 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.257.468 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
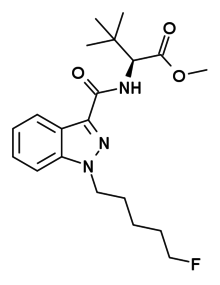
| Formula | C20H28FN3O3 |
| Molar mass | 377.460 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
5F-ADB (also known as MDMB-5F-PINACA using systematic EMCDDA nomenclature [2] and 5F-MDMB-PINACA) is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid from the indazole-3-carboxamide family, which has been used as an active ingredient in synthetic cannabis products and has been sold online as a designer drug. [3] [4] 5F-ADB is a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor, [5] though it is unclear whether it is selective for this target.
Contents
5F-ADB was first identified in November 2014 from post-mortem samples taken from an individual who had died after using a product containing this substance. Subsequent testing identified 5F-ADB to have been present in a total of ten people who had died from unexplained drug overdoses in Japan between September 2014 and December 2014. 5F-ADB is believed to be extremely potent based on the very low levels detected in tissue samples, and appears to be significantly more toxic than earlier synthetic cannabinoid drugs that had previously been sold. [6]
In 2018, 5F-ADB was the most common synthetic cannabinoid to be identified in Drug Enforcement Administration seizures. [7] 5F-ADB was also identified in cannabidiol (CBD) products from a US-based CBD manufacturer in 2018. [8]