Related Research Articles
Reverse-transcriptase inhibitors (RTIs) are a class of antiretroviral drugs used to treat HIV infection or AIDS, and in some cases hepatitis B. RTIs inhibit activity of reverse transcriptase, a viral DNA polymerase that is required for replication of HIV and other retroviruses.
ATC code B01Antithrombotic agents is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup B01 is part of the anatomical group B Blood and blood forming organs.
ATC code G01Gynecological antiinfectives and antiseptics is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup G01 is part of the anatomical group G Genito-urinary system and sex hormones.
ATC code M03Muscle relaxants is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup M03 is part of the anatomical group M Musculo-skeletal system.
ATC code N01Anesthetics is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup N01 is part of the anatomical group N Nervous system.
ATC code N05Psycholeptics is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup N05 is part of the anatomical group N Nervous system.
ATC code V03All other therapeutic products is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup V03 is part of the anatomical group V Various.
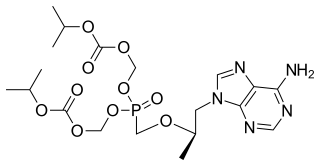
Tenofovir disoproxil, sold under the trade name Viread among others, is a medication used to treat chronic hepatitis B and to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. It is generally recommended for use with other antiretrovirals. It may be used for prevention of HIV/AIDS among those at high risk before exposure, and after a needlestick injury or other potential exposure. It is sold both by itself and together as emtricitabine/tenofovir and efavirenz/emtricitabine/tenofovir. It does not cure HIV/AIDS or hepatitis B. It is available by mouth as a tablet or powder.
Integrase inhibitors (INIs) are a class of antiretroviral drug designed to block the action of integrase, a viral enzyme that inserts the viral genome into the DNA of the host cell. Since integration is a vital step in retroviral replication, blocking it can halt further spread of the virus. Integrase inhibitors were initially developed for the treatment of HIV infection, but have been applied to other retroviruses. The class of integrase inhibitors called integrase strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs) are in established medical use. Other classes, such as integrase binding inhibitors (INBIs), are still experimental.

Elvitegravir (EVG) is an integrase inhibitor used to treat HIV infection. It was developed by the pharmaceutical company Gilead Sciences, which licensed EVG from Japan Tobacco in March 2008. The drug gained approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on August 27, 2012 for use in adult patients starting HIV treatment for the first time as part of the fixed dose combination known as Stribild. On September 24, 2014 the FDA approved Elvitegravir as a single pill formulation under the trade name Vitekta. On November 5, 2015 the FDA approved the drug for use in patients affected with HIV-1 as a part of a second fixed dose combination pill known as Genvoya.

Rilpivirine, sold under the brand names Edurant and Rekambys, is a medication, developed by Tibotec, used for the treatment of HIV/AIDS. It is a second-generation non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) with higher potency, longer half-life and reduced side-effect profile compared with older NNRTIs such as efavirenz.
ATCvet code QP51Antiprotozoals is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System for veterinary medicinal products, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products for veterinary use. Subgroup QP51 is part of the anatomical group QP Antiparasitic products, insecticides and repellents.
ATCvet code QP53Ectoparasiticides, including insecticides and repellents is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System for veterinary medicinal products, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products for veterinary use. Subgroup QP53 is part of the anatomical group QP Antiparasitic products, insecticides and repellents.

Cobicistat, sold under the brand name Tybost, is a medication for use in the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus infection (HIV/AIDS). Its major mechanism of action is through the inhibition of human CYP3A proteins.
Discovery and development of nucleoside and nucleotide reverse-transcriptase inhibitors began in the 1980s when the AIDS epidemic hit Western societies. NRTIs inhibit the reverse transcriptase (RT), an enzyme that controls the replication of the genetic material of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The first NRTI was zidovudine, approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1987, which was the first step towards treatment of HIV. Six NRTI agents and one NtRTI have followed. The NRTIs and the NtRTI are analogues of endogenous 2´-deoxy-nucleoside and nucleotide. Drug-resistant viruses are an inevitable consequence of prolonged exposure of HIV-1 to anti-HIV drugs.

Daniel Berger is a leading HIV specialist in the United States. A clinical associate professor at the Chicago campus of the University of Illinois College of Medicine, Berger is also founder and medical director of Northstar Medical Center, Chicago's largest private HIV/AIDS research and treatment center.
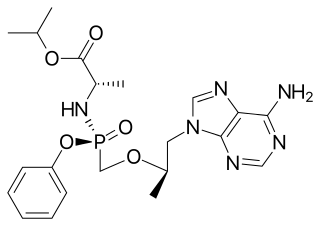
Tenofovir alafenamide, sold under the brand name Vemlidy, is a hepatitis B virus (HBV) nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor medication for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in adults with compensated liver disease. It is taken by mouth.

Abacavir/dolutegravir/lamivudine is a fixed-dose combination antiretroviral medication for the treatment of HIV/AIDS. It is a combination of three medications with different and complementary mechanisms of action: 600 mg abacavir, 50 mg dolutegravir and 300 mg lamivudine.
Chloe Meave Orkin is a British physician and Professor of HIV/AIDS medicine at Queen Mary University of London. She works as a consultant at the Royal London Hospital, Barts Health NHS Trust. She is an internationally renowned expert in HIV therapeutics and led the first phase III clinical trial of injectable anti-retrovirals. She is immediate past Chair of the British HIV Association, where she championed the Undetectable=Untransmittable (U=U) campaign within the United Kingdom. She is president elect of the Medical Women's Federation. Orkin is openly gay and was on the Top 100 Lesbian influencer lists in both the UK and in the US in 2020. She considers herself a medical activist and much of her work focuses on inequalities in healthcare and in Medicine.
References
- ↑ "ATC (Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System) – Synopsis". National Institutes of Health . Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- ↑ World Health Organization. "Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classification". World Health Organization. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
- ↑ "Structure and principles". WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. 15 February 2018. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
- ↑ "ATC/DDD Index 2022: code J05". WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology.
- ↑ "ATCvet Index 2022: code QJ05". WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology.