
Cannabinoids are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is also a major constituent of temperate cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 100 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea.

The cannabinoid receptor 2(CB2), is a G protein-coupled receptor from the cannabinoid receptor family that in humans is encoded by the CNR2 gene. It is closely related to the cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1), which is largely responsible for the efficacy of endocannabinoid-mediated presynaptic-inhibition, the psychoactive properties of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the active agent in cannabis, and other phytocannabinoids. The principal endogenous ligand for the CB2 receptor is 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG).
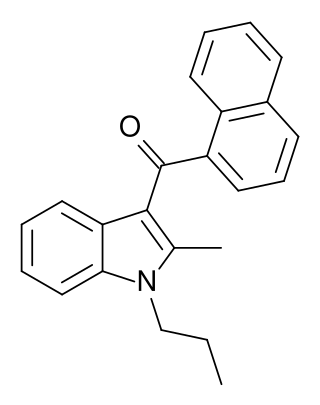
JWH-015 is a chemical from the naphthoylindole family that acts as a subtype-selective cannabinoid agonist. Its affinity for CB2 receptors is 13.8 nM, while its affinity for CB1 is 383 nM, meaning that it binds almost 28 times more strongly to CB2 than to CB1. However, it still displays some CB1 activity, and in some model systems can be very potent and efficacious at activating CB1 receptors, and therefore it is not as selective as newer drugs such as JWH-133. It has been shown to possess immunomodulatory effects, and CB2 agonists may be useful in the treatment of pain and inflammation. It was discovered and named after John W. Huffman.

JWH-051 is an analgesic drug which is a cannabinoid agonist. Its chemical structure is closely related to that of the potent cannabinoid agonist HU-210, with the only difference being the removal of the hydroxyl group at position 1 of the aromatic ring. It was discovered and named after John W. Huffman.

NESS-0327 is a drug used in scientific research which acts as an extremely potent and selective antagonist of the cannabinoid receptor CB1. It is much more potent an antagonist, and more selective for the CB1 receptor over CB2, than the more commonly used ligand rimonabant, with a Ki at CB1 of 350fM (i.e. 0.00035nM) and a selectivity of over 60,000x for CB1 over CB2. Independently, two other groups have described only modest nanomolar CB1 affinity for this compound (125nM and 18.4nM). Also unlike rimonabant, NESS-0327 does not appear to act as an inverse agonist at higher doses, instead being a purely neutral antagonist which blocks the CB1 receptor but does not produce any physiological effect of its own.
A cannabinoid receptor antagonist, also known simply as a cannabinoid antagonist or as an anticannabinoid, is a type of cannabinoidergic drug that binds to cannabinoid receptors (CBR) and prevents their activation by endocannabinoids. They include antagonists, inverse agonists, and antibodies of CBRs. The discovery of the endocannabinoid system led to the development of CB1 receptor antagonists. The first CBR inverse agonist, rimonabant, was described in 1994. Rimonabant blocks the CB1 receptor selectively and has been shown to decrease food intake and regulate body-weight gain. The prevalence of obesity worldwide is increasing dramatically and has a great impact on public health. The lack of efficient and well-tolerated drugs to cure obesity has led to an increased interest in research and development of CBR antagonists. Cannabidiol (CBD), a naturally occurring cannabinoid and a non-competitive CB1/CB2 receptor antagonist, as well as Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV), a naturally occurring cannabinoid, modulate the effects of THC via direct blockade of cannabinoid CB1 receptors, thus behaving like first-generation CB1 receptor inverse agonists, such as rimonabant. CBD is a very low-affinity CB1 ligand, that can nevertheless affect CB1 receptor activity in vivo in an indirect manner, while THCV is a high-affinity CB1 receptor ligand and potent antagonist in vitro and yet only occasionally produces effects in vivo resulting from CB1 receptor antagonism. THCV has also high affinity for CB2 receptors and signals as a partial agonist, differing from both CBD and rimonabant.

JWH-007 is an analgesic chemical from the naphthoylindole family, which acts as a cannabinoid agonist at both the CB1 and CB2 receptors. It was first reported in 1994 by a group including the noted cannabinoid chemist John W. Huffman. It was the most active of the first group of N-alkyl naphoylindoles discovered by the team led by John W Huffman, several years after the family was initially described with the discovery of the N-morpholinylethyl compounds pravadoline (WIN 48,098), JWH-200 (WIN 55,225) and WIN 55,212-2 by the Sterling Winthrop group. Several other N-alkyl substituents were found to be active by Huffman's team including the n-butyl, n-hexyl, 2-heptyl, and cyclohexylethyl groups, but it was subsequently determined that the 2-methyl group on the indole ring is not required for CB1 binding, and tends to increase affinity for CB2 instead. Consequently, the 2-desmethyl derivative of JWH-007, JWH-018, has slightly higher binding affinity for CB1, with an optimum binding of 9.00 nM at CB1 and 2.94 nM at CB2, and JWH-007 displayed optimum binding of 9.50 nM at CB1 and 2.94 nM at CB2.

A-834,735 is a drug developed by Abbott Laboratories that acts as a potent cannabinoid receptor full agonist at both the CB1 and CB2 receptors, with a Ki of 12 nM at CB1 and 0.21 nM at CB2. Replacing the aromatic 3-benzoyl or 3-naphthoyl group found in most indole derived cannabinoids with the 3-tetramethylcyclopropylmethanone group of A-834,735 and related compounds imparts significant selectivity for CB2, with most compounds from this group found to be highly selective CB2 agonists with little affinity for CB1. However, low nanomolar CB1 binding affinity is retained with certain heterocyclic 1-position substituents such as (N-methylpiperidin-2-yl)methyl (cf. AM-1220, AM-1248), or the (tetrahydropyran-4-yl)methyl substituent of A-834,735, resulting in compounds that still show significant affinity and efficacy at both receptors despite being CB2 selective overall.

A-796,260 is a drug developed by Abbott Laboratories that acts as a potent and selective cannabinoid CB2 receptor agonist. Replacing the aromatic 3-benzoyl or 3-naphthoyl group found in most indole derived cannabinoids with the 3-tetramethylcyclopropylmethanone group, imparts significant selectivity for CB2, and A-796,260 was found to be a highly selective CB2 agonist with little affinity for CB1, having a CB2Ki of 4.6 nM vs 945 nM at CB1. It has potent analgesic and anti-inflammatory actions in animal models, being especially effective in models of neuropathic pain, but without producing cannabis-like behavioral effects.

SER-601 (COR-167) is a drug which acts as a potent and selective cannabinoid CB2 receptor agonist, based on a quinolone-3-carboxylic acid core structure, with 190 times selectivity for CB2 over the related CB1 receptor. It has analgesic effects in animal studies, as well as neuroprotective effects, but without a "cannabis high" due to its low affinity for CB1. A number of related compounds are known, almost all of which have high selectivity for CB2.
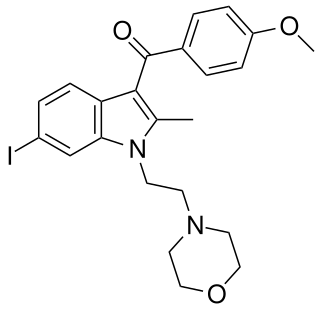
AM-630 (6-Iodopravadoline) is a drug that acts as a potent and selective inverse agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB2, with a Ki of 32.1 nM at CB2 and 165x selectivity over CB1, at which it acted as a weak partial agonist. It is used in the study of CB2 mediated responses and has been used to investigate the possible role of CB2 receptors in the brain. AM-630 is significant as one of the first indole derived cannabinoid ligands substituted on the 6-position of the indole ring, a position that has subsequently been found to be important in determining affinity and efficacy at both the CB1 and CB2 receptors, and has led to the development of many related derivatives.
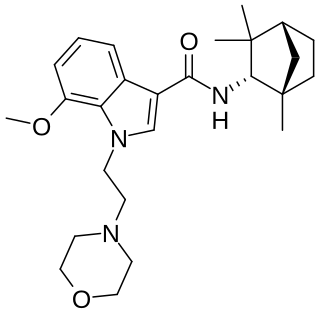
MN-25 (UR-12) is a drug invented by Bristol-Myers Squibb, that acts as a reasonably selective agonist of peripheral cannabinoid receptors. It has moderate affinity for CB2 receptors with a Ki of 11 nM, but 22x lower affinity for the psychoactive CB1 receptors with a Ki of 245 nM. The indole 2-methyl derivative has the ratio of affinities reversed however, with a Ki of 8 nM at CB1 and 29 nM at CB2, which contrasts with the usual trend of 2-methyl derivatives having increased selectivity for CB2 (cf. JWH-018 vs JWH-007, JWH-081 vs JWH-098).

UR-144 (TMCP-018, KM-X1, MN-001, YX-17) is a drug invented by Abbott Laboratories, that acts as a selective full agonist of the peripheral cannabinoid receptor CB2, but with much lower affinity for the psychoactive CB1 receptor.

AM-2389 is a classical cannabinoid derivative which acts as a potent and reasonably selective agonist for the CB1 receptor, with a Ki of 0.16 nM, and 26× selectivity over the related CB2 receptor. It has high potency in animal tests of cannabinoid activity, and a medium duration of action. Replacing the 1',1'-dimethyl substitution of the dimethylheptyl side chain of classical cannabinoids with cyclopropyl or cyclopentyl results in higher potency than cyclobutyl, but only the cyclobutyl derivatives show selectivity for CB1 over CB2. High selectivity for CB1 over CB2 is difficult to achieve (cf. AM-906, AM-1235), as almost all commonly used CB1 agonists have similar or greater affinity for CB2 than CB1, and the only truly highly selective CB1 agonists known as of 2012 are eicosanoid derivatives such as O-1812.

S-444,823 is a drug developed by Shionogi which is a cannabinoid agonist. It was developed as an antipruritic, and has moderate selectivity for the CB2 subtype, having a CB2 affinity of 18nM, and 32x selectivity over the CB1 receptor. In animal studies it showed analgesic effects and strongly reduced itching responses, but without producing side effects such as sedation and catalepsy that are seen with centrally acting CB1 agonists.

AM-1714 (part of the AM cannabinoid series) is a drug that acts as a reasonably selective agonist of the peripheral cannabinoid receptor CB2, with sub-nanomolar affinity and 490x selectivity over the related CB1 receptor. In animal studies it has both analgesic and anti-allodynia effects. The 9-methoxy derivative AM-1710 has similar CB2 affinity but only 54x selectivity over CB1.

FUBIMINA is a synthetic cannabinoid that is the benzimidazole analog of AM-2201 and has been used as an active ingredient in synthetic cannabis products. It was first identified in Japan in 2013, alongside MEPIRAPIM.

Cannabinor (PRS-211,375) is a drug which acts as a potent and selective cannabinoid CB2 receptor agonist. It is classed as a "nonclassical" cannabinoid with a chemical structure similar to that of cannabidiol. It has a CB2 affinity of 17.4 nM vs 5,585 nM at CB1, giving it over 300× selectivity for CB2. It showed analgesic effects in animal studies especially in models of neuropathic pain, but failed in Phase IIb human clinical trials due to lack of efficacy.

















