 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.055.494 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
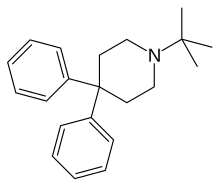
| Formula | C21H27N |
| Molar mass | 293.454 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Budipine (brand name Parkinsan) is an antiparkinson agent marketed for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. [2] [3] [4]
Contents
While its exact mechanism of action is not well characterized, [2] it is believed to be an NMDA receptor antagonist, [5] [6] but also promoting the synthesis of dopamine. [7]
Because it provides additional benefits relative to existing treatments, it probably does not precisely mimic the mechanism of an existing known treatment. [7] [8]
It is an hERG blocker and can produce long QT syndrome as a side effect. [9]
