
JWH-081 is an analgesic chemical from the naphthoylindole family, which acts as a cannabinoid agonist at both the CB1 and CB2 receptors. With a Ki of 1.2nM it is fairly selective for the CB1 subtype, its affinity at this subtype approximately 10x the affinity at CB2. It was discovered by and named after John W. Huffman.

JWH-210 is an analgesic chemical from the naphthoylindole family, which acts as a potent cannabinoid agonist at both the CB1 and CB2 receptors, with Ki values of 0.46 nM at CB1 and 0.69 nM at CB2. It is one of the most potent 4-substituted naphthoyl derivatives in the naphthoylindole series, having a higher binding affinity (i.e. lower Ki) at CB1 than both its 4-methyl and 4-n-propyl homologues JWH-122 (CB1 Ki 0.69 nM) and JWH-182 (CB1 Ki 0.65 nM) respectively, and than the 4-methoxy compound JWH-081 (CB1 Ki 1.2 nM). It was discovered by and named after John W. Huffman.
A-836,339 is a drug developed by Abbott Laboratories that acts as a potent cannabinoid receptor full agonist. It is selective for CB2, with Ki values of 0.64 nM at CB2 vs 270 nM at the psychoactive CB1 receptor, but while it exhibits selective analgesic, anti-inflammatory and anti-hyperalgesic effects at low doses, its high efficacy at both targets results in typical cannabis-like effects appearing at higher doses, despite its low binding affinity for CB1. In 2012 A-836,339 was detected via X-ray crystallography in a "dubious product" sold in Japan, though the product was described as a white powder, not herbal incense, it was suggested to be for human consumption.

A-834,735 is a drug developed by Abbott Laboratories that acts as a potent cannabinoid receptor full agonist at both the CB1 and CB2 receptors, with a Ki of 12 nM at CB1 and 0.21 nM at CB2. Replacing the aromatic 3-benzoyl or 3-naphthoyl group found in most indole derived cannabinoids, with the 3-tetramethylcyclopropylmethanone group of A-834,735 and related compounds, imparts significant selectivity for CB2, with most compounds from this group found to be highly selective CB2 agonists with little affinity for CB1. However low nanomolar CB1 binding affinity is retained with certain heterocyclic 1-position substituents such as (N-methylpiperidin-2-yl)methyl (cf. AM-1220, AM-1248), or the (tetrahydropyran-4-yl)methyl substituent of A-834,735, resulting in compounds that still show significant affinity and efficacy at both receptors despite being CB2 selective overall.
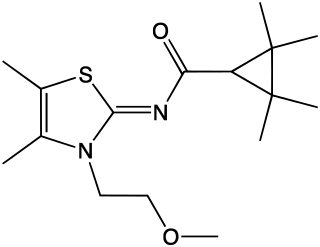
A-796,260 is a drug developed by Abbott Laboratories that acts as a potent and selective cannabinoid CB2 receptor agonist. Replacing the aromatic 3-benzoyl or 3-naphthoyl group found in most indole derived cannabinoids with the 3-tetramethylcyclopropylmethanone group, imparts significant selectivity for CB2, and A-796,260 was found to be a highly selective CB2 agonist with little affinity for CB1, having a CB2Ki of 4.6 nM vs 945 nM at CB1. It has potent analgesic and anti-inflammatory actions in animal models, being especially effective in models of neuropathic pain, but without producing cannabis-like behavioral effects.

AM-1221 is a drug that acts as a potent and selective agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB2, with a Ki of 0.28 nM at CB2 and 52.3 nM at the CB1 receptor, giving it around 180 times selectivity for CB2. The 2-methyl and 6-nitro groups on the indole ring both tend to increase CB2 affinity while generally reducing affinity at CB1, explaining the high CB2 selectivity of AM-1221. However, despite this relatively high selectivity for CB2, its CB1 affinity is still too strong to make it useful as a truly selective CB2 agonist, so the related compound AM-1241 is generally preferred for research purposes.
AM-630 (6-Iodopravadoline) is a drug that acts as a potent and selective inverse agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB2, with a Ki of 32.1 nM at CB2 and 165x selectivity over CB1, at which it acted as a weak partial agonist. It is used in the study of CB2 mediated responses and has been used to investigate the possible role of CB2 receptors in the brain. AM-630 is significant as one of the first indole derived cannabinoid ligands substituted on the 6-position of the indole ring, a position that has subsequently been found to be important in determining affinity and efficacy at both the CB1 and CB2 receptors, and has led to the development of many related derivatives.

AM-1248 is a drug that acts as a moderately potent agonist for both the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2, but with some dispute between sources over its exact potency and selectivity. Replacing the 3-(1-naphthoyl) group found in many indole derived cannabinoid ligands, with an adamantoyl group, generally confers significant CB2 selectivity, but reasonable CB1 affinity and selectivity is retained when an N-methylpiperidin-2-ylmethyl substitution is used at the indole 1-position. The related compound 1-pentyl-3-(1-adamantoyl)indole was identified as having been sold as a cannabinoid designer drug in Hungary in 2011, along with another synthetic cannabinoid AM-679.

AM-1220 is a drug that acts as a potent and moderately selective agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB1, with around 19 times selectivity for CB1 over the related CB2 receptor. It was originally invented in the early 1990s by a team led by Thomas D'Ambra at Sterling Winthrop, but has subsequently been researched by many others, most notably the team led by Alexandros Makriyannis at the University of Connecticut. The (piperidin-2-yl)methyl side chain of AM-1220 contains a stereocenter, so there are two enantiomers with quite different potency, the (R)-enantiomer having a Ki of 0.27 nM at CB1 while the (S)-enantiomer has a much weaker Ki of 217 nM.

AB-001 (1-pentyl-3-(1-adamantoyl)indole) is a designer drug that was found as an ingredient in synthetic cannabis smoking blends in Ireland in 2010 and Hungary and Germany in 2011. It is unclear who AB-001 was originally developed by, but it is structurally related to compounds such as AM-1248 and its corresponding 1-(tetrahydropyran-4-ylmethyl) analogue, which are known to be potent cannabinoid agonists with moderate to high selectivity for CB2 over CB1. The first published synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of AB-001 revealed that it acts as a full agonist at CB1 (EC50 = 35 nM) and CB2 receptors (EC50 = 48 nM). However, AB-001 was found to possess only weak cannabimimetic effects in rats at doses up to 30 mg/kg, making it less potent than the carboxamide analogue APICA, which possesses potent cannabimimetic activity at doses of 3 mg/kg.
MN-25 (UR-12) is a drug invented by Bristol-Myers Squibb, that acts as a reasonably selective agonist of peripheral cannabinoid receptors. It has moderate affinity for CB2 receptors with a Ki of 11 nM, but 22x lower affinity for the psychoactive CB1 receptors with a Ki of 245 nM. The indole 2-methyl derivative has the ratio of affinities reversed however, with a Ki of 8 nM at CB1 and 29 nM at CB2, which contrasts with the usual trend of 2-methyl derivatives having increased selectivity for CB2 (cf. JWH-018 vs JWH-007, JWH-081 vs JWH-098).

MDA-19 (also known as BZO-HEXOXIZID) is a drug that acts as a potent and selective agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB2, with reasonable selectivity over the psychoactive CB1 receptor, though with some variation between species. In animal studies it was effective for the treatment of neuropathic pain, but did not effect rat locomotor activity in that specific study. Although it should be noted the pharmacology of MDA-19 in rat cannabinoid receptors have been demonstrated to function differently than human cannabinoid receptors with MDA-19 binding to human CB1 receptors 6.9x higher than rat CB1 receptors.

UR-144 (TMCP-018, KM-X1, MN-001, YX-17) is a drug invented by Abbott Laboratories, that acts as a selective full agonist of the peripheral cannabinoid receptor CB2, but with much lower affinity for the psychoactive CB1 receptor.

JWH-047 is a selective cannabinoid ligand that binds to both CB1 and CB2. It has a bindining affinity of Ki = 0.9 nM for the CB2 subtype, and more than 65 times selectivity over the CB1.
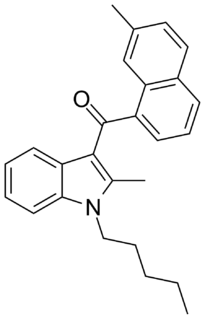
JWH-048 is a selective cannabinoid ligand, with a bindining affinity of Ki = 0.5 ± 0.1 nM for the CB2 subtype, and more than 22 times selectivity over the CB1.

XLR-11 (5"-fluoro-UR-144 or 5F-UR-144) is a drug that acts as a potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 with EC50 values of 98 nM and 83 nM, respectively. It is a 3-(tetramethylcyclopropylmethanoyl)indole derivative related to compounds such as UR-144, A-796,260 and A-834,735, but it is not specifically listed in the patent or scientific literature alongside these other similar compounds, and appears to have not previously been made by Abbott Laboratories, despite falling within the claims of patent WO 2006/069196. XLR-11 was found to produce rapid, short-lived hypothermic effects in rats at doses of 3 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg, suggesting that it is of comparable potency to APICA and STS-135.

APICA is an indole based drug that acts as a potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors.

AB-005 or [1-[(1-methylpiperidin-2-yl)methyl]-1H-indol-3-yl](2,2,3,3-tetramethylcyclopropyl)-methanone is a designer drug offered by online vendors as a cannabimimetic agent. The structure and pharmacological activity of AB-005 was published in 2010, prior to its commercial availability in 2012, where it was reported to have high affinity for both CB1 and CB2 receptors. AB-005 features groups found in other previously reported synthetic cannabinoids: the tetramethylcyclopropane group of UR-144 and XLR-11 as well as the (1-methyl-2-piperidinyl)methyl substituent of AM-1248 and AM-1220. No information regarding the in vivo activity of AB-005 has been published, and only anecdotal reports are known of its psychoactivity in humans.


















