This article needs more reliable medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources .(March 2015) |  |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 9,20,21,25-tetramethoxy-15,30-dimethyl-7,23-dioxa-15,30-diazaheptacyclo[22.6.2.23,6.18,12.114,18.027,31.022,33]hexatriaconta-3,5,8(34),9,11,18,20,22(33),24(32),25,27(31),35-dodecaene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.208.615 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| Properties | |
| C38H42N2O6 | |
| Molar mass | 622.74988 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
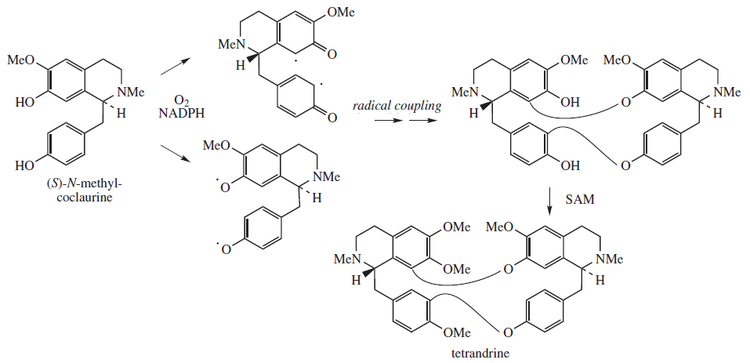
Tetrandrine, a bis-benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, is a calcium channel blocker. [1] It is isolated from the plant Stephania tetrandra , [2] and other Chinese and Japanese herbs.