Related Research Articles
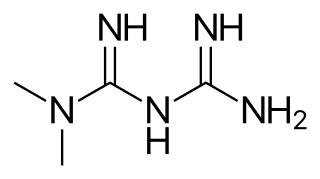
Metformin, sold under the brand name Glucophage, among others, is the main first-line medication for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, particularly in people who are overweight. It is also used in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome. It is not associated with weight gain and is taken by mouth. It is sometimes used as an off-label adjunct to lessen the risk of metabolic syndrome in people who take antipsychotics.
Drugs used in diabetes treat diabetes mellitus by altering the glucose level in the blood. With the exceptions of insulin, most GLP receptor agonists, and pramlintide, all are administered orally and are thus also called oral hypoglycemic agents or oral antihyperglycemic agents. There are different classes of anti-diabetic drugs, and their selection depends on the nature of the diabetes, age and situation of the person, as well as other factors.

Rosiglitazone is an antidiabetic drug in the thiazolidinedione class. It works as an insulin sensitizer, by binding to the PPAR in fat cells and making the cells more responsive to insulin. It is marketed by the pharmaceutical company GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) as a stand-alone drug or for use in combination with metformin or with glimepiride. First released in 1999, annual sales peaked at approximately $2.5-billion in 2006; however, following a meta-analysis in 2007 that linked the drug's use to an increased risk of heart attack, sales plummeted to just $9.5-million in 2012. The drug's patent expired in 2012.
ATC code A02Drugs for acid related disorders is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup A02 is part of the anatomical group A Alimentary tract and metabolism.
ATC code B02Antihemorrhagics is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup B02 is part of the anatomical group B Blood and blood forming organs.
ATC code B03Antianemic preparations is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup B03 is part of the anatomical group B Blood and blood forming organs.
ATC code C03Diuretics is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup C03 is part of the anatomical group C Cardiovascular system.
ATC code D10Anti-acne preparations is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup D10 is part of the anatomical group D Dermatologicals.
ATC code J07Vaccines is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup J07 is part of the anatomical group J Antiinfectives for systemic use.
ATC code L02Endocrine therapy is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup L02 is part of the anatomical group L Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents.
ATC code N01Anesthetics is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup N01 is part of the anatomical group N Nervous system.
ATC code N04Anti-parkinson drugs is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup N04 is part of the anatomical group N Nervous system.
ATC code N05Psycholeptics is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup N05 is part of the anatomical group N Nervous system.
ATC code P01Antiprotozoals is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup P01 is part of the anatomical group P Antiparasitic products, insecticides and repellents.

Inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 are a class of oral hypoglycemics that block the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4). They can be used to treat diabetes mellitus type 2.

Saxagliptin, sold under the brand name Onglyza, is an oral hypoglycemic of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class. Early development was solely by Bristol-Myers Squibb; in 2007 AstraZeneca joined with Bristol-Myers Squibb to co-develop the final compound and collaborate on the marketing of the drug.
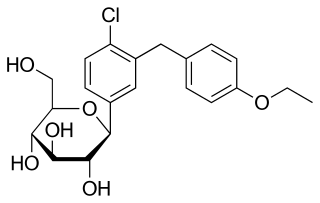
Dapagliflozin, sold under the brand names Farxiga (US) and Forxiga (EU) among others, is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is also used to treat adults with heart failure and chronic kidney disease.
ATCvet code QP53Ectoparasiticides, including insecticides and repellents is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System for veterinary medicinal products, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products for veterinary use. Subgroup QP53 is part of the anatomical group QP Antiparasitic products, insecticides and repellents.

Insulin degludec (INN/USAN) is an ultralong-acting basal insulin analogue that was developed by Novo Nordisk under the brand name Tresiba. It is administered via subcutaneous injection once daily to help control the blood sugar level of those with diabetes. It has a duration of action that lasts up to 42 hours, making it a once-daily basal insulin, that is one that provides a base insulin level, as opposed to the fast- and short-acting bolus insulins.
SGLT2 inhibitors, also called gliflozins or flozins, are a class of medications that modulate sodium-glucose transport proteins in the nephron, unlike SGLT1 inhibitors that perform a similar function in the intestinal mucosa. The foremost metabolic effect of this is to inhibit reabsorption of glucose in the kidney and therefore lower blood sugar. They act by inhibiting sodium-glucose transport protein 2 (SGLT2). SGLT2 inhibitors are used in the treatment of type II diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Apart from blood sugar control, gliflozins have been shown to provide significant cardiovascular benefit in patients with type II diabetes (T2DM). Several medications of this class have been approved or are currently under development. In studies on canagliflozin, a member of this class, the medication was found to enhance blood sugar control as well as reduce body weight and systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
References
- ↑ "ATC (Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System) – Synopsis". National Institutes of Health . Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- ↑ World Health Organization. "Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classification". World Health Organization. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
- ↑ "Structure and principles". WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. 15 February 2018. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
- ↑ "ATC/DDD Index 2022: code A10". WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology.
- ↑ "ATCvet Index 2022: code QA10". WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology.