
Synthetic cannabinoids are a class of designer drug molecules that bind to the same receptors to which cannabinoids in cannabis plants attach. These novel psychoactive substances should not be confused with synthetic phytocannabinoids or synthetic endocannabinoids from which they are in many aspects distinct.

AM-2201 is a recreational designer drug that acts as a potent but nonselective full agonist for the cannabinoid receptor. It is part of the AM series of cannabinoids discovered by Alexandros Makriyannis at Northeastern University.

AB-001 (1-pentyl-3-(1-adamantoyl)indole) is a designer drug that was found as an ingredient in synthetic cannabis smoking blends in Ireland in 2010 and Hungary and Germany in 2011. It is unclear who AB-001 was originally developed by, but it is structurally related to compounds such as AM-1248 and its corresponding 1-(tetrahydropyran-4-ylmethyl) analogue, which are known to be potent cannabinoid agonists with moderate to a high selectivity for CB2 over CB1. The first published synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of AB-001 revealed that it acts as a full agonist at CB1 (EC50 = 35 nM) and CB2 receptors (EC50 = 48 nM). However, AB-001 was found to possess only weak cannabimimetic effects in rats at doses up to 30 mg/kg, making it less potent than the carboxamide analogue APICA, which possesses potent cannabimimetic activity at doses of 3 mg/kg.

MDA-19 (also known as BZO-HEXOXIZID) is a drug that acts as a potent and selective agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB2, with reasonable selectivity over the psychoactive CB1 receptor, though with some variation between species. In animal studies it was effective for the treatment of neuropathic pain, but did not effect rat locomotor activity in that specific study. The pharmacology of MDA-19 in rat cannabinoid receptors have been demonstrated to function differently than human cannabinoid receptors with MDA-19 binding to human CB1 receptors 6.9× higher than rat CB1 receptors.

UR-144 (TMCP-018, KM-X1, MN-001, YX-17) is a drug invented by Abbott Laboratories, that acts as a selective full agonist of the peripheral cannabinoid receptor CB2, but with much lower affinity for the psychoactive CB1 receptor.
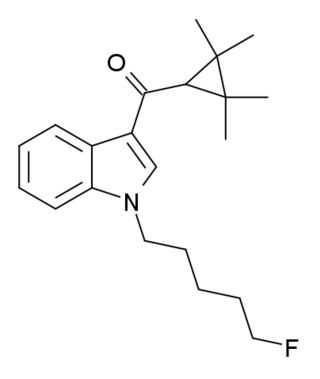
XLR-11 (5"-fluoro-UR-144 or 5F-UR-144) is a drug that acts as a potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 with EC50 values of 98 nM and 83 nM, respectively. It is a 3-(tetramethylcyclopropylmethanoyl)indole derivative related to compounds such as UR-144, A-796,260 and A-834,735, but it is not specifically listed in the patent or scientific literature alongside these other similar compounds, and appears to have not previously been made by Abbott Laboratories, despite falling within the claims of patent WO 2006/069196. XLR-11 was found to produce rapid, short-lived hypothermic effects in rats at doses of 3 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg, suggesting that it is of comparable potency to APICA and STS-135.

APICA is an indole based drug that acts as a potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors.

STS-135 (N-(adamantan-1-yl)-1-(5-fluoropentyl)-1H-indole-3-carboxamide, also called 5F-APICA) is a designer drug offered by online vendors as a cannabimimetic agent. The structure of STS-135 appears to use an understanding of structure-activity relationships within the indole class of cannabimimetics, although its design origins are unclear. STS-135 is the terminally-fluorinated analogue of SDB-001, just as AM-2201 is the terminally-fluorinated analogue of JWH-018, and XLR-11 is the terminally-fluorinated analogue of UR-144. STS-135 acts a potent cannabinoid receptor agonist in vitro, with an EC50 of 51 nM for human CB2 receptors, and 13 nM for human CB1 receptors. STS-135 produces bradycardia and hypothermia in rats at doses of 1–10 mg/kg, suggesting cannabinoid-like activity.

PB-22 is a designer drug offered by online vendors as a cannabimimetic agent, and detected being sold in synthetic cannabis products in Japan in 2013. PB-22 represents a structurally unique synthetic cannabinoid chemotype, since it contains an ester linker at the indole 3-position, rather than the precedented ketone of JWH-018 and its analogs, or the amide of APICA and its analogs.

5F-PB-22 is a designer drug which acts as a cannabinoid agonist. The structure of 5F-PB-22 appears to have been designed with an understanding of structure–activity relationships within the indole class of cannabinoids.
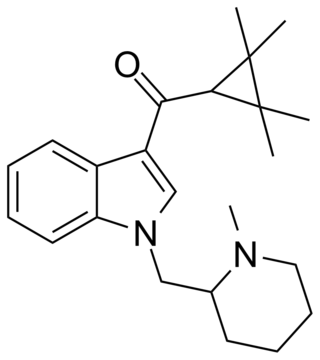
AB-005 or [1-[(1-methylpiperidin-2-yl)methyl]-1H-indol-3-yl](2,2,3,3-tetramethylcyclopropyl)-methanone is a designer drug offered by online vendors as a cannabimimetic agent. The structure and pharmacological activity of AB-005 was published in 2010, prior to its commercial availability in 2012, where it was reported to have high affinity for both CB1 (Ki = 5.5 nM) and CB2 receptors (Ki = 0.48 nM). AB-005 features groups found in other previously reported synthetic cannabinoids: the tetramethylcyclopropane group of UR-144 and XLR-11 as well as the (1-methyl-2-piperidinyl)methyl substituent of AM-1248 and AM-1220. No information regarding the in vivo activity of AB-005 has been published, and only anecdotal reports are known of its psychoactivity in humans.

SDB-006 is a drug that acts as a potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors, with an EC50 of 19 nM for human CB2 receptors, and 134 nM for human CB1 receptors. It was discovered during research into the related compound SDB-001 which had been sold illicitly as "2NE1". SDB-006 metabolism has been described in literature.
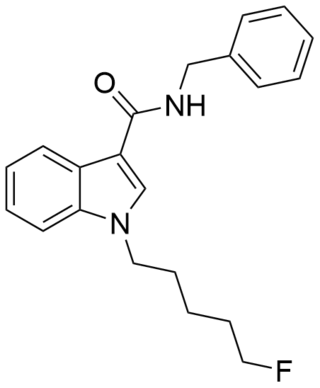
5F-SDB-006 is a drug that acts as a potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors, with an EC50 of 50 nM for human CB1 receptors, and 123 nM for human CB2 receptors. It was discovered during research into the related compound APICA which had been sold illicitly as "2NE1". 5F-SDB-006 is the terminally fluorinated analog of SDB-006, just as STS-135 is the terminally fluorinated analog of APICA. Given the known metabolic liberation (and presence as an impurity) of amantadine in the related compound APINACA, it is suspected that metabolic hydrolysis of the amide group of 5F-SDB-006 may release benzylamine.

5F-APINACA is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid that has been sold online as a designer drug. Structurally it closely resembles cannabinoid compounds from patent WO 2003/035005 but with a 5-fluoropentyl chain on the indazole 1-position, and 5F-APINACA falls within the claims of this patent, as despite not being disclosed as an example, it is very similar to the corresponding pentanenitrile and 4-chlorobutyl compounds which are claimed as examples 3 and 4.

FAB-144 is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid that is presumed to be a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor and has been sold online as a designer drug. It is the indazole analogue of XLR-11.

FUB-144 (also known as FUB-UR-144) is an indole-based synthetic cannabinoid that is presumed to be a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor and has been sold online as a designer drug. It is an analogue of UR-144 and XLR-11 where the pentyl chain has been replaced with fluorobenzyl.

5F-MDMB-PICA (MDMB-5F-PICA) is a designer drug and synthetic cannabinoid. In 2018, it was the fifth-most common synthetic cannabinoid identified in drugs seized by the Drug Enforcement Administration.

2F-QMPSB (SGT-13) is an arylsulfonamide-based synthetic cannabinoid that is a fluorinated derivative of QMPSB and has been sold as a designer drug. Its identification was first reported by a forensic laboratory in Italy in January 2019, and it was made illegal in Latvia shortly afterwards. Fluorination of the tail group is a common strategy to increase potency at cannabinoid receptors which is seen in many related series of compounds.

MDMB-4en-PINACA is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid that has been sold online as a designer drug. MDMB-4en-PINACA was first identified in Europe in 2017. In 2021, MDMB-4en-PINACA was the most common synthetic cannabinoid identified by the Drug Enforcement Administration in the United States. MDMB-4en-PINACA differs from 5F-MDMB-PINACA due to replacement of 5-fluoropentyl with a pent-4-ene moiety (4-en).



















