Mirtazapine, sold under the brand name Remeron among others, is an atypical tetracyclic antidepressant, and as such is used primarily to treat depression. Its effects may take up to four weeks but can also manifest as early as one to two weeks. It is often used in cases of depression complicated by anxiety or insomnia. The effectiveness of mirtazapine is comparable to other commonly prescribed antidepressants. It is taken by mouth.

5-HT receptors, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, or serotonin receptors, are a group of G protein-coupled receptor and ligand-gated ion channels found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The serotonin receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin, which acts as their natural ligand.

Azapirones are a class of drugs used as anxiolytics, antidepressants, and antipsychotics. They are commonly used as add-ons to other antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).

Pindolol, sold under the brand name Visken among others, is a nonselective beta blocker which is used in the treatment of hypertension. It is also an antagonist of the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor, preferentially blocking inhibitory 5-HT1A autoreceptors, and has been researched as an add-on therapy to various antidepressants, such as clomipramine and the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), in the treatment of depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder.

Trazodone, sold under many brand names, is an antidepressant medication, used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and insomnia. It is a phenylpiperazine compound of the serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor (SARI) class. The medication is taken orally.

Moclobemide, sold under the brand names Amira, Aurorix, Clobemix, Depnil and Manerix among others, is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA) drug primarily used to treat depression and social anxiety. It is not approved for use in the United States, but is approved in other Western countries such as Canada, the UK and Australia. It is produced by affiliates of the Hoffmann–La Roche pharmaceutical company. Initially, Aurorix was also marketed by Roche in South Africa, but was withdrawn after its patent rights expired and Cipla Medpro's Depnil and Pharma Dynamic's Clorix became available at half the cost.

Agomelatine, sold under the brand names Valdoxan and Thymanax, among others, is an atypical antidepressant most commonly used to treat major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder. One review found that it is as effective as other antidepressants with similar discontinuation rates overall but fewer discontinuations due to side effects. Another review also found it was similarly effective to many other antidepressants.

Pramipexole, sold under the brand Mirapex among others, is a medication used to treat Parkinson's disease (PD) and restless legs syndrome (RLS). In Parkinson's disease it may be used alone or together with levodopa. It is taken by mouth. Pramipexole is a dopamine agonist of the non-ergoline class.

The serotonin 1A receptor is a subtype of serotonin receptors, or 5-HT receptors, that binds serotonin, also known as 5-HT, a neurotransmitter. 5-HT1A is expressed in the brain, spleen, and neonatal kidney. It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), coupled to the Gi protein, and its activation in the brain mediates hyperpolarization and reduction of firing rate of the postsynaptic neuron. In humans, the serotonin 1A receptor is encoded by the HTR1A gene.

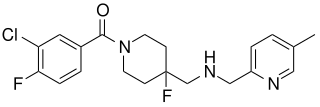
WAY-100635 is a piperazine drug and research chemical widely used in scientific studies. It was originally believed to act as a selective 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, but subsequent research showed that it also acts as potent full agonist at the D4 receptor. It is sometimes referred to as a silent antagonist at the former receptor. It is closely related to WAY-100135.

Medifoxamine, previously sold under the brand names Clédial and Gerdaxyl, is an atypical antidepressant with additional anxiolytic properties acting via dopaminergic and serotonergic mechanisms which was formerly marketed in France and Spain, as well as Morocco. The drug was first introduced in France sometime around 1990. It was withdrawn from the market in 1999 (Morocco) and 2000 (France) following incidences of hepatotoxicity.

Vilazodone, sold under the brand name Viibryd among others, is a medication used to treat major depressive disorder. It is classified as a serotonin modulator and is taken by mouth.

Zalospirone (WY-47,846) is a selective 5-HT1A partial agonist of the azapirone chemical class. It was found to be effective in the treatment of anxiety and depression in clinical trials, but a high proportion of subjects dropped out due to side effects and development was subsequently never completed.
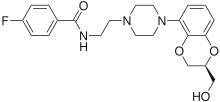
Befiradol is an experimental drug being studied for the treatment of levodopa-induced dyskinesia. It is a potent and selective 5-HT1A receptor full agonist.

Eptapirone (F-11,440) is a very potent and highly selective 5-HT1A receptor full agonist of the azapirone family. Its affinity for the 5-HT1A receptor was reported to be 4.8 nM (Ki), and its intrinsic activity approximately equal to that of serotonin.

Vortioxetine, sold under the brand name Trintellix among others, is an antidepressant of the serotonin modulator and stimulator (SMS) class. Its effectiveness is viewed as similar to that of other antidepressants. It is taken orally.
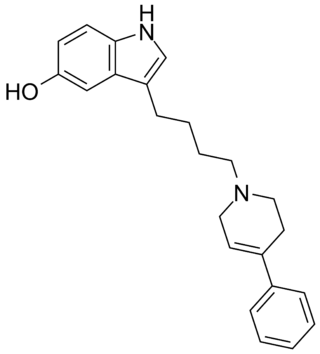
Roxindole (EMD-49,980) is a dopaminergic and serotonergic drug which was originally developed by Merck KGaA for the treatment of schizophrenia. In clinical trials its antipsychotic efficacy was only modest but it was unexpectedly found to produce potent and rapid antidepressant and anxiolytic effects. As a result, roxindole was further researched for the treatment of depression instead. It has also been investigated as a therapy for Parkinson's disease and prolactinoma.
A serotonin modulator and stimulator (SMS), sometimes referred to more simply as a serotonin modulator, is a type of drug with a multimodal action specific to the serotonin neurotransmitter system. To be precise, SMSs simultaneously modulate one or more serotonin receptors and inhibit the reuptake of serotonin. The term was created to describe the mechanism of action of the serotonergic antidepressant vortioxetine, which acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI), agonist of the 5-HT1A receptor, and antagonist of the 5-HT3 and 5-HT7 receptors. However, it can also technically be applied to vilazodone, which is an antidepressant as well and acts as an SRI and 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist.
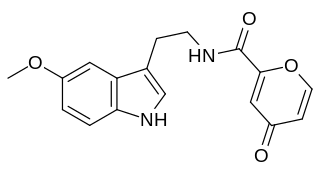
Piromelatine (Neu-P11) is a multimodal sleep drug under development by Neurim Pharmaceuticals. It is an agonist at melatonin MT1/MT2 and serotonin 5-HT1A/5-HT1D receptors. Neurim is conducting a phase II randomized, placebo controlled trial of cognitive and sleep effects in Alzheimer's disease.