This article needs to be updated.(January 2021) |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌtəˈnoʊfəvɪərˌæləˈfɛnəmaɪd/ |
| Trade names | Vemlidy, Tavin AF |
| Other names | GS-7340 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | ~80% [6] |
| Elimination half-life | 0.51 hour |
| Excretion | Feces (31.7%), urine (<1%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
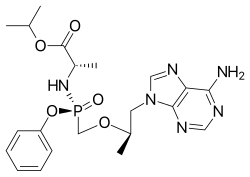
| Formula | C21H29N6O5P |
| Molar mass | 476.474 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |

Tenofovir alafenamide, sold under the brand name Vemlidy,Tavin AF is an antiviral medication used against hepatitis B and HIV. It is used for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in adults with compensated liver disease [8] and is given in combination with other medications for the prevention and treatment of HIV. It is taken by mouth. [6]
Contents
Tenofovir alafenamide is a nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor and is a prodrug of tenofovir. It was developed by Gilead Sciences based on the protide technology of Chris McGuigan and is applied in the form of tenofovir alafenamide fumarate (TAF). Closely related to the commonly used reverse-transcriptase inhibitor tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), TAF has greater antiviral activity and better distribution into lymphoid tissues than that agent. [9] [10] It was approved for use in the US for HIV in 2015, [11] and for hepatitis B in 2016. [12] Although the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved tenofovir alafenamide for manufacture as a generic medication, [13] it is not available. [14]
A generic combination of Emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (Viatris) received marketing authorization in the European Union in July 2025. [15]