Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as medications to decrease blood pressure in patients with hypertension. CCBs are particularly effective against large vessel stiffness, one of the common causes of elevated systolic blood pressure in elderly patients. Calcium channel blockers are also frequently used to alter heart rate, to prevent peripheral and cerebral vasospasm, and to reduce chest pain caused by angina pectoris.
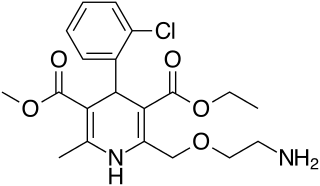
Amlodipine is a calcium channel blocker medication used to treat high blood pressure and coronary artery disease. While not typically recommended in heart failure, amlodipine may be used if other medications are not sufficient for treating high blood pressure or heart-related chest pain. It is taken by mouth and has an effect that lasts for at least a day.

Diltiazem, sold under the brand name Cardizem among others, is a calcium channel blocker medication used to treat high blood pressure, angina, and certain heart arrhythmias. It may also be used in hyperthyroidism if beta blockers cannot be used. It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein. When given by injection, effects typically begin within a few minutes and last a few hours.

Diproteverine is a calcium channel blocker.

Flunarizine, sold under the brand name Sibelium among others, is a medication of the calcium channel blocker class. It is used treat migraines, occlusive peripheral vascular disease, vertigo of central and peripheral origin, and as an adjuvant in the therapy of epilepsy. The drug was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica (R14950) in 1968.
The P-type calcium channel is a type of voltage-dependent calcium channel. Similar to many other high-voltage-gated calcium channels, the α1 subunit determines most of the channel's properties. The 'P' signifies cerebellar Purkinje cells, referring to the channel's initial site of discovery. P-type calcium channels play a similar role to the N-type calcium channel in neurotransmitter release at the presynaptic terminal and in neuronal integration in many neuronal types.
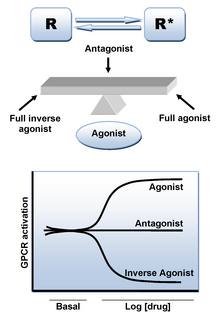
An adrenergic antagonist is a drug that inhibits the function of adrenergic receptors. There are five adrenergic receptors, which are divided into two groups. The first group of receptors are the beta (β) adrenergic receptors. There are β1, β2, and β3 receptors. The second group contains the alpha (α) adrenoreceptors. There are only α1 and α2 receptors. Adrenergic receptors are located near the heart, kidneys, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract. There are also α-adreno receptors that are located on vascular smooth muscle.

Benidipine is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker for the treatment of high blood pressure (hypertension). It is a triple L-, T-, and N-type calcium channel blocker. It is reno- and cardioprotective.

Cilnidipine is a calcium channel blocker. Cilnidipine is approved for use in Japan, China, India, Nepal, Korea, and some European countries to treat hypertension.

Gallopamil (INN) is an L-type calcium channel blocker that is an analog of verapamil. It is used in the treatment of abnormal heart rhythms.

Efonidipine (INN) is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker marketed by Shionogi & Co. of Japan. It was launched in 1995, under the brand name Landel (ランデル). The drug blocks both T-type and L-type calcium channels. Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) has approved the use of efonidipine in India. It is launched under the brand name "Efnocar".

Pranidipine is a calcium channel blocker. It is a long acting calcium channel antagonist of the dihydropyridine group.

Niludipine is a calcium channel blocker of the dihydropyridine class. It is a vasodilator that acts upon the coronary arteries of the heart-lung. It was found to produce a calcium antagonistic effect on the smooth muscle of hearts of canines and guinea pigs inhibiting myocardial oxidative metabolism.

Monatepil is a calcium channel blocker and α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist used as an antihypertensive.

Dimeditiapramine (Tiapamil) is a calcium channel blocker. Tiapamil has been described as an "antianginal agent".

Darodipine is an experimental calcium channel blocker that based on animal models may reduce neuronal cytoskeletal alterations during aging and in neurodegenerative disorders. Studies performed on rats have shown darodipine to have an effect on brain serotonergic systems. Darodipine increased the 5-HIAA/5-HT ratio within various parts of the brain. Darodipine has also been shown to impair memory and learning processes on mice.

Fostedil is a vasodilator acting as a calcium channel blocker which was under development for the treatment of heart conditions such as angina pectoris but was never marketed. It has antihypertensive and antiarrhythmic effects.
A channel modulator, or ion channel modulator, is a type of drug which modulates ion channels. They include channel blockers and channel openers.

Lomerizine (INN) is a diphenylpiperazine class L-type and T-type calcium channel blocker. This drug is currently used clinically for the treatment of migraines, while also being used experimentally for the treatment of glaucoma and optic nerve injury.

TRPV3-74a is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist for the TRPV3 calcium channel. It has analgesic effects in animal studies against both neuropathic pain and normal pain responses.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

















