Cheminformatics refers to the use of physical chemistry theory with computer and information science techniques—so called "in silico" techniques—in application to a range of descriptive and prescriptive problems in the field of chemistry, including in its applications to biology and related molecular fields. Such in silico techniques are used, for example, by pharmaceutical companies and in academic settings to aid and inform the process of drug discovery, for instance in the design of well-defined combinatorial libraries of synthetic compounds, or to assist in structure-based drug design. The methods can also be used in chemical and allied industries, and such fields as environmental science and pharmacology, where chemical processes are involved or studied.
The DrugBank database is a comprehensive, freely accessible, online database containing information on drugs and drug targets created and maintained by the University of Alberta and The Metabolomics Innovation Centre located in Alberta, Canada. As both a bioinformatics and a cheminformatics resource, DrugBank combines detailed drug data with comprehensive drug target information. DrugBank has used content from Wikipedia; Wikipedia also often links to Drugbank, posing potential circular reporting issues.

KEGG is a collection of databases dealing with genomes, biological pathways, diseases, drugs, and chemical substances. KEGG is utilized for bioinformatics research and education, including data analysis in genomics, metagenomics, metabolomics and other omics studies, modeling and simulation in systems biology, and translational research in drug development.
In chemistry, the term substrate is highly context-dependent. Broadly speaking, it can refer either to a chemical species being observed in a chemical reaction, or to a surface on which other chemical reactions or microscopy are performed.
ChemSpider is a freely accessible online database of chemicals owned by the Royal Society of Chemistry. It contains information on more than 100 million molecules from over 270 data sources, each of them receiving a unique identifier called ChemSpider Identifier.

Fenpentadiol (INN), also known as phenpentanediol, is a drug described as a tranquilizer and antidepressant that was formerly marketed in Europe. It also has stimulant, sedative, and anxiolytic effects, with the latter two occurring only at higher doses.
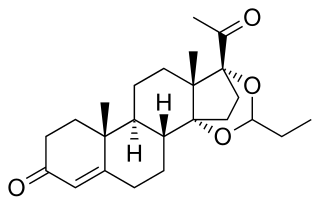
Proligestone, sold under the brand names Covinan and Delvosteron, is a progestin medication which is used in veterinary medicine.

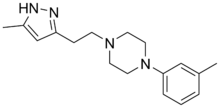
Lorpiprazole (INN) is a marketed anxiolytic drug of the phenylpiperazine group. It has been described as a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor (SARI) in the same group as trazodone, nefazodone, and etoperidone.

ChEMBL or ChEMBLdb is a manually curated chemical database of bioactive molecules with drug inducing properties. It is maintained by the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), based at the Wellcome Trust Genome Campus, Hinxton, UK.

Hydrocortamate is a synthetic glucocorticoid with anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. It is used topically to treat inflammation due to corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses.

Bucetin is an analgesic and antipyretic that is no longer marketed. Chemically, it is similar to phenacetin with which it shares the risk of carcinogenesis. Bucetin was withdrawn from use in 1986 due to renal toxicity.

Leptacline is a drug described as a respiratory stimulant that was never marketed. It has a similar chemical structure to various piperidine and piperazine psychostimulants.

Butidrine (INN), or butedrine or butydrine, also known as hydrobutamine or idrobutamine, is a beta blocker related to pronethalol and propranolol that was developed in the 1960s. Similarly to certain other beta blockers, butidrine also possesses local anesthetic properties.
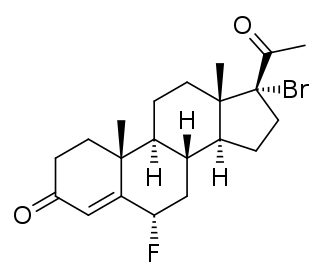
Haloprogesterone, sold under the brand name Prohalone, is a progestin medication which was previously marketed by Ayerst but is now no longer available.
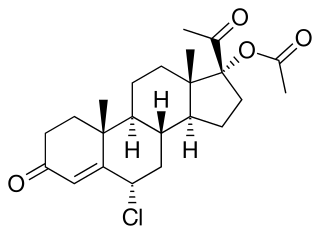
Hydromadinone acetate, also known as chloroacetoxyprogesterone (CAP), as well as 6α-chloro-17α-acetoxyprogesterone or 6α-chloro-17α-acetoxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, is a steroidal progestin of the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone group that was never marketed. It is the C17α acetate ester of hydromadinone, which, similarly, was never marketed.

Furostilbestrol (INN), also known as diethylstilbestrol di(2-furoate) or simply as diethylstilbestrol difuroate, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol, that was never marketed. It is an ester of diethylstilbestrol and was described in the literature in 1952.

Mestilbol, also known as diethylstilbestrol monomethyl ether, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol. It was developed by Wallace & Tiernan Company, patented in 1940, and introduced for medical use in the 1940s, but is now no longer marketed. Mestilbol was available both as oral tablets and in oil for intramuscular injection. The drug is gradually demethylated in the body into diethylstilbestrol and hence is a prodrug of diethylstilbestrol. Mestilbol is a highly active estrogen, although somewhat less so than diethylstilbestrol, but is longer-lasting in comparison.
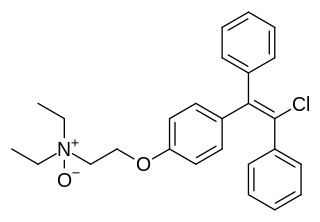
Clomifenoxide (INN), also known as clomifene N-oxide, is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group that is described as an antiestrogen and "gonad stimulant" and was never marketed. It is an active metabolite of clomifene.
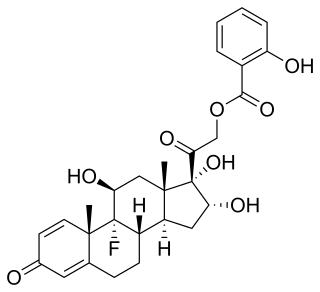
Cortobenzolone, also known as betamethasone salicylate, is a synthetic glucocorticoid corticosteroid and corticosteroid ester which is marketed in Spain.

Estrone methyl ether, or estrone 3-methyl ether, is a synthetic estrogen and estrogen ether – specifically, the C3 methyl ether of estrone – which was never marketed. It has been used to synthesize mestranol.