
AM-694 (1-(5-fluoropentyl)-3-(2-iodobenzoyl)indole) is a designer drug that acts as a potent and selective agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB1. It is used in scientific research for mapping the distribution of CB1 receptors.

APINACA (AKB48, N-(1-adamantyl)-1-pentyl-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide) is a drug that acts as a reasonably potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors. It is a full agonist at CB1 with an EC50 of 142 nM and Ki of 3.24 nM (compared to the Ki of Δ9-THC at 28.35 nM and JWH-018 at 9.62 nM), while at CB2 it acts as a partial agonist with an EC50 of 141 nM and Ki of 1.68 nM (compared to the Ki of Δ9-THC at 37.82 nM and JWH-018 at 8.55 nM). Its pharmacological characterization has also been reported in a discontinued patent application. It had never previously been reported in the scientific or patent literature, and was first identified by laboratories in Japan in March 2012 as an ingredient in synthetic cannabis smoking blends, along with a related compound APICA. Structurally, it closely resembles cannabinoid compounds from a University of Connecticut patent, but with a simple pentyl chain on the indazole 1-position, and APINACA falls within the claims of this patent despite not being disclosed as an example.

APICA is an indole based drug that acts as a potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors.

AB-FUBINACA (AMB-FUBINACA) is a psychoactive drug that acts as a potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors, with Ki values of 0.9 nM at CB1 and 23.2 nM at CB2 and EC50 values of 1.8 nM at CB1 and 3.2 nM at CB2. It was originally developed by Pfizer in 2009 as an analgesic medication but was never pursued for human use. In 2012, it was discovered as an ingredient in synthetic cannabinoid blends in Japan, along with a related compound AB-PINACA, which had not previously been reported.

AB-PINACA is a compound that was first identified as a component of synthetic cannabis products in Japan in 2012.

PB-22 is a designer drug offered by online vendors as a cannabimimetic agent, and detected being sold in synthetic cannabis products in Japan in 2013. PB-22 represents a structurally unique synthetic cannabinoid chemotype, since it contains an ester linker at the indole 3-position, rather than the precedented ketone of JWH-018 and its analogs, or the amide of APICA and its analogs.

ADB-FUBINACA (ADMB-FUBINACA) is a designer drug identified in synthetic cannabis blends in Japan in 2013. In 2018, it was the third-most common synthetic cannabinoid identified in drugs seized by the Drug Enforcement Administration.

SDB-006 is a drug that acts as a potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors, with an EC50 of 19 nM for human CB2 receptors, and 134 nM for human CB1 receptors. It was discovered during research into the related compound SDB-001 which had been sold illicitly as "2NE1". SDB-006 metabolism has been described in literature.

AB-CHMINACA is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid. It is a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor (Ki = 0.78 nM) and CB2 receptor (Ki = 0.45 nM) and fully substitutes for Δ9-THC in rat discrimination studies, while being 16x more potent. Continuing the trend seen in other cannabinoids of this generation, such as AB-FUBINACA and AB-PINACA, it contains a valine amino acid amide residue as part of its structure, where older cannabinoids contained a naphthyl or adamantane residue.

AB-CHFUPYCA is a compound that was first identified as a component of synthetic cannabis products in Japan in 2015. The name "AB-CHFUPYCA" is an acronym of its systematic name N-(1-Amino-3-methyl-1-oxoButan-2-yl)-1-(CycloHexylmethyl)-3-(4-FlUorophenyl)-1H-PYrazole-5-CarboxAmide. There are two known regioisomers of AB-CHFUPYCA: 3,5-AB-CHMFUPPYCA (pictured) and 5,3-AB-CHMFUPPYCA. The article[1] refers to both 3,5-AB-CHMFUPPYCA and 5,3-AB-CHMFUPPYCA as AB-CHMFUPPYCA isomers, so AB-CHMFUPPYCA and AB-CHFUPYCA are not names for a unique chemical structure.
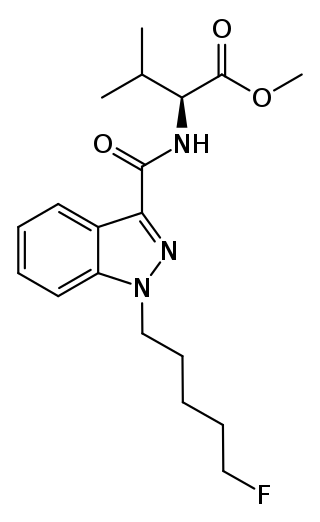
5F-AMB (also known as 5F-MMB-PINACA and 5F-AMB-PINACA) is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid from the indazole-3-carboxamide family, which has been used as an active ingredient in synthetic cannabis products. It was first identified in Japan in early 2014. Although only very little pharmacological information about 5F-AMB itself exists, its 4-cyanobutyl analogue (instead of 5-fluoropentyl) has been reported to be a potent agonist for the CB1 receptor (KI = 0.7 nM).

FUBIMINA is a synthetic cannabinoid that is the benzimidazole analog of AM-2201 and has been used as an active ingredient in synthetic cannabis products. It was first identified in Japan in 2013, alongside MEPIRAPIM.

MEPIRAPIM is an indole-based cannabinoid which differs from JWH-018 by having a 4-methylpiperazine group in place of the naphthyl group and has been used as an active ingredient in synthetic cannabis products. It was first identified in Japan in 2013, alongside FUBIMINA. MEPIRAPIM acts as a T-type calcium channel inhibitor and is only minimally active at the central CB1 receptor.

5F-AB-PINACA is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid that is derived from a series of compounds originally developed by Pfizer in 2009 as an analgesic medication, and has been sold online as a designer drug.

5F-APINACA is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid that has been sold online as a designer drug. Structurally it closely resembles cannabinoid compounds from patent WO 2003/035005 but with a 5-fluoropentyl chain on the indazole 1-position, and 5F-APINACA falls within the claims of this patent, as despite not being disclosed as an example, it is very similar to the corresponding pentanenitrile and 4-chlorobutyl compounds which are claimed as examples 3 and 4.

THJ-018 (SGT-17) is a synthetic cannabinoid that is the indazole analogue of JWH-018 and has been sold online as a designer drug.

NM-2201 (also known as CBL-2201 and NA-5F-PIC) is an indole-based synthetic cannabinoid that presumably has similar properties to the closely related 5F-PB-22 and NNE1, which are both full agonists and unselectively bind to CB1 and CB2 receptors with low nanomolar affinity.
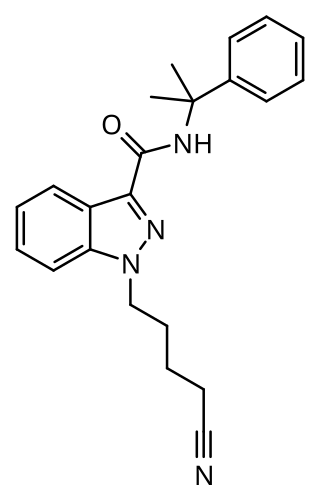
CUMYL-4CN-BINACA (also known as CUMYL-CYBINACA or SGT-78) is an indazole-3-carboxamide based synthetic cannabinoid that has been sold online as a designer drug. It is a potent agonist for cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2, with in vitro EC50 values of 0.58 nM and 6.12 nM, respectively. In mice, CUMYL-4CN-BINACA produces hypothermic and pro-convulsant effects via the CB1 receptor, and anecdotal reports suggest it has an active dose of around 0.1 mg in humans.

ADB-HEXINACA is a cannabinoid designer drug that has been found as an ingredient in some synthetic cannabis products, first appearing in early 2021. It is a longer chain homologue of previously encountered synthetic cannabinoid compounds such as ADB-BUTINACA and ADB-PINACA.



















