
Cannabis is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: Cannabis sativa, C. indica, and C. ruderalis. Alternatively, C. ruderalis may be included within C. sativa, or all three may be treated as subspecies of C. sativa, or C. sativa may be accepted as a single undivided species. The genus is widely accepted as being indigenous to and originating from Asia.
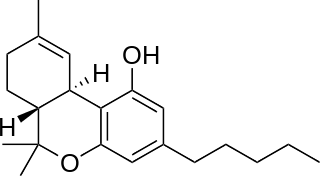
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is a cannabinoid found in cannabis. It is the principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified on the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) describes multiple isomers, the term THC usually refers to the delta-9-THC isomer with chemical name (−)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. It is a colorless oil.

The short-termeffects of cannabis are caused by many chemical compounds in the cannabis plant, including 113 different cannabinoids, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and 120 terpenes, which allow its drug to have various psychological and physiological effects on the human body. Different plants of the genus Cannabis contain different and often unpredictable concentrations of THC and other cannabinoids and hundreds of other molecules that have a pharmacological effect, so the final net effect cannot reliably be foreseen. Acute effects while under the influence can sometimes include euphoria or anxiety. Although some assert that cannabidiol (CBD), another cannabinoid found in cannabis in varying amounts, may alleviate the adverse effects of THC that some users experience, little is known about CBD's effects on humans. Cannabinoid receptor antagonists have previously been tested as antidotes for cannabis intoxication with success, reducing or eliminating the physiological and psychological effects of intoxication. Some of these products are currently in development as cannabis antidotes.

Medical cannabis, medicinal cannabis or medical marijuana (MMJ), refers to cannabis products and cannabinoid molecules that are prescribed by physicians for their patients. The use of cannabis as medicine has a long history, but has not been as rigorously tested as other medicinal plants due to legal and governmental restrictions, resulting in limited clinical research to define the safety and efficacy of using cannabis to treat diseases.

Cannabis sativa is an annual herbaceous flowering plant. The species was first classified by Carl Linnaeus in 1753. The specific epithet sativa means 'cultivated'. Indigenous to Eastern Asia, the plant is now of cosmopolitan distribution due to widespread cultivation. It has been cultivated throughout recorded history and used as a source of industrial fiber, seed oil, food, and medicine. It is also used as a recreational drug and for religious and spiritual purposes.

Cannabis, commonly known as marijuana, weed, and pot, among other names, is a non-chemically uniform drug from the cannabis plant. Native to Central or South Asia, the cannabis plant has been used as a drug for both recreational and entheogenic purposes and in various traditional medicines for centuries. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the main psychoactive component of cannabis, which is one of the 483 known compounds in the plant, including at least 65 other cannabinoids, such as cannabidiol (CBD). Cannabis can be used by smoking, vaporizing, within food, or as an extract.

Nabiximols (USAN) sold under the brand name Sativex, is a specific Cannabis extract that was approved in 2010 as a botanical drug in the United Kingdom. Nabiximols is sold as a mouth spray intended to alleviate neuropathic pain, spasticity, overactive bladder, and other symptoms of multiple sclerosis; it was developed by the UK company GW Pharmaceuticals. In 2019, it was proposed that following application of the spray, nabiximols is washed away from the oral mucosa by the saliva flow and ingested into the stomach, with subsequent absorption from the gastro-intestinal tract. Nabiximols is a combination drug standardized in composition, formulation, and dose. Its principal active components are the cannabinoids: tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Each spray delivers a dose of 2.7 mg THC and 2.5 mg CBD.
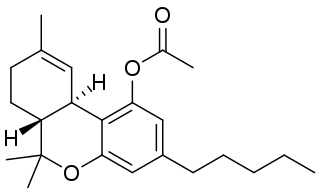
THC-O-acetate is the acetate ester of THC. The term THC-O-acetate and its variations are commonly used for two types of the substance, dependent on which cannabinoid it is synthesized from. The difference between Δ8-THC and Δ9-THC is bond placement on the cyclohexene ring.

Dimethylheptylpyran is a synthetic analog of THC, which was invented in 1949 during attempts to elucidate the structure of Δ9-THC, one of the active components of Cannabis. DMHP is a pale yellow, viscous oil which is insoluble in water but dissolves in alcohol or non-polar solvents.
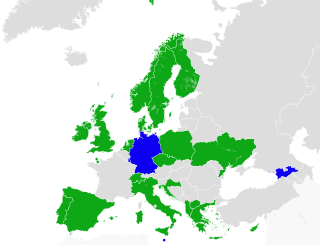
Cannabis in the United Kingdom is illegal for recreational use and is classified as a Class B drug. In 2004, the United Kingdom made cannabis a Class C drug with less severe penalties, but it was moved back to Class B in 2009. Medical use of cannabis, when prescribed by a registered specialist doctor, was legalised in November 2018.

In the United States, the use of cannabis for medical purposes is legal in 38 states, four out of five permanently inhabited U.S. territories, and the District of Columbia, as of March 2023. Ten other states have more restrictive laws limiting THC content, for the purpose of allowing access to products that are rich in cannabidiol (CBD), a non-psychoactive component of cannabis. There is significant variation in medical cannabis laws from state to state, including how it is produced and distributed, how it can be consumed, and what medical conditions it can be used for.

Dronabinol, sold under the brand names Marinol and Syndros, is the generic name for the molecule of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in the pharmaceutical context. It has indications as an appetite stimulant, antiemetic, and sleep apnea reliever and is approved by the U.S. FDA as safe and effective for HIV/AIDS-induced anorexia and chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.

Cannabis use disorder (CUD), also known as cannabis addiction or marijuana addiction, is a psychiatric disorder defined in the fifth revision of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) and ICD-10 as the continued use of cannabis despite clinically significant impairment.
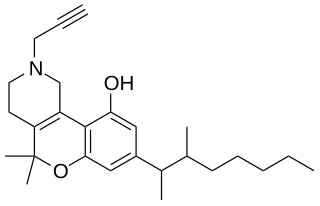
A-40174 (SP-1) is an analgesic drug which acts as a potent cannabinoid receptor agonist, and was developed by Abbott Laboratories in the 1970s. It's a structural analog of dronabinol and dimethylheptylpyran.

Menabitan, or menabitan hydrochloride (USAN), is a synthetic drug which acts as a potent cannabinoid receptor agonist. It is closely related to natural cannabinoids of the tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) group, differing mainly by its longer and branched side chain, and the replacement of the 9-position carbon with a nitrogen. It's a structural analog of Nabitan and Dimethylheptylpyran. It was studied as an analgesic in the 1970s and was found to possess antinociceptive effects in both humans and animals but was never marketed.

GW Pharmaceuticals Limited is a British pharmaceutics company known for its multiple sclerosis treatment product nabiximols which was the first natural cannabis plant derivative to gain market approval in any country. Another cannabis-based product, Epidiolex, was approved for treatment of epilepsy by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2018. It is a subsidiary of Jazz Pharmaceuticals.

Cannabis in Germany has been legal for recreational usage by adults in a limited capacity since 1 April 2024, making it the ninth country in the world to legalise the drug. As of February 2024, it has been assessed that 4.5 million Germans use cannabis.

Cannabis in Serbia is illegal. Possession is punishable by a fine or by imprisonment of up to 3 years. Sale and transport are punishable by imprisonment from 3 to 12 years. Cultivation is punishable by imprisonment from 6 months to 5 years. Penalties are higher for organized crime.
The list includes and details significant events that occurred in the global history of national-level implementations of, or changes made to, laws surrounding the use, sale, or production of the psychoactive drug cannabis.
Cannabis in Mauritania is illegal, but the country serves as a major transit point for Moroccan cannabis en route to Europe.















