Local anesthesia is any technique to induce the absence of sensation in a specific part of the body, generally for the aim of inducing local analgesia, i.e. local insensitivity to pain, although other local senses may be affected as well. It allows patients to undergo surgical and dental procedures with reduced pain and distress. In many situations, such as cesarean section, it is safer and therefore superior to general anesthesia.

A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of all sensation in a specific body part without loss of consciousness, as opposed to a general anesthetic, which eliminates all sensation in the entire body and causes unconsciousness. Local anesthetics are most commonly used to eliminate pain during or after surgery. When it is used on specific nerve pathways, paralysis also can be induced.

Lidocaine, also known as lignocaine and sold under the brand name Xylocaine among others, is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia. When used for local anaesthesia or in nerve blocks, lidocaine typically begins working within several minutes and lasts for half an hour to three hours. Lidocaine mixtures may also be applied directly to the skin or mucous membranes to numb the area. It is often used mixed with a small amount of adrenaline (epinephrine) to prolong its local effects and to decrease bleeding.

Fluorescein is an organic compound and dye based on the xanthene tricyclic structural motif, formally belonging to triarylmethine dyes family. It is available as a dark orange/red powder slightly soluble in water and alcohol. It is widely used as a fluorescent tracer for many applications.
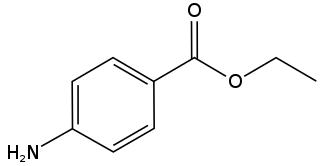
Benzocaine, sold under the brand name Orajel amongst others, is a local anesthetic, belonging to the amino ester drug class, commonly used as a topical painkiller or in cough drops. It is the active ingredient in many over-the-counter anesthetic ointments such as products for oral ulcers. It is combined with antipyrine to form A/B ear drops. In the US, products containing benzocaine for oral application are contraindicated in children younger than two years old. In the European Union, the contraindication applies to children under 12 years of age.

An anesthetic or anaesthetic is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into two broad classes: general anesthetics, which result in a reversible loss of consciousness, and local anesthetics, which cause a reversible loss of sensation for a limited region of the body without necessarily affecting consciousness.
Benzonatate, sold under the brand name Tessalon among others, is a medication that is used for the symptomatic relief of cough. It is taken by mouth. Use is not recommended in those under the age of ten. Effects generally begin within 20 minutes and last up to eight hours.

Bupivacaine, marketed under the brand name Marcaine among others, is a medication used to decrease feeling in a specific area. In nerve blocks, it is injected around a nerve that supplies the area, or into the spinal canal's epidural space. It is available mixed with a small amount of epinephrine to increase the duration of its action. It typically begins working within 15 minutes and lasts for 2 to 8 hours.

Corneal abrasion is a scratch to the surface of the cornea of the eye. Symptoms include pain, redness, light sensitivity, and a feeling like a foreign body is in the eye. Most people recover completely within three days.
Oxybuprocaine (INN), also known as benoxinate or BNX, is an ester-type local anesthetic, which is used especially in ophthalmology and otolaryngology. Oxybuprocaine is sold by Novartis under the brand names Novesine or Novesin.
A topical anesthetic is a local anesthetic that is used to numb the surface of a body part. They can be used to numb any area of the skin as well as the front of the eyeball, the inside of the nose, ear or throat, the anus and the genital area. Topical anesthetics are available in creams, ointments, aerosols, sprays, lotions, and jellies. Examples include benzocaine, butamben, dibucaine, lidocaine, oxybuprocaine, pramoxine, proxymetacaine (proparacaine), and tetracaine.
Articaine is a dental amide-type local anesthetic. It is the most widely used local anesthetic in a number of European countries and is available in many countries. It is the only local anaesthetic to contain a thiophene ring, meaning it can be described as 'thiophenic'; this conveys lipid solubility.

Prilocaine is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type first prepared by Claes Tegner and Nils Löfgren. In its injectable form, it is often used in dentistry. It is also often combined with lidocaine as a topical preparation for dermal anesthesia, for treatment of conditions like paresthesia. As it has low cardiac toxicity, it is commonly used for intravenous regional anaesthesia (IVRA).

Etidocaine, marketed under the trade name Duranest, is an amide-type local anesthetic given by injection during surgical procedures and labor and delivery. Etidocaine has a long duration of activity, and the main disadvantage of using during dentistry is increased bleeding during surgery.
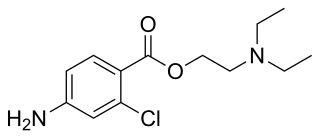
Chloroprocaine is a local anesthetic given by injection during surgical procedures and labor and delivery. Chloroprocaine vasodilates; this is in contrast to cocaine which vasoconstricts. Chloroprocaine is an ester anesthetic.

Cinchocaine (INN/BAN) or dibucaine (USAN) is an amide local anesthetic. Among the most potent and toxic of the long-acting local anesthetics, current use of cinchocaine is generally restricted to spinal and topical anesthesia. It is sold under the brand names Cincain, Nupercainal, Nupercaine and Sovcaine.
A stress ulcer is a single or multiple mucosal defect usually caused by physiological stress which can become complicated by upper gastrointestinal bleeding. This ulcers can be caused by shock, sepsis, trauma or other conditions and are found in patients with chronic illnesses. These ulcers are a significant issue in patients in critical and intensive care.
Dental anesthesia is the application of anesthesia to dentistry. It includes local anesthetics, sedation, and general anesthesia.
Cetacaine is a topical anesthetic that contains the active ingredients benzocaine (14%), butamben (2%), and tetracaine hydrochloride (2%). Cetacaine also contains small amounts of benzalkonium chloride at 0.5% and 0.005% of cetyl dimethyl ethyl ammonium bromide all in a bland water-soluble base. Although Cetacaine has been widely used in the medical and dental fields, it has yet to be officially approved by the FDA. Cetacaine is produced by the company Cetylite Industries, Inc. and they provide Cetacaine in three forms: liquid, gel, and spray.