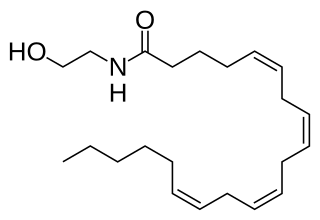
Anandamide (ANA), also referred to as N-arachidonoylethanolamine (AEA) is a fatty acid neurotransmitter belonging to the fatty acid derivative group known as N-acylethanolamine (NAE). Anandamide takes its name from the Sanskrit word ananda, meaning "joy, bliss, delight," plus amide. Anandamide, the first discovered endocannabinoid, engages with the body's endocannabinoid system by binding to the same cannabinoid receptors that THC found in cannabis acts on. Anandamide can be found within tissues in a wide range of animals. It has also been found in plants, such as the cacao tree.

Cannabinoid receptors, located throughout the body, are part of the endocannabinoid system of vertebrates– a class of cell membrane receptors in the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. As is typical of G protein-coupled receptors, the cannabinoid receptors contain seven transmembrane spanning domains. Cannabinoid receptors are activated by three major groups of ligands:

Tetrahydrocannabivarin is a homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) having a propyl (3-carbon) side chain instead of pentyl (5-carbon), making it non-psychoactive in lower doses. It has been shown to exhibit neuroprotective activity, appetite suppression, glycemic control and reduced side effects compared to THC, making it a potential treatment for management of obesity and diabetes. THCV was studied by Roger Adams as early as 1942.

The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a biological system composed of endocannabinoids, which are neurotransmitters that bind to cannabinoid receptors, and cannabinoid receptor proteins that are expressed throughout the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. The endocannabinoid system is still not fully understood, but may be involved in regulating physiological and cognitive processes, including fertility, pregnancy, pre- and postnatal development, various activity of immune system, appetite, pain-sensation, mood, and memory, and in mediating the pharmacological effects of cannabis. The ECS plays an important role in multiple aspects of neural functions, including the control of movement and motor coordination, learning and memory, emotion and motivation, addictive-like behavior and pain modulation, among others.
The lateral hypothalamus (LH), also called the lateral hypothalamic area (LHA), contains the primary orexinergic nucleus within the hypothalamus that widely projects throughout the nervous system; this system of neurons mediates an array of cognitive and physical processes, such as promoting feeding behavior and arousal, reducing pain perception, and regulating body temperature, digestive functions, and blood pressure, among many others. Clinically significant disorders that involve dysfunctions of the orexinergic projection system include narcolepsy, motility disorders or functional gastrointestinal disorders involving visceral hypersensitivity, and eating disorders.

Desformylflustrabromine (dFBr) is a NMT derivative indole alkaloid which was first isolated from the marine bryozoan Flustra foliacea.

Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1), is a G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptor that in humans is encoded by the CNR1 gene. And discovered, by determination and characterization in 1988, and cloned in 1990 for the first time. The human CB1 receptor is expressed in the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system. It is activated by endogenous cannabinoids called endocannabinoids, a group of retrograde neurotransmitters that include lipids, such as anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol; plant phytocannabinoids, such as docosatetraenoylethanolamide found in wild daga, the compound tetrahydrocannabinol which is an active constituent of the psychoactive drug cannabis; and synthetic analogs of tetrahydrocannabinol. CB1 is antagonized by the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabivarin at low doses and at higher doses, it activate the CB1 receptor as an agonist, but with less potency than tetrahydrocannabinol.
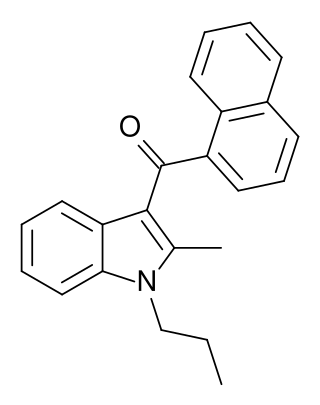
JWH-015 is a chemical from the naphthoylindole family that acts as a subtype-selective cannabinoid agonist. Its affinity for CB2 receptors is 13.8 nM, while its affinity for CB1 is 383 nM, meaning that it binds almost 28 times more strongly to CB2 than to CB1. However, it still displays some CB1 activity, and in some model systems can be very potent and efficacious at activating CB1 receptors, and therefore it is not as selective as newer drugs such as JWH-133. It has been shown to possess immunomodulatory effects, and CB2 agonists may be useful in the treatment of pain and inflammation. It was discovered and named after John W. Huffman.

CGP-7930 was the first positive allosteric modulator of GABAB receptors described in literature. CGP7930 is also a GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator and a blocker of Potassium channels.

3β-(4-Methylphenyl)-2β-[3-(4-chlorophenyl)isoxazol-5-yl]tropane (RTI-4229-371) is a phenyltropane derived drug which acts as a potent and selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor in vitro, yet unusually for this class of compound, both RTI-371 and the closely related compound RTI-370 failed to produce locomotor stimulation in mice. In addition to this, in drug substitution tests RTI-370 weakly generalized to cocaine whereas RTI-371 did not generalize at all.

Abnormal cannabidiol (Abn-CBD) is a synthetic regioisomer of cannabidiol, which unlike most other cannabinoids produces vasodilator effects, lowers blood pressure, and induces cell migration, cell proliferation and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in microglia, but without producing any psychoactive or sedative effects. Abn-CBD can be found as an impurity in synthetic cannabidiol.
RVD-Hpα (pepcan-12) is an endogenous neuropeptide found in human and mammalian brain, which was originally proposed to act as a selective agonist for the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. It is a 12-amino acid polypeptide having the amino acid sequence Arg-Val-Asp-Pro-Val-Asn-Phe-Lys-Leu-Leu-Ser-His and is an N-terminal extended form of hemopressin, a 9-AA polypeptide derived from the α1 subunit of hemoglobin which has previously been shown to act as a CB1 inverse agonist. All three polypeptides have been isolated from various mammalian species, with RVD-Hpα being one of the more abundant neuropeptides expressed in mouse brain, and these neuropeptides represent a new avenue for cannabinoid research distinct from the previously known endogenous lipid-derived cannabinoid agonists such as anandamide. Recently it was shown that RVD-Hpα (also called Pepcan-12) is a potent negative allosteric modulator at CB1 receptors, together with other newly described N-terminally extended peptides (pepcans).
Hemopressin (Hp) is an alpha hemoglobin fragment with the sequence PVNFKFLSH, originally identified in extracts of rat brain using an enzyme capture technique. It binds cannabinoid receptors, acting as an inverse agonist at CB1 receptors. Longer forms of hemopressin containing 2-3 additional amino acids on the N-terminus have been identified in extracts of mouse brain. These longer hemopressin peptides, named RVD-Hpα and VD-Hpα, bind to CB1 receptors and were originally reported to be agonists. In addition to the Hp peptides from alpha hemoglobin, a related peptide from beta hemoglobin has been found in mouse brain extracts; this peptide, named VD-Hpβ, is also an agonist at CB1 cannabinoid receptors. Hemopressin is not an endogenous peptide but rather an extraction artefact. The only endogenous peptide found endogenously at physiological conditions is RVD-hemopressin (pepcan-12), which has more recently been shown to be a negative allosteric modulator of CB1 receptors and positive allosteric modulator of CB2 receptors. RVD-hemopressin (pepcan-12) is generated from a pro-peptide called pepcan-23 and these peptides are exclusively found in noradrenergic neurons in the brain and in the adrenal medulla.

Org 27569 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective negative allosteric modulator of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. Studies in vitro suggest that it binds to a regulatory site on the CB1 receptor target, causing a conformational change that increases the binding affinity of CB1 agonists such as CP 55,940, while decreasing the binding affinity of CB1 antagonists or inverse agonists such as rimonabant. However while Org 27569 increases the ability of CB1 agonists to bind to the receptor, it decreases their efficacy at stimulating second messenger signalling once bound, and so in practice behaves as an insurmountable antagonist of CB1 receptor function.
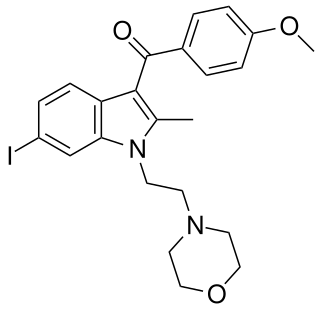
AM-630 (6-Iodopravadoline) is a drug that acts as a potent and selective inverse agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB2, with a Ki of 32.1 nM at CB2 and 165x selectivity over CB1, at which it acted as a weak partial agonist. It is used in the study of CB2 mediated responses and has been used to investigate the possible role of CB2 receptors in the brain. AM-630 is significant as one of the first indole derived cannabinoid ligands substituted on the 6-position of the indole ring, a position that has subsequently been found to be important in determining affinity and efficacy at both the CB1 and CB2 receptors, and has led to the development of many related derivatives.
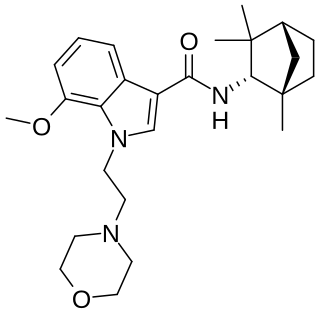
MN-25 (UR-12) is a drug invented by Bristol-Myers Squibb, that acts as a reasonably selective agonist of peripheral cannabinoid receptors. It has moderate affinity for CB2 receptors with a Ki of 11 nM, but 22x lower affinity for the psychoactive CB1 receptors with a Ki of 245 nM. The indole 2-methyl derivative has the ratio of affinities reversed however, with a Ki of 8 nM at CB1 and 29 nM at CB2, which contrasts with the usual trend of 2-methyl derivatives having increased selectivity for CB2 (cf. JWH-018 vs JWH-007, JWH-081 vs JWH-098).

AM-2389 is a classical cannabinoid derivative which acts as a potent and reasonably selective agonist for the CB1 receptor, with a Ki of 0.16 nM, and 26× selectivity over the related CB2 receptor. It has high potency in animal tests of cannabinoid activity, and a medium duration of action. Replacing the 1',1'-dimethyl substitution of the dimethylheptyl side chain of classical cannabinoids with cyclopropyl or cyclopentyl results in higher potency than cyclobutyl, but only the cyclobutyl derivatives show selectivity for CB1 over CB2. High selectivity for CB1 over CB2 is difficult to achieve (cf. AM-906, AM-1235), as almost all commonly used CB1 agonists have similar or greater affinity for CB2 than CB1, and the only truly highly selective CB1 agonists known as of 2012 are eicosanoid derivatives such as O-1812.
GAT100 is a negative allosteric modulator of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor.
PSNCBAM-1 is a negative allosteric modulator of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor.

Cannabidiphorol, the heptyl-homologue of cannabidiol was identified as a natural phytocannabinoid and named cannabidiphorol (CBDP) in 2019. It had previously been reported as a synthetic compound, but was not identified as a natural product prior to 2019. Recently, CBDP has been gained popularity due to it being synthesized and available on a commercial level.