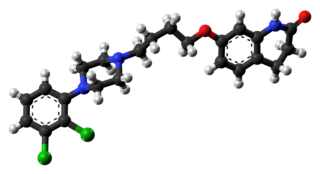
Aripiprazole, sold under the brand names Abilify and Aristada, among others, is an atypical antipsychotic. It is primarily used in the treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder; other uses include as an add-on treatment in major depressive disorder and obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD), tic disorders, and irritability associated with autism. Aripiprazole is taken by mouth or via injection into a muscle. A Cochrane review found low-quality evidence of effectiveness in treating schizophrenia.

Mirtazapine, sold under the brand name Remeron among others, is an atypical tetracyclic antidepressant, and as such is used primarily to treat depression. Its effects may take up to four weeks but can also manifest as early as one to two weeks. It is often used in cases of depression complicated by anxiety or insomnia. The effectiveness of mirtazapine is comparable to other commonly prescribed antidepressants. It is taken by mouth.

Pergolide, sold under the brand name Permax and Prascend (veterinary) among others, is an ergoline-based dopamine receptor agonist used in some countries for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Parkinson's disease is associated with reduced dopamine synthesis in the substantia nigra of the brain. Pergolide acts on many of the same receptors as dopamine to increase receptor activity.

Azapirones are a class of drugs used as anxiolytics, antidepressants, and antipsychotics. They are commonly used as add-ons to other antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).

The 5-HT2A receptor is a subtype of the 5-HT2 receptor that belongs to the serotonin receptor family and is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). The 5-HT2A receptor is a cell surface receptor, but has several intracellular locations.

A serotonin receptor agonist is an agonist of one or more serotonin receptors. They activate serotonin receptors in a manner similar to that of serotonin, a neurotransmitter and hormone and the endogenous ligand of the serotonin receptors.

Bifeprunox (INN) (code name DU-127,090) is an atypical antipsychotic which, similarly to aripiprazole, combines minimal D2 receptor agonism with serotonin receptor agonism. It was under development for the treatment of schizophrenia, psychosis and Parkinson's disease.

The serotonin 1A receptor is a subtype of serotonin receptors, or 5-HT receptors, that binds serotonin, also known as 5-HT, a neurotransmitter. 5-HT1A is expressed in the brain, spleen, and neonatal kidney. It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), coupled to the Gi protein, and its activation in the brain mediates hyperpolarization and reduction of firing rate of the postsynaptic neuron. In humans, the serotonin 1A receptor is encoded by the HTR1A gene.

WAY-100635 is a piperazine drug and research chemical widely used in scientific studies. It was originally believed to act as a selective 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, but subsequent research showed that it also acts as potent full agonist at the D4 receptor. It is sometimes referred to as a silent antagonist at the former receptor. It is closely related to WAY-100135.

Nemonapride, also previously known as emonapride and sold under the brand name Emilace, is an atypical antipsychotic which is used in the treatment of schizophrenia. It is taken by mouth.
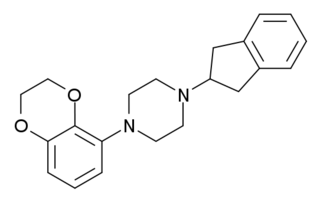
S-15535 is a phenylpiperazine drug which is a potent and highly selective 5-HT1A receptor ligand that acts as an agonist and antagonist at the presynaptic and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors, respectively. It has anxiolytic properties.
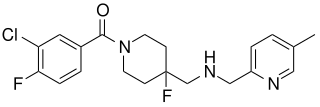
Befiradol is an experimental drug being studied for the treatment of levodopa-induced dyskinesia. It is a potent and selective 5-HT1A receptor full agonist.
A serenic, or anti-aggressive drug, is a type of drug which reduces the capacity for aggression.

Eptapirone (F-11,440) is a very potent and highly selective 5-HT1A receptor full agonist of the azapirone family. Its affinity for the 5-HT1A receptor was reported to be 4.8 nM (Ki), and its intrinsic activity approximately equal to that of serotonin.
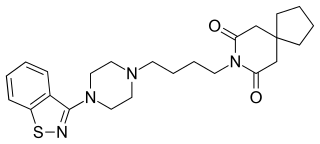
Tiospirone (BMY-13,859), also sometimes called tiaspirone or tiosperone, is an atypical antipsychotic of the azapirone class. It was investigated as a treatment for schizophrenia in the late 1980s and was found to have an effectiveness equivalent to those of typical antipsychotics in clinical trials but without causing extrapyramidal side effects. However, development was halted and it was not marketed. Perospirone, another azapirone derivative with antipsychotic properties, was synthesized and assayed several years after tiospirone. It was found to be both more potent and more selective in comparison and was commercialized instead.
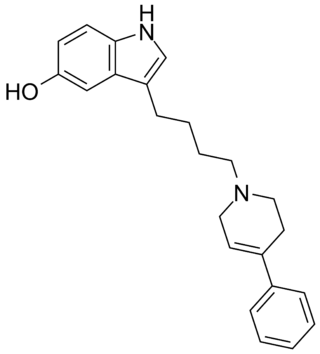
Roxindole (EMD-49,980) is a dopaminergic and serotonergic drug which was originally developed by Merck KGaA for the treatment of schizophrenia. In clinical trials its antipsychotic efficacy was only modest but it was unexpectedly found to produce potent and rapid antidepressant and anxiolytic effects. As a result, roxindole was further researched for the treatment of depression instead. It has also been investigated as a therapy for Parkinson's disease and prolactinoma.
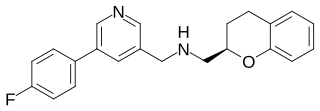
Sarizotan (EMD-128,130) is a selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist and D2 receptor antagonist, which has antipsychotic effects, and has also shown efficacy in reducing dyskinesias resulting from long-term anti-Parkinsonian treatment with levodopa.

F-15,063 is an orally active potential antipsychotic, and an antagonist at the D2/D3 receptors, partial agonist at the D4 receptor, and agonist at the 5-HT1A receptors. It has greater efficacy at the 5-HT1A receptors than other antipsychotics, such as clozapine, aripiprazole, and ziprasidone. This greater efficacy may lead to enhanced antipsychotic properties, as antipsychotics that lack 5-HT1A affinity are associated with increased risk of extrapyramidal symptoms, and lack of activity against the negative symptoms of schizophrenia.

Neurolixis is a biopharmaceutical company focused on novel drugs for the treatment of human central nervous system diseases.
A serotonin modulator and stimulator (SMS), sometimes referred to more simply as a serotonin modulator, is a type of drug with a multimodal action specific to the serotonin neurotransmitter system. To be precise, SMSs simultaneously modulate one or more serotonin receptors and inhibit the reuptake of serotonin. The term was created to describe the mechanism of action of the serotonergic antidepressant vortioxetine, which acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI), agonist of the 5-HT1A receptor, and antagonist of the 5-HT3 and 5-HT7 receptors. However, it can also technically be applied to vilazodone, which is an antidepressant as well and acts as an SRI and 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist.


















