
5-HT receptors, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, or serotonin receptors, are a group of G protein-coupled receptor and ligand-gated ion channels found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The serotonin receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin, which acts as their natural ligand.

The 5-HT2A receptor is a subtype of the 5-HT2 receptor that belongs to the serotonin receptor family and is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). The 5-HT2A receptor is a cell surface receptor, but has several intracellular locations. 5-HT is short for 5-hydroxy-tryptamine or serotonin. This is the main excitatory receptor subtype among the GPCRs for serotonin, although 5-HT2A may also have an inhibitory effect on certain areas such as the visual cortex and the orbitofrontal cortex. This receptor was first noted for its importance as a target of serotonergic psychedelic drugs such as LSD and psilocybin mushrooms. Later it came back to prominence because it was also found to be mediating, at least partly, the action of many antipsychotic drugs, especially the atypical ones.

A serotonin receptor agonist is an agonist of one or more serotonin receptors. They activate serotonin receptors in a manner similar to that of serotonin, a neurotransmitter and hormone and the endogenous ligand of the serotonin receptors.

5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HTR4 gene.

The serotonin 1A receptor is a subtype of serotonin receptor, or 5-HT receptor, that binds serotonin, also known as 5-HT, a neurotransmitter. 5-HT1A is expressed in the brain, spleen, and neonatal kidney. It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), coupled to the Gi protein, and its activation in the brain mediates hyperpolarisation and reduction of firing rate of the postsynaptic neuron. In humans, the serotonin 1A receptor is encoded by the HTR1A gene.

5-Hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 5A, also known as HTR5A, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HTR5A gene. Agonists and antagonists for 5-HT receptors, as well as serotonin uptake inhibitors, present promnesic (memory-promoting) and/or anti-amnesic effects under different conditions, and 5-HT receptors are also associated with neural changes.

The 5HT6 receptor is a subtype of 5HT receptor that binds the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5HT). It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is coupled to Gs and mediates excitatory neurotransmission. HTR6 denotes the human gene encoding for the receptor.

The 5-HT7 receptor is a member of the GPCR superfamily of cell surface receptors and is activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) The 5-HT7 receptor is coupled to Gs (stimulates the production of the intracellular signaling molecule cAMP) and is expressed in a variety of human tissues, particularly in the brain, the gastrointestinal tract, and in various blood vessels. This receptor has been a drug development target for the treatment of several clinical disorders. The 5-HT7 receptor is encoded by the HTR7 gene, which in humans is transcribed into 3 different splice variants.
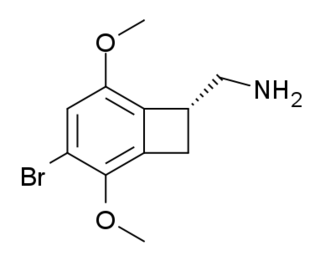
TCB-2 is a hallucinogen discovered in 2006 by Thomas McLean working in the lab of David Nichols at Purdue University. It is a conformationally-restricted derivative of the phenethylamine 2C-B, also a hallucinogen, and acts as a potent agonist for the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors with a Ki of 0.26 nM at the human 5-HT2A receptor. In drug-substitution experiments in rats, TCB-2 was found to be of similar potency to both LSD and Bromo-DragonFLY, ranking it among the most potent phenethylamine hallucinogens yet discovered. This high potency and selectivity has made TCB-2 useful for distinguishing 5-HT2A mediated responses from those produced by other similar receptors. TCB-2 has similar but not identical effects in animals to related phenethylamine hallucinogens such as DOI, and has been used for studying how the function of the 5-HT2A receptor differs from that of other serotonin receptors in a number of animal models, such as studies of cocaine addiction and neuropathic pain.
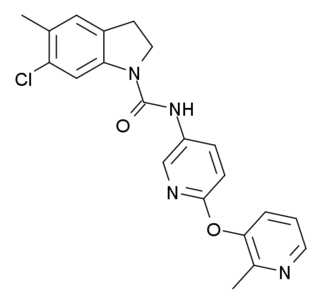
SB-242084 is a psychoactive drug and research chemical which acts as a selective antagonist for the 5HT2C receptor. It has anxiolytic effects, and enhances dopamine signalling in the limbic system, as well as having complex effects on the dopamine release produced by cocaine, increasing it in some brain regions but reducing it in others. It has been shown to increase the effectiveness of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class of antidepressants, and may also reduce their side effects. In animal studies, SB-242084 produced stimulant-type activity and reinforcing effects, somewhat similar to but much weaker than cocaine or amphetamines.

CP-94253 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective serotonin 5-HT1B receptor agonist, with approximately 25x and 40x selectivity over the closely related 5-HT1D and 5-HT1A receptors. It has a range of behavioral effects, based on animal testing. The effects include the following: promoting wakefulness by increasing dopamine release in the brain; reducing food intake and promoting satiety; enhancing the reinforcing effects of cocaine; and possible antidepressant effects.

SB-269970 is a drug and research chemical developed by GlaxoSmithKline used in scientific studies. It is believed to act as a selective 5-HT7 receptor antagonist (EC50 = 1.25 nM) (or possibly inverse agonist). A subsequent study in guinea pig at a concentration of 10 μM showed that it also blocks the α2-adrenergic receptor. The large difference in test concentrations however confirms the selectivity of SB-269970 for the 5-HT7 receptor.
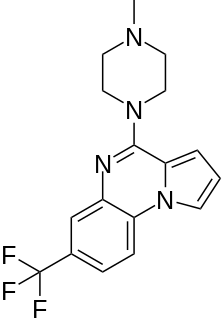
CGS-12066A is a drug which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the 5-HT1B receptor with lower affinity for the three 5-HT2 receptor subtypes. It is used for studying the role of the 5-HT1B receptor in various processes including perception of pain and the sleep-wake cycle.
Osemozotan (MKC-242) is a selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist with some functional selectivity, acting as a full agonist at presynaptic and a partial agonist at postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors. 5-HT1A receptor stimulation influences the release of various neurotransmitters including serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, and acetylcholine. 5-HT1A receptors are inhibitory G protein-coupled receptor. Osemozotan has antidepressant, anxiolytic, antiobsessional, serenic, and analgesic effects in animal studies, and is used to investigate the role of 5-HT1A receptors in modulating the release of dopamine and serotonin in the brain, and their involvement in addiction to abused stimulants such as cocaine and methamphetamine.
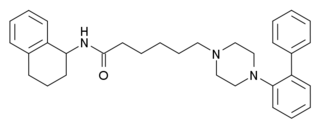
LP-12 is a drug which acts as a potent agonist at the 5HT7 serotonin receptor, with very high selectivity over other tested receptor subtypes such as the serotonin 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A, and the dopamine D2 receptor. It has been used to research the involvement of the 5-HT7 receptor in as yet poorly understood processes such as allodynia and hyperalgesia.

LP-44 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective agonist at the 5HT7 serotonin receptor. While LP-44 is less selective than the related compound LP-12, it has been more widely used in research and has been used to show the complex role of 5-HT7 receptors in several aspects of brain function, including regulation of the sleep-wake cycle and roles in stress, learning and memory.

E-55888 is a drug developed by Esteve, which acts as a potent and selective full agonist at the 5HT7 serotonin receptor, and is used for investigating the role of 5-HT7 receptors in the perception of pain. When administered by itself, E-55888 is anti-hyperalgesic but not analgesic, but when administered alongside morphine, E-55888 was found to significantly increase the analgesic effects.

1-(2-Diphenyl)piperazine, also known as RA-7, is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist at the 5HT7 serotonin receptor. It was discovered as an active metabolite of the synthetic 5-HT7 agonists LP-12 and LP-211, and unexpectedly turned out to be a potent antagonist with selectivity approaching that of the parent molecules, despite its much simpler structure.

SR-57227 is a potent and selective agonist at the 5HT3 receptor, with high selectivity over other serotonin receptor subtypes and good blood-brain barrier penetration.


















