
A beta-lactam (β-lactam) ring is a four-membered lactam. A lactam is a cyclic amide, and beta-lactams are named so because the nitrogen atom is attached to the β-carbon atom relative to the carbonyl. The simplest β-lactam possible is 2-azetidinone. β-lactams are significant structural units of medicines as manifested in many β-lactam antibiotics Up to 1970, most β-lactam research was concerned with the penicillin and cephalosporin groups, but since then, a wide variety of structures have been described.
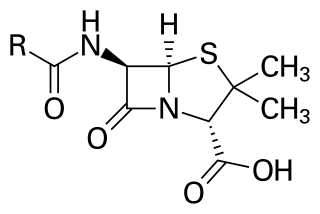
Penicillins are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from Penicillium moulds, principally P. chrysogenum and P. rubens. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using deep tank fermentation and then purified. A number of natural penicillins have been discovered, but only two purified compounds are in clinical use: penicillin G and penicillin V. Penicillins were among the first medications to be effective against many bacterial infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci. They are still widely used today for different bacterial infections, though many types of bacteria have developed resistance following extensive use.

Halothane, sold under the brand name Fluothane among others, is a general anaesthetic. It can be used to induce or maintain anaesthesia. One of its benefits is that it does not increase the production of saliva, which can be particularly useful in those who are difficult to intubate. It is given by inhalation.

Cyclopropane is the cycloalkane with the molecular formula (CH2)3, consisting of three methylene groups (CH2) linked to each other to form a ring. The small size of the ring creates substantial ring strain in the structure. Cyclopropane itself is mainly of theoretical interest but many of its derivatives are of commercial or biological significance.
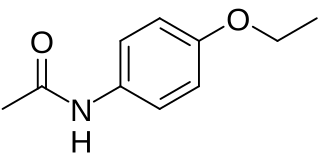
Phenacetin is a pain-relieving and fever-reducing drug, which was widely used following its introduction in 1887. It was withdrawn from medicinal use as dangerous from the 1970s.

Phenylpropanolamine (PPA) is a sympathomimetic agent which is used as a decongestant and appetite suppressant. It was commonly used in prescription and over-the-counter cough and cold preparations. In veterinary medicine, it is used to control urinary incontinence in dogs.
In the physical sciences, a partition coefficient (P) or distribution coefficient (D) is the ratio of concentrations of a compound in a mixture of two immiscible solvents at equilibrium. This ratio is therefore a comparison of the solubilities of the solute in these two liquids. The partition coefficient generally refers to the concentration ratio of un-ionized species of compound, whereas the distribution coefficient refers to the concentration ratio of all species of the compound.

Dextropropoxyphene is an analgesic in the opioid category, patented in 1955 and manufactured by Eli Lilly and Company. It is an optical isomer of levopropoxyphene. It is intended to treat mild pain and also has antitussive and local anaesthetic effects. The drug has been taken off the market in Europe and the US due to concerns of fatal overdoses and heart arrhythmias. It is still available in Australia, albeit with restrictions after an application by its manufacturer to review its proposed banning. Its onset of analgesia is said to be 20–30 minutes and peak effects are seen about 1.5–2.0 hours after oral administration.

Vidarabine or 9-β-D-arabinofuranosyladenine (ara-A) is an antiviral drug which is active against herpes simplex and varicella zoster viruses.
The Ugi reaction is a multi-component reaction in organic chemistry involving a ketone or aldehyde, an amine, an isocyanide and a carboxylic acid to form a bis-amide. The reaction is named after Ivar Karl Ugi, who first reported this reaction in 1959.
In organic chemistry, the Mannich reaction is a three-component organic reaction that involves the amino alkylation of an acidic proton next to a carbonyl functional group by formaldehyde and a primary or secondary amine or ammonia. The final product is a β-amino-carbonyl compound also known as a Mannich base. Reactions between aldimines and α-methylene carbonyls are also considered Mannich reactions because these imines form between amines and aldehydes. The reaction is named after Carl Mannich.
Ernest Henry Volwiler was an American chemist. He spent his career at Abbott Laboratories working his way from staff chemist to CEO. He was a pioneer in the field of anesthetic pharmacology, assisting in the development of two breakthrough drugs, Nembutal and Pentothal. Volwiler also helped Abbott Laboratories to achieve commercial success for its pharmaceutical products including the commercialization of penicillin and sulfa drugs during World War II.

Quinbolone, sold under the brand names Anabolicum and Anabolvis, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) which was previously marketed in Italy. It was developed by Parke-Davis as a viable orally administered AAS with little or no liver toxicity.
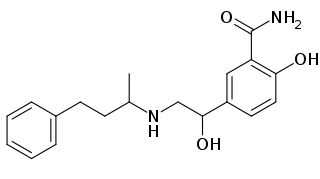
Labetalol is a medication used to treat high blood pressure and in long term management of angina. This includes essential hypertension, hypertensive emergencies, and hypertension of pregnancy. In essential hypertension it is generally less preferred than a number of other blood pressure medications. It can be given by mouth or by injection into a vein.

Methoxyflurane, sold under the brand name Penthrox among others, is an inhaled medication primarily used to reduce pain following trauma. It may also be used for short episodes of pain as a result of medical procedures. Onset of pain relief is rapid and of a short duration. Use is only recommended with direct medical supervision.

Fluoxymesterone, sold under the brand names Halotestin and Ultandren among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men, delayed puberty in boys, breast cancer in women, and anemia. It is taken by mouth.

Alfaxalone, also known as alphaxalone or alphaxolone and sold under the brand name Alfaxan, is a neuroactive steroid and general anesthetic which is used currently in veterinary practice as an induction agent for anesthesia and as an injectable anesthetic. Though it is more expensive than other induction agents, it often preferred due to the lack of depressive effects on the cardiovascular system. The most common side effect seen in current veterinary practice is respiratory depression when Alfaxan is administered concurrently with other sedative and anesthetic drugs; when premedications aren't given, veterinary patients also become agitated and hypersensitive when waking up.

Martha Annie Whiteley, was an English chemist and mathematician. She was instrumental in advocating for women's entry into the Chemical Society, and was best known for her dedication to advancing women's equality in the field of chemistry. She is identified as one of the Royal Society of Chemistry's 175 Faces of Chemistry.
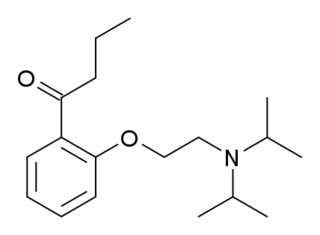
Ketocaine (INN) is an amino ether local anesthetic of the butyrophenone family used topically for pain relief. It is marketed in Italy.
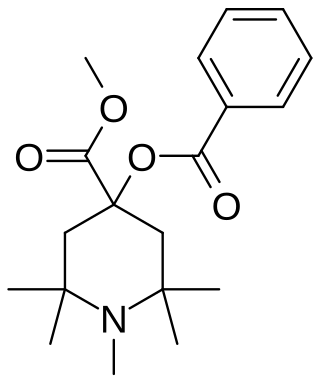
α-Eucaine (alpha-eucaine) is a drug that was previously used as a local anesthetic. It was designed as an analog of cocaine and was one of the first synthetic chemical compounds to find general use as an anesthetic.

















