 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Rescriptor |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a600034 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 85% |
| Protein binding | 98% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP3A4- and CYP2D6-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 5.8 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney (51%) and feces (44%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
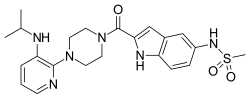
| Formula | C22H28N6O3S |
| Molar mass | 456.57 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Delavirdine (DLV) (brand name Rescriptor) is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) that was marketed by ViiV Healthcare. It was used as part of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) for the treatment of HIV-1 in the late 1990s and early 2000s. It is presented as the mesylate. The recommended dosage is 400 mg (as four 100-mg tablets or two 200-mg tablets) three times a day.
Contents
Although delavirdine was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 1997, its efficacy was found to be lower than other NNRTIs, especially efavirenz, and it also had an inconvenient dosing schedule. These factors have led the U.S. DHHS not to recommend its use as part of initial therapy. [1] The risk of cross-resistance across the NNRTI class, as well as its complex set of drug interactions, made the place of delavirdine in second-line and salvage therapy unclear, and it was very rarely used.
As of 2018, its manufacturing and distribution was discontinued in the United States and Canada. [2] [3] [4] It has not been used in other countries.
