The alpha-2 (α2) adrenergic receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) associated with the Gi heterotrimeric G-protein. It consists of three highly homologous subtypes, including α2A-, α2B-, and α2C-adrenergic. Some species other than humans express a fourth α2D-adrenergic receptor as well. Catecholamines like norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) signal through the α2-adrenergic receptor in the central and peripheral nervous systems.

Zolazepam (Flupyrazapon) is a pyrazolodiazepinone derivative structurally related to the benzodiazepine drugs, which is used as an anaesthetic for a wide range of animals in veterinary medicine. Zolazepam is usually administered in combination with other drugs such as the NMDA antagonist tiletamine or the α2 adrenergic receptor agonist xylazine, depending on what purpose it is being used for. It is around four times the potency of diazepam but it is both water-soluble and un-ionized at physiological pH meaning that its onset is very fast.
Phenyltropanes (PTs) were originally developed to reduce cocaine addiction and dependency. In general these compounds act as inhibitors of the plasmalemmal monoamine reuptake transporters. This research has spanned beyond the last couple decades, and has picked up its pace in recent times, creating numerous phenyltropanes as research into cocaine analogues garners interest to treat addiction.

Alpha-adrenergic agonists are a class of sympathomimetic agents that selectively stimulates alpha adrenergic receptors. The alpha-adrenergic receptor has two subclasses α1 and α2. Alpha 2 receptors are associated with sympatholytic properties. Alpha-adrenergic agonists have the opposite function of alpha blockers. Alpha adrenoreceptor ligands mimic the action of epinephrine and norepinephrine signaling in the heart, smooth muscle and central nervous system, with norepinephrine being the highest affinity. The activation of α1 stimulates the membrane bound enzyme phospholipase C, and activation of α2 inhibits the enzyme adenylate cyclase. Inactivation of adenylate cyclase in turn leads to the inactivation of the secondary messenger cyclic adenosine monophosphate and induces smooth muscle and blood vessel constriction.
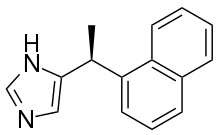
Medetomidine is a synthetic drug used as both a surgical anesthetic and analgesic. It is often used as the hydrochloride salt, medetomidine hydrochloride, a crystalline white solid. It is an α2 adrenergic agonist that can be administered as an intravenous drug solution with sterile water.

The alpha-2C adrenergic receptor, also known as ADRA2C, is an alpha-2 adrenergic receptor, and also denotes the human gene encoding it.

The alpha-1A adrenergic receptor, also known as ADRA1A, formerly known also as the alpha-1C adrenergic receptor, is an alpha-1 adrenergic receptor, and also denotes the human gene encoding it. There is no longer a subtype α1C receptor. At one time, there was a subtype known as α1C, but it was found to be identical to the previously discovered α1A receptor subtype. To avoid confusion, the naming convention was continued with the letter D.

The 5-HT7 receptor is a member of the GPCR superfamily of cell surface receptors and is activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT). The 5-HT7 receptor is coupled to Gs (stimulates the production of the intracellular signaling molecule cAMP) and is expressed in a variety of human tissues, particularly in the brain, the gastrointestinal tract, and in various blood vessels. This receptor has been a drug development target for the treatment of several clinical disorders. The 5-HT7 receptor is encoded by the HTR7 gene, which in humans is transcribed into 3 different splice variants.

Idazoxan (INN) is a drug which is used in scientific research. It acts as both a selective α2 adrenergic receptor antagonist, and an antagonist for the imidazoline receptor. Idazoxan has been under investigation as an antidepressant, but it did not reach the market as such. More recently, it is under investigation as an adjunctive treatment in schizophrenia. Due to its α2 receptor antagonism it is capable of enhancing therapeutic effects of antipsychotics, possibly by enhancing dopamine neurotransmission in the prefrontal cortex of the brain, a brain area thought to be involved in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia.
Atipamezole, sold under the brand name Antisedan among others, is a synthetic α2 adrenergic receptor antagonist used for the reversal of the sedative and analgesic effects of dexmedetomidine and medetomidine in dogs. Its reversal effect works by competing with the sedative for α2-adrenergic receptors and displacing them. It is mainly used in veterinary medicine, and while it is only licensed for dogs and for intramuscular use, it has been used intravenously, as well as in cats and other animals(intravenous use in cats and dogs is not recommended due to the potential for cardiovascular collapse. This occurs due to profound hypotension caused by reversal of the alpha 1 effects while the reflex bradycardia is still in effect.). There is a low rate of side effects, largely due to atipamezole's high specificity for the α2-adrenergic receptor. Atipamezole has a very quick onset, usually waking an animal up within 5 to 10 minutes.

AM-906 (part of the AM cannabinoid series) is an analgesic drug which is a cannabinoid agonist. It is conformationally restricted by virtue of the double bond on its side chain, leading an increased affinity for and selectivity between CB1 and CB2 receptors. It is a potent and selective agonist for the CB1 cannabinoid receptor, with a Ki of 0.8 nM at CB1 and 9.5 nM at CB2, a selectivity of almost 12x.
Alpha-2 blockers are a subset of the alpha blocker class of drugs and are antagonists to the α2 adrenergic receptor. They are mainly used in research, having found limited clinical application in human medicine. Alpha-2 blockers increase noradrenaline release.

Efaroxan is an α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist and antagonist of the imidazoline receptor.

Imiloxan is a drug which is used in scientific research. It acts as a selective antagonist for the α2B adrenergic receptor, and has been useful for distinguishing the actions of the different α2 adrenergic subtypes.

L-765,314 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist of the α1-adrenergic receptor subtype α1B. It has mainly been used to investigate the role of α1B-adrenergic receptors in the regulation of blood pressure. The α1B receptor is also thought to have an important role in the brain; however, L-765,314 does not cross the blood–brain barrier.
6-Fluoronorepinephrine (6-FNE) is a selective α1- and α2-adrenergic receptor full agonist related to norepinephrine. It is the only selective full agonist for the α-adrenergic receptors known to date and has been used to study their function in scientific research. Infusion of 6-FNE into the locus coeruleus of rodents produces marked hyperactivity and behavioral disinhibition by suppressing activity in the area via stimulation of α1-adrenergic receptors.
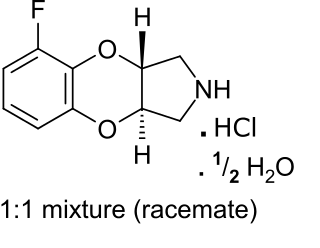
Fluparoxan is a potent α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist with excellent selectivity for this receptor over the α1-adrenergic receptor (2,630-fold), and is the only well-studied α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist in its structural family which does not antagonize any variant of the imidazoline receptor. It was shown to possess central α2-adrenoceptor antagonist activity after oral doses in man and was patented as an antidepressant by Glaxo in the early 1980s, but its development was discontinued when the compound failed to show a clear clinical advantage over existing therapies.

Nafimidone is an anticonvulsant drug of the imidazole class. It contains a naphthyl group. It seems to have been discovered by accident during a search for antifungal agents.

MCOPPB is a drug which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the nociceptin receptor, with a pKi of 10.07 and much weaker activity at other opioid receptors. It has only moderate affinity for the mu opioid receptor, weak affinity for the kappa opioid receptor and negligible binding at the delta opioid receptor. In animal studies, MCOPPB produces potent anxiolytic effects, with no inhibition of memory or motor function, and only slight sedative side effects which do not appear until much higher doses than the effective anxiolytic dose range.

WB-4101 is a compound which acts as an antagonist at the α1B-adrenergic receptor. It was one of the first selective antagonists developed for this receptor and was invented in 1969, but is still commonly used in research into adrenergic receptors, especially as a lead compound from which to develop more selective drugs.