
5-HT receptors, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, or serotonin receptors, are a group of G protein-coupled receptor and ligand-gated ion channels found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The serotonin receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin, which acts as their natural ligand.

Ketanserin (INN, USAN, BAN) (brand name Sufrexal; former developmental code name R41468) is a drug used clinically as an antihypertensive agent and in scientific research to study the serotonergic system; specifically, the 5-HT2 receptor family. It was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1980. It is not available in the United States.

Pindolol, sold under the brand name Visken among others, is a nonselective beta blocker which is used in the treatment of hypertension. It is also an antagonist of the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor, preferentially blocking inhibitory 5-HT1A autoreceptors, and has been researched as an add-on therapy to various antidepressants, such as clomipramine and the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), in the treatment of depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder.

The 5-HT2A receptor is a subtype of the 5-HT2 receptor that belongs to the serotonin receptor family and is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). The 5-HT2A receptor is a cell surface receptor, but has several intracellular locations.

The serotonin 1A receptor is a subtype of serotonin receptors, or 5-HT receptors, that binds serotonin, also known as 5-HT, a neurotransmitter. 5-HT1A is expressed in the brain, spleen, and neonatal kidney. It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), coupled to the Gi protein, and its activation in the brain mediates hyperpolarization and reduction of firing rate of the postsynaptic neuron. In humans, the serotonin 1A receptor is encoded by the HTR1A gene.

Altanserin is a compound that binds to the 5-HT2A receptor. Labeled with the isotope fluorine-18 it is used as a radioligand in positron emission tomography (PET) studies of the brain, i.e., studies of the 5-HT2A neuroreceptors. Besides human neuroimaging studies altanserin has also been used in the study of rats.

DASB, also known as 3-amino-4-(2-dimethylaminomethylphenylsulfanyl)-benzonitrile, is a compound that binds to the serotonin transporter. Labeled with carbon-11 — a radioactive isotope — it has been used as a radioligand in neuroimaging with positron emission tomography (PET) since around year 2000. In this context it is regarded as one of the superior radioligands for PET study of the serotonin transporter in the brain, since it has high selectivity for the serotonin transporter.

WAY-100635 is a piperazine drug and research chemical widely used in scientific studies. It was originally believed to act as a selective 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, but subsequent research showed that it also acts as potent full agonist at the D4 receptor. It is sometimes referred to as a silent antagonist at the former receptor. It is closely related to WAY-100135.

MPPF, with the full name 2'-methoxyphenyl-(N-2'-pyridinyl)-p-fluoro-benzamidoethyipiperazine, is a compound that binds to the serotonin-1A receptor. Labeled with fluorine-18 it has been used as a radioligand with positron emission tomography. It has, e.g., been used to examine the difference in neuroreceptor binding in the human brain across sex and age.
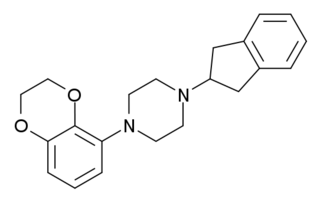
S-15535 is a phenylpiperazine drug which is a potent and highly selective 5-HT1A receptor ligand that acts as an agonist and antagonist at the presynaptic and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors, respectively. It has anxiolytic properties.
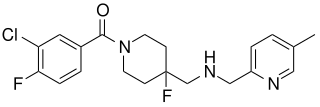
Befiradol is an experimental drug being studied for the treatment of levodopa-induced dyskinesia. It is a potent and selective 5-HT1A receptor full agonist.

Pardoprunox (INN) is an antiparkinsonian drug developed by Solvay for the treatment of Parkinson's disease that reached phase III clinical trials before being discontinued. It was also being investigated for the treatment of depression and anxiety but these indications appear to have been abandoned as well.

Osemozotan (MKC-242) is a selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist with some functional selectivity, acting as a full agonist at presynaptic and a partial agonist at postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors. 5-HT1A receptor stimulation influences the release of various neurotransmitters including serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, and acetylcholine. 5-HT1A receptors are inhibitory G protein-coupled receptor.
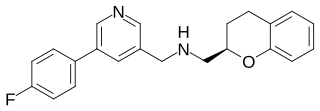
Sarizotan (EMD-128,130) is a selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist and D2 receptor antagonist, which has antipsychotic effects, and has also shown efficacy in reducing dyskinesias resulting from long-term anti-Parkinsonian treatment with levodopa.

BP-897 is a drug used in scientific research which acts as a potent selective dopamine D3 receptor partial agonist with an in vitro intrinsic activity of ~0.6 and ~70x greater affinity for D3 over D2 receptors and is suspected to have partial agonist or antagonist activity in vivo. It has mainly been used in the study of treatments for cocaine addiction. A study comparing BP-897 with the potent, antagonistic, and highly D3 selective SB-277,011-A found, "SB 277011-A (1–10 mg/kg) was able to block cue-induced reinstatement of nicotine-seeking, indicating that DRD3 selective antagonism may be an effective approach to prevent relapse for nicotine. In contrast, BP 897 did not block the cue-induced reinstatement of nicotine-seeking or nicotine-taking under the FR5 schedule."
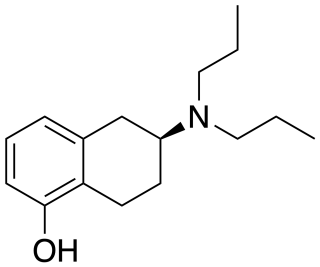
5-OH-DPAT is a synthetic compound that acts as a dopamine receptor agonist with selectivity for the D2 receptor and D3 receptor subtypes. Only the (S)-enantiomer is active as an agonist, with the (R)-enantiomer being a weak antagonist at D2 receptors. Radiolabelled 11C-5-OH-DPAT is used as an agonist radioligand for mapping the distribution and function of D2 and D3 receptors in the brain, and the drug is also being studied in the treatment of Parkinson's disease.

Brain positron emission tomography is a form of positron emission tomography (PET) that is used to measure brain metabolism and the distribution of exogenous radiolabeled chemical agents throughout the brain. PET measures emissions from radioactively labeled metabolically active chemicals that have been injected into the bloodstream. The emission data from brain PET are computer-processed to produce multi-dimensional images of the distribution of the chemicals throughout the brain.

PipISB is a drug used in scientific research which acts as a potent and selective inverse agonist of the cannabinoid receptor CB1. It is highly selective for the CB1 receptor over CB2, with a Kd at CB1 of 1.5nM vs over 7000nM at CB2, has good blood–brain barrier penetration, and can be conveniently radiolabelled with either 11C or 18F, making it useful for mapping the distribution of CB1 receptors in the brain.
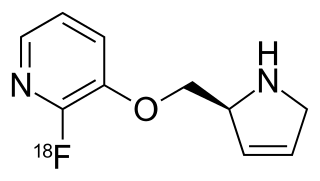
Nifene is a high affinity, selective nicotinic α4β2* receptor partial agonist used in medical research for nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, usually in the form of nifene (18F) as a positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer.

F-11,461 is a drug that acts as an agonist of the 5-HT1A receptor (Ki = 1.36 nM) that has been used as a radioligand in PET studies. It possesses modest affinity for the 5-HT7 (Ki = 9.1 nM) and D4 (Ki = 8.5 nM) receptors, although the interaction of F-11,461 with these receptors is not detectable with PET due to their relative scarcity in the brain.





















