 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
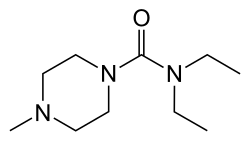
| Other names | DEC, N, N-diethyl-4-methyl-1-piperazine carboxamide |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.840 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H21N3O |
| Molar mass | 199.298 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 47 to 49 °C (117 to 120 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Diethylcarbamazine is a medication used in the treatment of filariasis including lymphatic filariasis, tropical pulmonary eosinophilia, and loiasis. [1] It may also be used for prevention of loiasis in those at high risk. [1] While it has been used for onchocerciasis (river blindness), ivermectin is preferred. [2] It is taken by mouth. [3]
Contents
- Medical uses
- Contraindications
- Mechanism
- Society and culture
- Brand names
- Veterinary uses
- References
- External links
Common side effects include itching, facial swelling, headaches, and feeling tired. [3] Other side effects include vision loss and dizziness. [3] It is a recommended treatment in pregnancy and appears to be safe for the baby. [4] [5] The World Health Organization; however, recommends waiting until after pregnancy for treatment when feasible. [2] It is made from 4-methyl-piperazine. [6]
Diethylcarbamazine was discovered in 1947 [7] by Yellapragada Subbarow. [8] [9] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. [10] It is not commercially available in the United States but can be acquired from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. [1]