Mucoactive agents are a class of chemical agents that aid in the clearance of mucus or sputum from the upper and lower airways, including the lungs, bronchi, and trachea. Mucoactive drugs include expectorants, mucolytics, mucoregulators, and mucokinetics. These medications are used in the treatment of respiratory diseases that are complicated by the oversecretion or inspissation of mucus. These drugs can be further categorized by their mechanism of action.
214 is the natural number following 213 and preceding 215.

Ethocybin is a homologue of the mushroom alkaloid psilocybin, and a semi-synthetic psychedelic alkaloid of the tryptamine family. Effects of ethocybin are comparable to those of a shorter LSD or psilocybin trip, although intensity and duration vary depending on dosage, individual physiology, and set and setting.

Cinchonidine is an alkaloid found in Cinchona officinalis and Gongronema latifolium. It is used in asymmetric synthesis in organic chemistry.

Oxolamine is a cough suppressant that is available as a generic drug in many jurisdictions.

Omoconazole is an azole antifungal drug.

Emetine is a drug used as both an anti-protozoal and to induce vomiting. It is produced from the ipecac root. It takes its name from its emetic properties.

Fentiazac is a thiazole-based nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) developed for use in joint and muscular pain. Like most other NSAIDs, it acts through inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis, via non-selective inhibition of both COX-1 and COX-2. First described in 1974, it was synthesized using the Hantzsch thiazole synthesis.

Kebuzone is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used for the treatment of inflammatory conditions such as thrombophlebitis and rheumatoid arthritis (RA).

Balofloxacin (INN) is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic. It is sold under the brand name Q-Roxin in Korea, and under various names in India. It is not approved by the FDA for use in the United States.

Zorubicin (INN) is a benzoylhydrazone derivative of the anthracycline antineoplastic antibiotic daunorubicin. Zorubicin intercalates into DNA; it as well interacts with topoisomerase II and inhibits DNA polymerases and therefore is used to treat cancer.
Ecallantide is a drug used for the treatment of hereditary angioedema (HAE) and in the prevention of blood loss in cardiothoracic surgery. It is an inhibitor of the protein kallikrein and a 60-amino acid polypeptide which was developed from a Kunitz domain through phage display to mimic antibodies inhibiting kallikrein.

Dihexyverine is an anticholinergic spasmolytic. It is not approved for use in the United States but is sold in France under the trade name Spasmodex.

Methylatropine is a belladonna derivative.

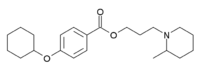
Trepibutone is a drug used for functional gastrointestinal disorders. Trepibutone promotes secretion of the bile and pancreatic juice, and accelerates flaccidity of the smooth muscle in the gastrointestinal tract to lower internal pressure of the gallbladder and bile duct. It improves the symptoms of the bile duct and pancreatic disease. It is usually used for improvement of cramp and bile secretion associated with cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, cholangitis, dyskinesia of the biliary tract or postcholecystectomy syndrome, or pain and gastrointestinal symptoms associated with chronic pancreatitis.

Trolnitrate is an organic nitrate with vasodilator activity that is used to prevent or ameliorate attacks of angina pectoris. Trolnitrate dilates the coronary vessels because of its basic action as a smooth muscle depressant, just as do nitroglycerin and other organic nitrates.

Etozolin is a loop diuretic used in Europe. It is believed to be discontinued.
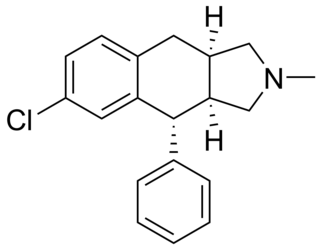
Losindole (BI-27,062) is an antidepressant with a tricyclic structure. It was never marketed.
The National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) was established on December 23, 2011 and is located in Bethesda, Maryland. NCATS is one of 27 institutes and centers of the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), an agency of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The mission of NCATS is to transform scientific discoveries into new treatments and cures for disease that can be delivered faster to patients. The budget provided to NCATS for fiscal year 2018 is $557,373,000.

Zolamine is an antihistamine and anticholinergic used as an antipruritic.