CBE is the initialism for Commander of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire, a grade within the British order of chivalry.
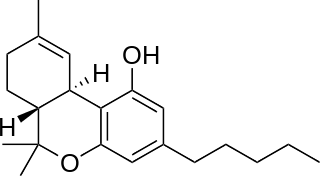
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is a cannabinoid found in cannabis. It is the principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified on the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) describes multiple isomers, the term THC usually refers to the delta-9-THC isomer with chemical name (−)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. It is a colorless oil.

Cannabinoids are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is also a major constituent of temperate cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 100 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea.

Cannabis sativa is an annual herbaceous flowering plant. The species was first classified by Carl Linnaeus in 1753. The specific epithet sativa means 'cultivated'. Indigenous to Eastern Asia, the plant is now of cosmopolitan distribution due to widespread cultivation. It has been cultivated throughout recorded history and used as a source of industrial fiber, seed oil, food, and medicine. It is also used as a recreational drug and for religious and spiritual purposes.
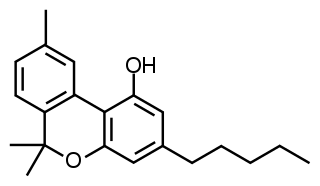
Cannabinol (CBN) is a mildly psychoactive phytocannabinoid that acts as a low affinity partial agonist at both CB1 and CB2 receptors. This activity at CB1 and CB2 receptors constitutes interaction of CBN with the endocannabinoid system (ECS).

Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid, one of 113 identified cannabinoids in cannabis plants, along with tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and accounts for up to 40% of the plant's extract. Medically, it is an anticonvulsant used to treat multiple forms of epilepsy. It was discovered in 1940 and, as of 2024 clinical research on CBD included studies related to the treatment of anxiety, addiction, psychosis, movement disorders, and pain, but there is insufficient high-quality evidence that CBD is effective for these conditions. CBD is sold as an herbal dietary supplement and promoted with yet unproven claims of particular therapeutic effects.

11-Hydroxy-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, usually referred to as 11-hydroxy-THC is the main active metabolite of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is formed in the body after Δ9-THC is consumed.

9-Nor-9β-hydroxyhexahydrocannabinol is a cannabinoid first discovered from early modifications to the structure of THC, in a search for the simplest compound that could still fulfill the binding requirements to produce cannabis-like activity.

Dronabinol, sold under the brand names Marinol and Syndros, is the generic name for the molecule of (−)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in the pharmaceutical context. It has indications as an appetite stimulant, antiemetic, and sleep apnea reliever and is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as safe and effective for HIV/AIDS-induced anorexia and chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.
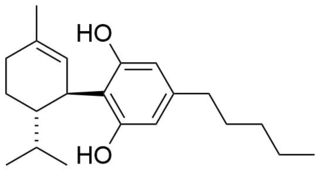
8,9-Dihydrocannabidiol is a synthetic cannabinoid that is closely related to cannabidiol (CBD) itself. that was first synthesized by Alexander R. Todd in 1940 derived from the catalytic hydrogenation of cannabidiol.

Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), is a cannabinoid produced in cannabis plants. It is the precursor to cannabidiol (CBD). It is most abundant in the glandular trichomes on the female seedless flowers or more accurately infructescence often colloquially referred to as buds or flowers.

7-Hydroxycannabidiol (7-OH-CBD) is an active metabolite of cannabidiol, generated in the body from cannabidiol by the action of the enzyme CYP2C19. While methods have been developed for its synthetic production, and measurement of levels in the body following consumption of cannabidiol, its pharmacology has been relatively little studied, though it has been found to possess similar anticonvulsant effects to cannabidiol itself, as well as lowering blood triglyceride levels. Like its precursor CBD, it is not known to exhibit any psychoactive effects on the body and is known to counter the psychoactive effects of THC if it is present at the same time. This mode of action in 2015 was discovered to be at least contributing in part by being a non competitive negative allosteric modulator of the Cannabinoid receptor type 1.

Cannabichromenic acid (CBCA) is minor cannabinoid and precursor of cannabichromene.

Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is a hydrogenated derivative of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). It is a naturally occurring phytocannabinoid that has rarely been identified as a trace component in Cannabis sativa, but can also be produced synthetically by firstly acid cyclization of cannabidiol and then hydrogenation of tetrahydrocannabinol. The synthesis and bioactivity of HHC was first reported in 1940 by Roger Adams.

11-Hydroxy-Δ-8-tetrahydrocannabinol is an active metabolite of Δ8-THC, a psychoactive cannabinoid found in small amounts in cannabis. It is an isomer of 11-OH-Δ9-THC, and is produced via the same metabolic pathway. It was the first cannabinoid metabolite discovered in 1970.

11-Hydroxyhexahydrocannabinol is an active metabolite of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and a metabolite of the trace cannabinoid hexahydrocannabinol (HHC).

Cannabicitran (CBTC) is a phytocannabinoid first isolated in 1974 as a trace component of Cannabis sativa. Structurally related compounds can be found in some other plants. It is not psychoactive, but was found to reduce intraocular pressure in tests on rabbits, which may reflect agonist activity at the NAGly receptor that is known to be a target of many structurally related cannabinoids.

Cannabimovone (CBM) is a phytocannabinoid first isolated from a non-psychoactive strain of Cannabis sativa in 2010, which is thought to be a rearrangement product of cannabidiol. It lacks affinity for cannabinoid receptors, but acts as an agonist at both TRPV1 and PPARγ.

The Medical Marijuana and Cannabidiol Research Expansion Act is an Act of Congress allowing medical research on cannabis. The act is "the first standalone marijuana-related bill approved by both chambers of the United States Congress".
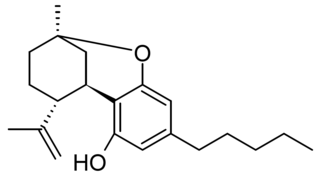
Isotetrahydrocannabinol (iso-THC) is a phytocannabinoid similar in structure to cannabicitran which has been identified as a trace component of Cannabis, but is more commonly found as an impurity in synthetic THC which has been made from cannabidiol. iso-THC is present with other isomers with the double bond in a different position and the saturated dihydro derivative. iso-THC can be described as the upper cyclization product of CBD, while THC is the lower cyclization product of CBD. Its pharmacology has not been studied, though it is commonly found as a trace impurity in commercially marketed Δ8-THC products.



















