of the psychoactive drug cannabis; and synthetic analogs of tetrahydrocannabinol. CB1 is antagonized by the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabivarin at low doses and at higher doses, it activate the CB1 receptor as an agonist, but with less potency than tetrahydrocannabinol.

The cannabinoid receptor 2(CB2), is a G protein-coupled receptor from the cannabinoid receptor family that in humans is encoded by the CNR2 gene. It is closely related to the cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1), which is largely responsible for the efficacy of endocannabinoid-mediated presynaptic-inhibition, the psychoactive properties of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the active agent in cannabis, and other phytocannabinoids. The principal endogenous ligand for the CB2 receptor is 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG).

JWH-073, a synthetic cannabinoid, is an analgesic chemical from the naphthoylindole family that acts as a full agonist at both the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors. It is somewhat selective for the CB1 subtype, with affinity at this subtype approximately 5× the affinity at CB2. The abbreviation JWH stands for John W. Huffman, one of the inventors of the compound.
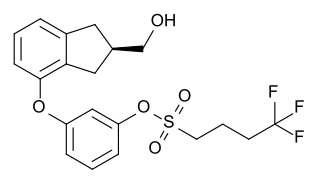
Originally synthesized by chemist Wayne E. Kenney, BAY 38-7271 (KN 38-7271) is a drug which is a cannabinoid receptor agonist developed by Bayer AG. It has analgesic and neuroprotective effects and is used in scientific research, with proposed uses in the treatment of traumatic brain injury. It is a full agonist with around the same potency as CP 55,940 in animal studies, and has fairly high affinity for both CB1 and CB2 receptors, with Ki values of 2.91nM at CB1 and 4.24nM at CB2. It has been licensed to KeyNeurotek Pharmaceuticals for clinical development, and was in Phase II trials in 2008 but its development appears to have stopped.

CP 55,244 is a chemical compound which is a cannabinoid receptor agonist. It has analgesic effects and is used in scientific research. It is an extremely potent CB1 full agonist with a Ki of 0.21 nM, making it more potent than the commonly used full agonist HU-210.
A cannabinoid receptor antagonist, also known simply as a cannabinoid antagonist or as an anticannabinoid, is a type of cannabinoidergic drug that binds to cannabinoid receptors (CBR) and prevents their activation by endocannabinoids. They include antagonists, inverse agonists, and antibodies of CBRs. The discovery of the endocannabinoid system led to the development of CB1 receptor antagonists. The first CBR inverse agonist, rimonabant, was described in 1994. Rimonabant blocks the CB1 receptor selectively and has been shown to decrease food intake and regulate body-weight gain. The prevalence of obesity worldwide is increasing dramatically and has a great impact on public health. The lack of efficient and well-tolerated drugs to cure obesity has led to an increased interest in research and development of CBR antagonists. Cannabidiol (CBD), a naturally occurring cannabinoid and a non-competitive CB1/CB2 receptor antagonist, as well as Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV), a naturally occurring cannabinoid, modulate the effects of THC via direct blockade of cannabinoid CB1 receptors, thus behaving like first-generation CB1 receptor inverse agonists, such as rimonabant. CBD is a very low-affinity CB1 ligand, that can nevertheless affect CB1 receptor activity in vivo in an indirect manner, while THCV is a high-affinity CB1 receptor ligand and potent antagonist in vitro and yet only occasionally produces effects in vivo resulting from CB1 receptor antagonism. THCV has also high affinity for CB2 receptors and signals as a partial agonist, differing from both CBD and rimonabant.

Abnormal cannabidiol (Abn-CBD) is a synthetic regioisomer of cannabidiol, which unlike most other cannabinoids produces vasodilator effects, lowers blood pressure, and induces cell migration, cell proliferation and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in microglia, but without producing any psychoactive or sedative effects. Abn-CBD can be found as an impurity in synthetic cannabidiol.
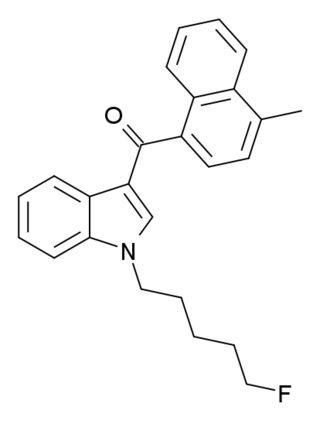
MAM-2201 is a drug that presumably acts as a potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors. It had never previously been reported in the scientific or patent literature, and was first identified by laboratories in the Netherlands and Germany in June 2011 as an ingredient in synthetic cannabis smoking blends. Like RCS-4 and AB-001, MAM-2201 thus appears to be a novel compound invented by "research chemical" suppliers specifically for grey-market recreational use. Structurally, MAM-2201 is a hybrid of two known cannabinoid compounds JWH-122 and AM-2201, both of which had previously been used as active ingredients in synthetic cannabis blends before being banned in many countries.

O-1602 is a synthetic compound most closely related to abnormal cannabidiol, and more distantly related in structure to cannabinoid drugs such as THC. O-1602 does not bind to the classical cannabinoid receptors CB1 or CB2 with any significant affinity, but instead is an agonist at several other receptors which appear to be related to the cannabinoid receptors, particularly GPR18 and GPR55. These previously orphan receptors have been found to be targets for a number of endogenous and synthetic cannabinoid compounds, and are thought to be responsible for most of the non-CB1, non-CB2 mediated effects that have become evident in the course of cannabinoid research. O-1602 produces some effects shared with classical cannabinoid compounds such as analgesic and antiinflammatory effects and appetite stimulation, but it does not produce sedation or psychoactive effects, and has several actions in the gut and brain that are not shared with typical cannabinoid agonists.
O-1918 is a synthetic compound related to cannabidiol, which is an antagonist at two former orphan receptors GPR18 and GPR55, that appear to be related to the cannabinoid receptors. O-1918 is used in the study of these receptors, which have been found to be targets for a number of endogenous and synthetic cannabinoid compounds, and are thought to be responsible for most of the non-CB1, non-CB2 mediated effects that have become evident in the course of cannabinoid research.