
CX717 is an ampakine compound created by Christopher Marrs and Gary Rogers in 1996 at Cortex Pharmaceuticals. It affects the neurotransmitter glutamate, with trials showing the drug improves cognitive functioning and memory.

Molindone, sold under the brand name Moban, is an antipsychotic medication which is used in the United States in the treatment of schizophrenia. It is taken by mouth.

The 5HT6 receptor is a subtype of 5HT receptor that binds the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5HT). It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is coupled to Gs and mediates excitatory neurotransmission. HTR6 denotes the human gene encoding for the receptor.
An H3 receptor antagonist is a type of antihistaminic drug used to block the action of histamine at H3 receptors.

Xanomeline is a small molecule muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist that was first synthesized in a collaboration between Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk as an investigational therapeutic being studied for the treatment of central nervous system (CNS) disorders.

SB-258585 is a drug which is used in scientific research. It acts as a potent, selective and orally active 5-HT6 receptor antagonist, with a Ki of 8.9nM. It is used in its 125I radiolabelled form to map the distribution of 5-HT6 receptors in the brain.

SB-399885 is a drug which is used in scientific research. It acts as a potent, selective and orally active 5-HT6 receptor antagonist, with a Ki of 9.0nM. SB-399885 and other 5-HT6 antagonists show nootropic effects in animal studies, as well as antidepressant and anxiolytic effects which are comparable to and synergistic with drugs such as imipramine and diazepam, and have been proposed as potential novel treatments for cognitive disorders such as schizophrenia and Alzheimer's disease.

SB-357134 is a drug which is used in scientific research. It acts as a potent, selective and orally active 5-HT6 receptor antagonist. SB-357134 and other 5-HT6 antagonists show nootropic effects in animal studies, and have been proposed as potential novel treatments for cognitive disorders such as schizophrenia and Alzheimer's disease.

Pimavanserin, sold under the brand name Nuplazid, is an atypical antipsychotic which is approved for the treatment of Parkinson's disease psychosis. It is taken by mouth.

Pomaglumetad (LY-404,039) is an amino acid analog drug that acts as a highly selective agonist for the metabotropic glutamate receptor group II subtypes mGluR2 and mGluR3. Pharmacological research has focused on its potential antipsychotic and anxiolytic effects. Pomaglumetad is intended as a treatment for schizophrenia and other psychotic and anxiety disorders by modulating glutamatergic activity and reducing presynaptic release of glutamate at synapses in limbic and forebrain areas relevant to these disorders. Human studies investigating therapeutic use of pomaglumetad have focused on the prodrug LY-2140023, a methionine amide of pomaglumetad (also called pomaglumetad methionil) since pomaglumetad exhibits low oral absorption and bioavailability in humans.
Idalopirdine (INN) (code names Lu AE58054,) is a potent and selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist under development by Lundbeck as an augmentation therapy for the treatment of cognitive deficits associated with Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia. As of October 2013 it is in phase III clinical trials.

Intepirdine (INN; developmental codes SB-742457, RVT-101) is a selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist with potential cognition, memory, and learning-enhancing effects. It was under development by GlaxoSmithKline for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and demonstrated some preliminary efficacy in phase II clinical trials. GSK chose not to continue development and sold the rights to Axovant Sciences for $5 million in December 2014.
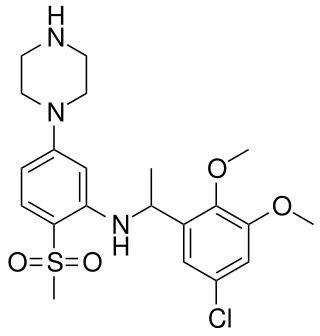
PRX-07034 is a selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist. It has cognition and memory-enhancing properties and potently decreases food intake and body weight in rodents. PRX-07034 was under development by Epix Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of obesity and cognitive impairment associated with Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia but upon the company collapsing due to lack of funds the compound was auctioned to another corporation.

Cerlapirdine is a drug which was under development by Wyeth/Pfizer for the treatment of cognitive disorders associated with Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia. In a phase II clinical trial it demonstrated a trend toward efficacy along with a good side effect profile and no incidence of serious adverse events, but no further development has occurred since 2011.

Brexpiprazole, sold under the brand name Rexulti among others, is an atypical antipsychotic medication used for the treatment of major depressive disorder, schizophrenia, and agitation associated with dementia due to Alzheimer's disease.
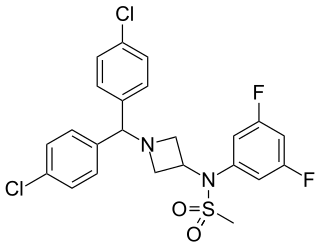
Drinabant (INN; AVE-1625) is a drug that acts as a selective CB1 receptor antagonist, which was under investigation varyingly by Sanofi-Aventis as a treatment for obesity, schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and nicotine dependence. Though initially studied as a potential treatment for a variety of different medical conditions, Sanofi-Aventis eventually narrowed down the therapeutic indications of the compound to just appetite suppression. Drinabant reached phase IIb clinical trials for this purpose in the treatment of obesity but was shortly thereafter discontinued, likely due to the observation of severe psychiatric side effects including anxiety, depression, and thoughts of suicide in patients treated with the now-withdrawn rimonabant, another CB1 antagonist that was also under development by Sanofi-Aventis.

Brilaroxazine, also known as oxaripiprazole, is an investigational atypical antipsychotic which is under development by Reviva Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of neuropsychiatric and inflammatory disorders. It has currently completed the first of two phase III clinical trials for schizophrenia. Reviva Pharmaceuticals also intends to investigate brilaroxazine for the treatment of bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), irritability in autism, tics, psychosis/agitation associated with Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease psychosis, as well as the inflammatory disorders pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), and psoriasis. The FDA granted brilaroxazine orphan drug designation for the treatment of PAH and IPF.

Maritupirdine (developmental code name AVN-101), a close structural analogue of latrepirdine, is a selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist which is under development by Avineuro Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and anxiety disorders. As of November 2013, it was in phase II clinical trials for these indications.

AVN-322 is a 5-hydroxytryptamine subtype 6 receptor antagonist manufactured by Avineuro Pharmaceuticals Inc. that could potentially be used to combat Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia. AVN-322 also reverses the negative effects of scopolamine and MK-80.
AVN-397 is a 5-hydroxytryptamine subtype 6 receptor antagonist drug developed by Avineuro Pharmaceuticals Inc. that can potentially be used to treat Alzheimer's disease and general anxiety disorder (GAD). Avineuro announced that it would start Phase II clinical trials in 2009, and those trials are ongoing as of 2012.

















