Anticonvulsants are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Anticonvulsants suppress the excessive rapid firing of neurons during seizures. Anticonvulsants also prevent the spread of the seizure within the brain.
Topiramate, sold under the brand name Topamax among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy and prevent migraines. It has also been used in alcohol dependence and essential tremor. For epilepsy this includes treatment for generalized or focal seizures. It is taken orally.

Lamotrigine, sold under the brand name Lamictal among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy and stabilize mood in bipolar disorder. For epilepsy, this includes focal seizures, tonic-clonic seizures, and seizures in Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. In bipolar disorder, lamotrigine has not been shown to reliably treat acute depression for all groups except in the severely depressed; but for patients with bipolar disorder who are not currently symptomatic, it appears to reduce the risk of future episodes of depression.

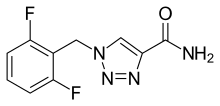
Oxcarbazepine, sold under the brand name Trileptal among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy. For epilepsy it is used for both focal seizures and generalized seizures. It has been used both alone and as add-on therapy in people with bipolar disorder who have had no success with other treatments. It is taken by mouth.
Levetiracetam, sold under the brand name Keppra among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy. It is used for partial-onset, myoclonic, or tonic–clonic seizures and is taken either by mouth as an immediate or extended release formulation or by injection into a vein.

Vigabatrin, sold under the brand names Sabril and Vigpoder, is a medication used to treat epilepsy. It became available as a generic medication in 2019.

Lennox–Gastaut syndrome (LGS) is a complex, rare, and severe childhood-onset epilepsy syndrome. It is characterized by multiple and concurrent seizure types including tonic seizure, cognitive dysfunction, and slow spike waves on electroencephalogram (EEG), which are very abnormal. Typically, it presents in children aged 3–5 years and most of the time persists into adulthood with slight changes in the electroclinical phenotype. It has been associated with perinatal injuries, congenital infections, brain malformations, brain tumors, genetic disorders such as tuberous sclerosis and numerous gene mutations. Sometimes LGS is observed after infantile epileptic spasm syndrome. The prognosis for LGS is marked by a 5% mortality in childhood and persistent seizures into adulthood.
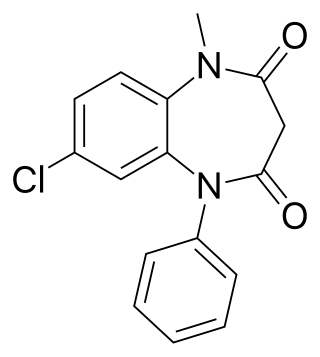
Clobazam, sold under the brand names Frisium, Onfi and others, is a benzodiazepine class medication that was patented in 1968. Clobazam was first synthesized in 1966 and first published in 1969. Clobazam was originally marketed as an anxioselective anxiolytic since 1970, and an anticonvulsant since 1984. The primary drug-development goal was to provide greater anxiolytic, anti-obsessive efficacy with fewer benzodiazepine-related side effects.
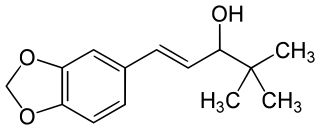
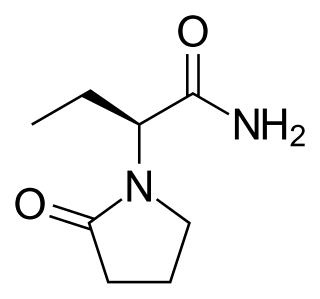
Stiripentol, sold under the brand name Diacomit, is an anticonvulsant medication used for the treatment of Dravet syndrome - a serious genetic brain disorder.
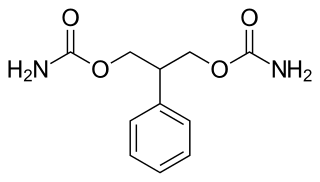
Felbamate is an anticonvulsant used in the treatment of epilepsy. It is used to treat partial seizures in adults and partial and generalized seizures associated with Lennox–Gastaut syndrome in children. However, an increased risk of potentially fatal aplastic anemia and/or liver failure limit the drug's usage to severe refractory epilepsy.
Dravet syndrome (DS), previously known as severe myoclonic epilepsy of infancy (SMEI), is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder which causes a catastrophic form of epilepsy, with prolonged seizures that are often triggered by hot temperatures or fever. It is very difficult to treat with anticonvulsant medications. It often begins before one year of age, with six months being the age that seizures, characterized by prolonged convulsions and triggered by fever, usually begin.
Ring chromosome 20, ring-shaped chromosome 20 or r(20) syndrome is a rare human chromosome abnormality where the two arms of chromosome 20 fuse to form a ring chromosome. The syndrome is associated with epileptic seizures, behaviour disorders and intellectual disability.

Generalized epilepsy is a form of epilepsy characterised by generalised seizures with no apparent cause. Generalized seizures, as opposed to focal seizures, are a type of seizure that impairs consciousness and distorts the electrical activity of the whole or a larger portion of the brain.

Brivaracetam, sold under the brand name Briviact among others, is a chemical analog of levetiracetam, a racetam derivative with anticonvulsant (antiepileptic) properties. It is marketed by the pharmaceutical company UCB.

Lacosamide, sold under the brand name Vimpat among others, is a medication used for the treatment of partial-onset seizures and primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures. It is used by mouth or intravenously.
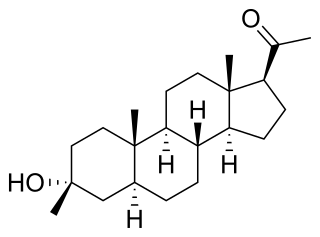
Ganaxolone, sold under the brand name Ztalmy, is a medication used to treat seizures in people with cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 (CDKL5) deficiency disorder. Ganaxolone is a neuroactive steroid gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor positive modulator.

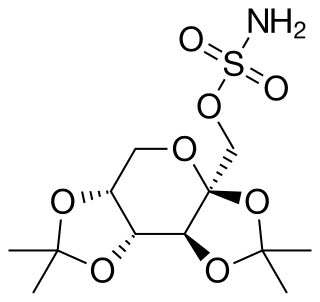
Retigabine (INN) or ezogabine (USAN) is an anticonvulsant used as an adjunctive treatment for partial epilepsies in treatment-experienced adult patients. The drug was developed by Valeant Pharmaceuticals and GlaxoSmithKline. It was approved by the European Medicines Agency under the trade name Trobalt on March 28, 2011, and by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA), under the trade name Potiga, on June 10, 2011. Production was discontinued in June 2017.

Perampanel, sold under the brand name Fycompa, is an anti-epileptic medication developed by Eisai Co. that is used in addition to other drugs to treat partial seizures and generalized tonic-clonic seizures for people older than twelve years. It was first approved in 2012, and as of 2016, its optimal role in the treatment of epilepsy relative to other drugs was not clear. It was the first antiepileptic drug in the class of selective non-competitive antagonist of AMPA receptors.

Eslicarbazepine acetate (ESL), sold under the brand names Aptiom and Zebinix among others, is an anticonvulsant medication approved for use in Europe and the United States as monotherapy or as additional therapy for partial-onset seizures epilepsy.
Cenobamate, sold under the brand names Xcopri (US) and Ontozry (EU), is a medication used for the treatment of partial-onset seizures, a kind of epilepsy, in adults. It is taken by mouth.