
Aconitine is an alkaloid toxin produced by various plant species belonging to the genus Aconitum, known also commonly by the names wolfsbane and monkshood. Monkshood is notorious for its toxic properties.

Salvinorin A is the main active psychotropic molecule in Salvia divinorum. Salvinorin A is considered a dissociative hallucinogen.
An antiemetic is a drug that is effective against vomiting and nausea. Antiemetics are typically used to treat motion sickness and the side effects of opioid analgesics, general anaesthetics, and chemotherapy directed against cancer. They may be used for severe cases of gastroenteritis, especially if the patient is dehydrated.
The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeably with "terpenes", terpenoids contain additional functional groups, usually containing oxygen. When combined with the hydrocarbon terpenes, terpenoids comprise about 80,000 compounds. They are the largest class of plant secondary metabolites, representing about 60% of known natural products. Many terpenoids have substantial pharmacological bioactivity and are therefore of interest to medicinal chemists.
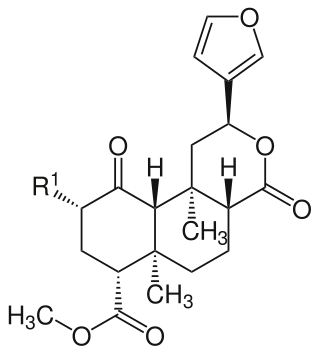
Salvinorins are a group of natural chemical compounds and their structural analogs. Several salvinorins have been isolated from Salvia divinorum. They are classified as diterpenoid furanolactones. Salvinorin A is a hallucinogen with dissociative effects.

Ginkgolides are biologically active terpenic lactones present in Ginkgo biloba. They are diterpenoids with 20-carbon skeletons, which are biosynthesized from geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate.
Diterpenes are a class of terpenes composed of four isoprene units, often with the molecular formula C20H32. They are biosynthesized by plants, animals and fungi via the HMG-CoA reductase pathway, with geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate being a primary intermediate. Diterpenes form the basis for biologically important compounds such as retinol, retinal, and phytol. They are known to be antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory.

Euphorbia helioscopia, the sun spurge or madwoman's milk, is a species of flowering plant in the spurge family Euphorbiaceae. It is a herbaceous annual plant, native to most of Europe, northern Africa, and eastward through most of Asia.

A furanolactone is a heterocyclic chemical compound that contains both lactone and furan rings in its chemical structure.

Etlingera elatior is a species of herbaceous perennial plant in the family Zingiberaceae; it is native to Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia and New Guinea.

The 5-HT3 antagonists, informally known as "setrons", are a class of drugs that act as receptor antagonists at the 5-HT3 receptor, a subtype of serotonin receptor found in terminals of the vagus nerve and in certain areas of the brain. With the notable exceptions of alosetron and cilansetron, which are used in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome, all 5-HT3 antagonists are antiemetics, used in the prevention and treatment of nausea and vomiting. They are particularly effective in controlling the nausea and vomiting produced by cancer chemotherapy and are considered the gold standard for this purpose.

Salvia candelabrum is a species of flowering plant in the family Lamiaceae, native to southern Spain. It is a woody-based perennial growing to 100 cm (39 in), with woolly grey-green leaves that resemble those of the common sage, S. officinalis, and emit a similar scent when crushed. In summer it bears violet-blue flowers on branching stems held high above the foliage.

Totarol is a naturally produced diterpene that is bioactive as totarol. It was first isolated by McDowell and Easterfield from the heartwood of Podocarpus totara, a conifer tree found in New Zealand. Podocarpus totara was investigated for unique molecules due to the tree's increased resistance to rotting. Recent studies have confirmed totarol's unique antimicrobial and therapeutic properties. Consequently, totarol is a candidate for a new source of drugs and has been the goal of numerous syntheses.

Taxodone is a naturally occurring diterpenoid found in Taxodium distichum, Rosmarinus officinalis (rosemary), several salvia species and other plants, along with its oxidized rearrangement product, taxodione. Taxodone and taxodione exhibit anticancer, antibacterial, antioxidant, antifungal, insecticide, and antifeedant activities.
Cassumunar ginger: Zingiber cassumunar, now thought to be a synonym of Zingiber montanum (J.König) Link ex A.Dietr., is a species of plant in the ginger family and is also a relative of galangal. It is called plai (ไพล) in Thailand, in addition to in Isan language and in northern Thai language. The rhizome of variant 'Roxburgh' is used medicinally in massage and even in food in Thailand, and somewhat resembles ginger root or galangal. In aromatherapy, plai oil is used as an essential oil and is believed to ease pain and inflammation. It is also known as ponlei (ពន្លៃ) in Cambodia.

A quinone methide is a type of conjugated organic compound that contain a cyclohexadiene with a carbonyl and an exocyclic methylidene or extended alkene unit. It is analogous to a quinone, but having one of the double bonded oxygens replaced with a carbon. The carbonyl and methylidene are usually oriented either ortho or para to each other. There are some examples of transient synthetic meta quinone methides.
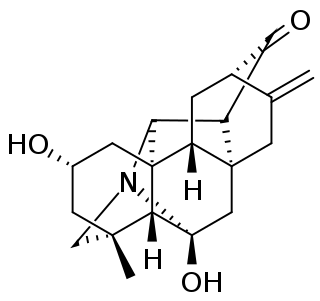
Panicudine (6-hydroxy-11-deoxy-13-dehydrohetisane) is a C20-diterpene alkaloid of the hetisine type, first isolated from Aconitum paniculatum. It has empirical formula C20H25NO3 and a melting point of 249–250 °C. The structure was determined to be a hetisine type diterpene by noting infrared spectrum absorption bands of 3405 cm−1 (OH), 1718 (C=O), and 1650 (C=C), a proton magnetic resonance spectrum with "secondary hydroxy (4.02 ppm, m, 1H, W1/2 = 10 Hz), exomethylene (4.87 and 4.76 ppm, br.s, 1H each), and tertiary methyl (1.29 ppm, s, 3H) groups and the absence of N-methyl, N-ethyl, and methoxy groups." Additional ultraviolet spectrum and carbon-13 NMR data, confirmed by high resolution mass spectrometry, completed the determination of the structure.

β-Araneosene is a molecule first isolated in 1975 from the mold Sordaria araneosa by Borschberg. This unprecedented diterpene framework was given the name “araneosene”. In 1976, the skeletal class was renamed to “dolabellane” due to the isolation of several compounds containing this framework found from the sea hare Dolabella californica. Since their initial discovery, there are now more than 150 known dolabellanes, mostly isolated from marine sources.

Tinosporide is a chemical compound classified as a diterpenoid and a furanolactone. It was first isolated from the plant Tinospora cordifolia, from which it derives its name. It has since been found in other plants of the genus Tinospora, such as Tinospora glabra.

Hydnellum scabrosum, also called bitter tooth or bitter hedgehog, is a species of tooth fungus in the family Bankeraceae.
















