
5-HT receptors, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, or serotonin receptors, are a group of G protein-coupled receptor and ligand-gated ion channels found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The serotonin receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin, which acts as their natural ligand.
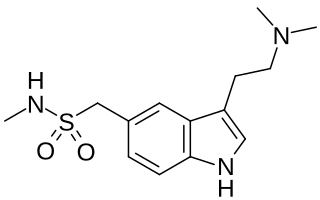
Triptans are a family of tryptamine-based drugs used as abortive medication in the treatment of migraines and cluster headaches. This drug class was first commercially introduced in the 1990s. While effective at treating individual headaches, they do not provide preventive treatment and are not considered a cure. They are not effective for the treatment of tension–type headache, except in persons who also experience migraines. Triptans do not relieve other kinds of pain.

A serotonin receptor agonist is an agonist of one or more serotonin receptors. They activate serotonin receptors in a manner similar to that of serotonin, a neurotransmitter and hormone and the endogenous ligand of the serotonin receptors.

meta-Chlorophenylpiperazine (mCPP) is a psychoactive drug of the phenylpiperazine class. It was initially developed in the late-1970s and used in scientific research before being sold as a designer drug in the mid-2000s. It has been detected in pills touted as legal alternatives to illicit stimulants in New Zealand and pills sold as "ecstasy" in Europe and the United States.

Mesulergine (INNTooltip International Nonproprietary Name) (developmental code name CU-32085) is a drug of the ergoline group which was never marketed. It acts on serotonin and dopamine receptors. Specifically, it is an agonist of dopamine D2-like receptors and serotonin 5-HT6 receptors and an antagonist of serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, 5-HT2C, and 5-HT7 receptors.. It also has affinity for the 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D, 5-HT1F, and 5-HT5A receptors. The compound had entered clinical trials for the treatment of Parkinson's disease; however, further development was halted due to adverse histological abnormalities in rats. It was also investigated for the treatment of hyperprolactinemia (high prolactin levels).

The serotonin 1A receptor is a subtype of serotonin receptors, or 5-HT receptors, that binds serotonin, also known as 5-HT, a neurotransmitter. 5-HT1A is expressed in the brain, spleen, and neonatal kidney. It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), coupled to the Gi protein, and its activation in the brain mediates hyperpolarization and reduction of firing rate of the postsynaptic neuron. In humans, the serotonin 1A receptor is encoded by the HTR1A gene.

5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1B also known as the 5-HT1B receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HTR1B gene. The 5-HT1B receptor is a 5-HT receptor subtype.

8-OH-DPAT is a research chemical of the aminotetralin chemical class which was developed in the 1980s and has been widely used to study the function of the 5-HT1A receptor. It was one of the first major 5-HT1A receptor full agonists to have been discovered.

Tertatolol is a medication in the class of beta blockers, used in the treatment of high blood pressure. It was discovered by the French pharmaceutical company Servier and is marketed in Europe.

CP-94253 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective serotonin 5-HT1B receptor agonist, with approximately 25× and 40× selectivity over the closely related 5-HT1D and 5-HT1A receptors. It has a range of behavioral effects, based on animal testing. The effects include the following: promoting wakefulness by increasing dopamine release in the brain; reducing food intake and promoting satiety; enhancing the reinforcing effects of cocaine; and possible antidepressant effects. A recent study found that "Regardless of sex, CP94253 decreased cocaine intake after abstinence and during resumption of SA [self-administration] and decreased cue reactivity" suggesting that agonism of the inhibitory 5-HT2B receptors may diminish the cognitive reward of cocaine usage and increased use of the drug without a period of abstinence may be a product of test subjects trying to achieve a previously rewarding experience through larger dosages of cocaine.

SB-216641 is a drug which is a selective antagonist for the serotonin receptor 5-HT1B, with around 25x selectivity over the closely related 5-HT1D receptor. It is used in scientific research, and has demonstrated anxiolytic effects in animal studies.

Eltoprazine is a serotonergic drug of the phenylpiperazine class which is described as a serenic or antiaggressive agent. It acts as an agonist of the serotonin 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors and as an antagonist of the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor. The drug is closely related to fluprazine and batoprazine, which are similarly acting agents, and is also a known chemical precursor to S-15535 and lecozotan. Eltoprazine is or was under development for the treatment of aggression, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), cognition disorders, and drug-induced dyskinesia, but no recent development has been reported for these indications as of February 2022. It was also under development for the treatment of psychotic disorders, but development for this indication was discontinued. Eltoprazine was originated by Solvay and was developed by Elto Pharma, PsychoGenics, and Solvay.

Fluprazine (DU-27,716) is a drug of the phenylpiperazine class. It is a so-called serenic or antiaggressive agent. It is closely related to several other piperazines, including eltoprazine and batoprazine, and TFMPP, as well as more distantly to the azapirones such as buspirone. The pharmacology of fluprazine is unknown, but it is likely to act as an agonist at the 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors like its sister compound eltoprazine.

Isamoltane (CGP-361A) is a drug used in scientific research. It acts as an antagonist at the β-adrenergic, 5-HT1A, and 5-HT1B receptors. It has about five times the potency for the 5-HT1B receptor over the 5-HT1A receptor. It has anxiolytic effects in rodents.
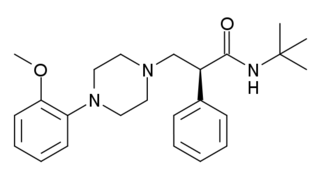
WAY-100135 is a serotonergic drug of the phenylpiperazine family which is used in scientific research. It acts as potent 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, and was originally believed to be highly selective, but further studies have demonstrated that it also acts as a partial agonist of the 5-HT1D receptor (pKi = 7.58; virtually the same affinity for 5-HT1A), and to a much lesser extent, of the 5-HT1B receptor (pKi = 5.82). These findings may have prompted the development of the related compound WAY-100635, another purportedly selective and even more potent 5-HT1A antagonist, which was synthesized shortly thereafter. However, WAY-100635 turned out to be non-selective as well, having been shown to act additionally as a potent D4 receptor agonist later on.
A serenic, or antiaggressive agent, is a type of drug which reduces the capacity for irritability and aggression.

CGS-12066A is a drug which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the 5-HT1B receptor with lower affinity for the three 5-HT2 receptor subtypes. It is used for studying the role of the 5-HT1B receptor in various processes including perception of pain and the sleep-wake cycle.
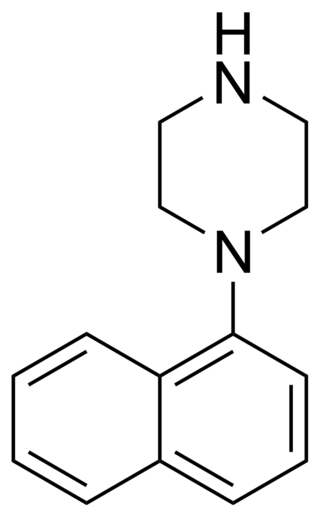
1-(1-Naphthyl)piperazine (1-NP) is a drug which is a phenylpiperazine derivative. It acts as a non-selective, mixed serotonergic agent, exerting partial agonism at the 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D, 5-HT1E, and 5-HT1F receptors, while antagonizing the 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C receptors. It has also been shown to possess high affinity for the 5-HT3, 5-HT5A, 5-HT6, and 5-HT7 receptors, and may bind to 5-HT4 and the SERT as well. In animals it produces effects including hyperphagia, hyperactivity, and anxiolysis, of which are all likely mediated predominantly or fully by blockade of the 5-HT2C receptor.

CP-93129 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective serotonin 5-HT1B receptor agonist, with approximately 150x and 200x selectivity over the closely related 5-HT1D and 5-HT1A receptors. It is used in the study of 5-HT1B receptors in the brain, particularly their role in modulating the release of other neurotransmitters.

Enciprazine is an anxiolytic and antipsychotic of the phenylpiperazine class which was never marketed. It shows high affinity for the α1-adrenergic receptor and 5-HT1A receptor, among other sites. The drug was initially anticipated to produce ortho-methoxyphenylpiperazine (oMeOPP), a serotonin receptor agonist with high affinity for the 5-HT1A receptor, as a significant active metabolite, but subsequent research found this not to be the case.


















