| |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Manyper, Caldine, etc. |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C35H38N4O6 |
| Molar mass | 610.711 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
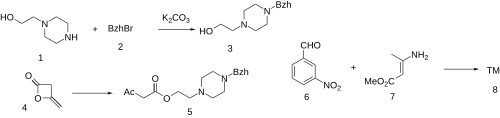
Manidipine is a calcium channel blocker (dihydropyridine type) that is used clinically as an antihypertensive. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5]
It was patented in 1982 and approved for medical use in 1990. [6]