 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Dymelor |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| MedlinePlus | a602021 |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 90% |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.301 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
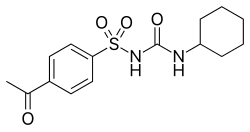
| Formula | C15H20N2O4S |
| Molar mass | 324.40 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 188 to 190 °C (370 to 374 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Acetohexamide (trade name Dymelor) is a first-generation sulfonylurea medication used to treat diabetes mellitus type 2, particularly in people whose diabetes cannot be controlled by diet alone. [1]