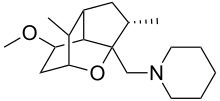
Tromantadine is an antiviral medicine used to treat herpes simplex virus. It is available in a topical gel under trade names Viru-Merz and Viru-Merz Serol. Its performance is similar to aciclovir.

Camazepam is a benzodiazepine psychoactive drug, marketed under the brand names Albego, Limpidon and Paxor. It is the dimethyl carbamate ester of temazepam, a metabolite of diazepam. While it possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, skeletal muscle relaxant and hypnotic properties it differs from other benzodiazepines in that its anxiolytic properties are particularly prominent but has comparatively limited anticonvulsant, hypnotic and skeletal muscle relaxant properties.

Lercanidipine is an antihypertensive drug. It belongs to the dihydropyridine class of calcium channel blockers, which work by relaxing and opening the blood vessels allowing the blood to circulate more freely around the body. This lowers the blood pressure and allows the heart to work more efficiently.

Ambroxol is a drug that breaks up phlegm, used in the treatment of respiratory diseases associated with viscid or excessive mucus. Ambroxol is often administered as an active ingredient in cough syrup.

Chlorphenoxamine (Phenoxene) is an antihistamine and anticholinergic used as an antipruritic and antiparkinsonian agent. It is an analog of diphenhydramine.

Budipine is an antiparkinson agent marketed for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.

Metaclazepam is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It is a relatively selective anxiolytic with less sedative or muscle relaxant properties than other benzodiazepines such as diazepam or bromazepam. It has an active metabolite N-desmethylmetaclazepam, which is the main metabolite of metaclazepam. There is no significant difference in metabolism between younger and older individuals.
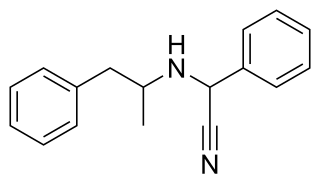
Amfetaminil is a stimulant drug derived from amphetamine, which was developed in the 1970s and used for the treatment of obesity, ADHD, and narcolepsy. It has largely been withdrawn from clinical use following problems with abuse. The drug is a prodrug to amphetamine.

Mabuterol is a selective β2 adrenoreceptor agonist.
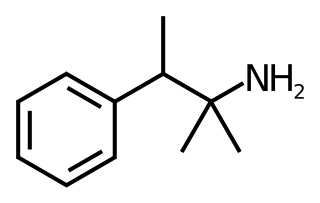
Pentorex (Modatrop), also known as phenpentermine or α,β-dimethylamphetamine, is a stimulant drug related to phentermine which is used as an anorectic to assist with weight loss. It also acts as a diuretic. Pentorex was developed by Nordmark in the 1960s.

Niludipine is a calcium channel blocker of the dihydropyridine class. It is a vasodilator that acts upon the coronary arteries of the heart-lung. It was found to produce a calcium antagonistic effect on the smooth muscle of hearts of canines and guinea pigs inhibiting myocardial oxidative metabolism.
Almagate is an aluminium- and magnesium-containing antacid. It was first described in 1984.

Tolonidine is an antihypertensive. It is an imidazoline receptor agonist, like moxonidine and rilmenidine.
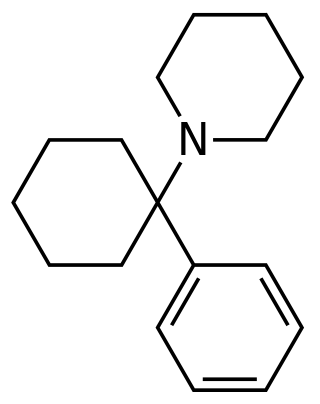
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs.

Fenpentadiol (INN), also known as phenpentanediol, is a drug described as a tranquilizer and antidepressant that was formerly marketed in Europe. It also has stimulant, sedative, and anxiolytic effects, with the latter two occurring only at higher doses.

Fostedil is a vasodilator acting as a calcium channel blocker which was under development for the treatment of heart conditions such as angina pectoris but was never marketed. It has antihypertensive and antiarrhythmic effects.

Fluperlapine, also known as fluoroperlapine, is a morphanthridine (11H-dibenzo[b,e]azepine) atypical antipsychotic with additional antidepressant and sedative effects. It was first synthesized in 1979, and then subsequently studied in animals and humans in 1984 and beyond, but despite demonstrating efficacy in the treatment of a variety of medical conditions including schizophrenia, psychosis associated with Parkinson's disease, depressive symptoms, and dystonia, it was never marketed. This was perhaps due to its capacity for producing potentially life-threatening agranulocytosis, similarly to clozapine, which it closely resembles both structurally and pharmacologically.

SL-164, also known as dicloqualone or DCQ, is an analogue of methaqualone developed in the late 1960s by a team at Sumitomo. SL-164 has similar sedative, hypnotic and properties to the parent compound, but was never marketed for clinical use, due to higher risk of convulsions. Like other 4-substituted analogues, like methylmethaqualone, SL-164 may cause seizures.

Clocental (dolcental) is a carbamate-derived sedative hypnotic.

Mespirenone (INN), also known as Δ1-15β,16β-methylenespironolactone, is a steroidal antimineralocorticoid of the spirolactone group related to spironolactone that was never marketed. Animal research found that it was 3.3-fold more potent as an antimineralocorticoid relative to spironolactone. In addition to its antimineralocorticoid properties, mespirenone is also a progestogen, antigonadotropin, and antiandrogen. It is 2- to 3-fold as potent as spironolactone as a progestogen and antigonadotropin but its antiandrogenic activity is markedly reduced and weak in comparison. Mespirenone is also a potent and specific enzyme inhibitor of 18-hydroxylase and thus of mineralocorticoid biosynthesis. The drug was under development by Schering and reached phase II clinical trials but was discontinued in 1989.