
Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction.
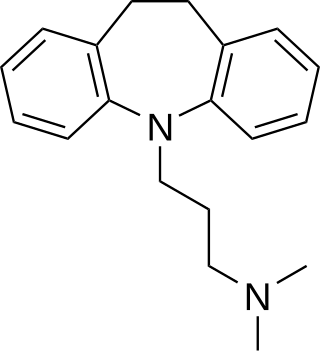
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are a class of medications that are used primarily as antidepressants, which is important for the management of depression. They are second-line drugs next to SSRIs. TCAs were discovered in the early 1950s and were marketed later in the decade. They are named after their chemical structure, which contains three rings of atoms. Tetracyclic antidepressants (TeCAs), which contain four rings of atoms, are a closely related group of antidepressant compounds.

Psychopharmacology is the scientific study of the effects drugs have on mood, sensation, thinking, behavior, judgment and evaluation, and memory. It is distinguished from neuropsychopharmacology, which emphasizes the correlation between drug-induced changes in the functioning of cells in the nervous system and changes in consciousness and behavior.

Citalopram, sold under the brand name Celexa among others, is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class. It is used to treat major depressive disorder, obsessive compulsive disorder, panic disorder, and social phobia. The antidepressant effects may take one to four weeks to occur. It is taken by mouth.
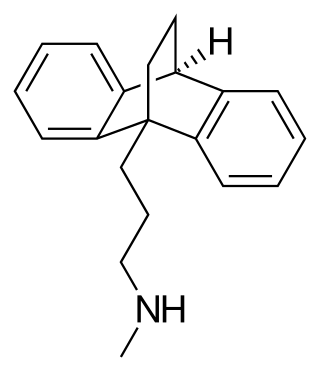
Maprotiline, sold under the brand name Ludiomil among others, is a tetracyclic antidepressant (TeCA) that is used in the treatment of depression. It may alternatively be classified as a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA), specifically a secondary amine. In terms of its chemistry and pharmacology, maprotiline is closely related to other secondary amine TCAs like nortriptyline and protriptyline, and has similar effects to them.

Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are a class of antidepressant medications used to treat major depressive disorder (MDD), anxiety disorders, obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD), social phobia, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), chronic neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS), and menopausal symptoms. SNRIs are monoamine reuptake inhibitors; specifically, they inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters are thought to play an important role in mood regulation. SNRIs can be contrasted with the more widely used selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which act upon serotonin only.

Nefazodone, sold formerly under the brand names Serzone, Dutonin, and Nefadar among others, is an atypical antidepressant medication which is used in the treatment of depression and for other uses. Nefazodone is available in the United States, but was withdrawn from other countries due to rare liver toxicity. The medication is taken by mouth.
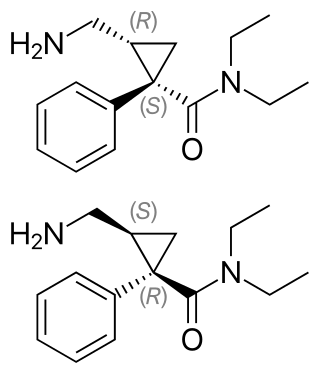
Milnacipran is a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) used in the clinical treatment of fibromyalgia. It is not approved for the clinical treatment of major depressive disorder in the US, but it is in other countries.
A serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI), also known as a triple reuptake inhibitor (TRI), is a type of drug that acts as a combined reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. It does this by concomitantly inhibiting the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and dopamine transporter (DAT), respectively. Inhibition of the reuptake of these neurotransmitters increases their extracellular concentrations and, therefore, results in an increase in serotonergic, adrenergic, and dopaminergic neurotransmission.
The number of new psychiatric drugs, and especially antidepressants on the market in Japan, is significantly less than Western countries.

NS-2359 (GSK-372,475) is a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor. It was under development by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) as an antidepressant, but was discontinued in 2009 when phase II clinical trials showed the drug was not effective and not well tolerated. The results did not support further effort by the company. NS-2359 was also in clinical trials for the treatment of ADHD, phase II having been completed in 2007. A phase I clinical trial exploring the effect of NS-2359 on cocaine-dependent individuals was completed in 2002.

Norepinephrine and dopamine disinhibitors (NDDIs) are a class of drugs which act at specific sites to disinhibit downstream norepinephrine and dopamine release in the brain.

Vortioxetine, sold under the brand names Trintellix and Brintellix among others, is a medication used to treat major depressive disorder. Effectiveness is viewed as similar to that of other antidepressants. It is taken by mouth.
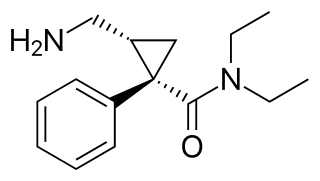
Levomilnacipran is an antidepressant which was approved in the United States in 2013 for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) in adults. It is the levorotatory enantiomer of milnacipran, and has similar effects and pharmacology, acting as a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI).

Brexpiprazole, sold under the brand name Rexulti among others, is a medication used for the treatment of major depressive disorder and schizophrenia. It is an atypical antipsychotic.
A serotonin modulator and stimulator (SMS), sometimes referred to more simply as a serotonin modulator, is a type of drug with a multimodal action specific to the serotonin neurotransmitter system. To be precise, SMSs simultaneously modulate one or more serotonin receptors and inhibit the reuptake of serotonin. The term was created to describe the mechanism of action of the serotonergic antidepressant vortioxetine, which acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI), agonist of the 5-HT1A receptor, and antagonist of the 5-HT3 and 5-HT7 receptors. However, it can also technically be applied to vilazodone, which is an antidepressant as well and acts as an SRI and 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist.

Toludesvenlafaxine, also formerly known as ansofaxine and sold under the brand name Ruoxinlin, is an antidepressant which is approved for the treatment of major depressive disorder in China. It is also under development for use in other countries like the United States. It is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI) and was developed by Luye Pharma Group.

Dextromethorphan/bupropion (DXM/BUP), sold under the brand name Auvelity, is a combination medication for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). It contains an extended-release combination of dextromethorphan (DXM) and bupropion. The medication is modestly more effective in the treatment of depression than placebo or bupropion alone. It is taken as a tablet by mouth.
















