 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | GS-9669 |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
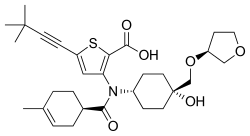
| Formula | C30H41NO6S |
| Molar mass | 543.72 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Radalbuvir (INN, [1] also known as GS-9669) is an experimental antiviral drug for the treatment of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection developed by Gilead Sciences. Radalbuvir acts as an NS5B inhibitor. It is currently in clinical trials. [2] It targets NS5B polymerase. [3]