Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that lead to damage of the optic nerve, which transmits visual information from the eye to the brain. Glaucoma may cause vision loss if left untreated. It has been called the "silent thief of sight" because the loss of vision usually occurs slowly over a long period of time. A major risk factor for glaucoma is increased pressure within the eye, known as intraocular pressure (IOP). It is associated with old age, a family history of glaucoma, and certain medical conditions or medications. The word glaucoma comes from the Ancient Greek word γλαυκός, meaning 'gleaming, blue-green, gray'.

The ciliary body is a part of the eye that includes the ciliary muscle, which controls the shape of the lens, and the ciliary epithelium, which produces the aqueous humor. The aqueous humor is produced in the non-pigmented portion of the ciliary body. The ciliary body is part of the uvea, the layer of tissue that delivers oxygen and nutrients to the eye tissues. The ciliary body joins the ora serrata of the choroid to the root of the iris.
Oxymetazoline, sold under the brand name Afrin among others, is a topical decongestant and vasoconstrictor medication. It is available over-the-counter as a nasal spray to treat nasal congestion and nosebleeds, as eye drops to treat eye redness due to minor irritation, and as a prescription topical cream to treat persistent facial redness due to rosacea in adults. Its effects begin within minutes and last for up to six hours. Intranasal use for longer than three days may cause congestion to recur or worsen, resulting in physical dependence.

Betaxolol is a selective beta1 receptor blocker used in the treatment of hypertension and angina. It is also a adrenergic blocker with no partial agonist action and minimal membrane stabilizing activity. Being selective for beta1 receptors, it typically has fewer systemic side effects than non-selective beta-blockers, for example, not causing bronchospasm as timolol may. Betaxolol also shows greater affinity for beta1 receptors than metoprolol. In addition to its effect on the heart, betaxolol reduces the pressure within the eye. This effect is thought to be caused by reducing the production of the liquid within the eye. The precise mechanism of this effect is not known. The reduction in intraocular pressure reduces the risk of damage to the optic nerve and loss of vision in patients with elevated intraocular pressure due to glaucoma.
Latanoprost, sold under the brand name Xalatan among others, is a medication used to treat increased pressure inside the eye. This includes ocular hypertension and open-angle glaucoma. Latanaprost is applied as eye drops to the eyes. Onset of effects is usually within four hours, and they last for up to a day.

Timolol is a beta blocker medication used either by mouth or as eye drops. As eye drops it is used to treat increased pressure inside the eye such as in ocular hypertension and glaucoma. By mouth it is used for high blood pressure, chest pain due to insufficient blood flow to the heart, to prevent further complications after a heart attack, and to prevent migraines.
Ocular hypertension is the presence of elevated fluid pressure inside the eye, usually with no optic nerve damage or visual field loss.
Dorzolamide/timolol, sold under the brand name Cosopt among others, is a medication used to treat high pressure inside the eye including glaucoma. It is a combination of dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate. It may be used when a beta blocker, like timolol, is not sufficient alone. It is used as an eye drop.
Apraclonidine (INN), also known under the brand name Iopidine, is a sympathomimetic used in glaucoma therapy. It is an α2 adrenergic receptor agonist and a weak α1 adrenergic receptor agonist.
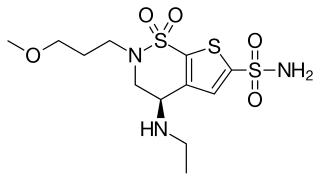
Brinzolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor used to lower intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.

Dorzolamide, sold under the brand name Trusopt among others, is a medication used to treat high pressure inside the eye, including in cases of glaucoma. It is used as an eye drop. Effects begin within three hours and last for at least eight hours. It is also available as the combination dorzolamide/timolol.

Levobunolol is a non-selective beta blocker. It is used topically in the form of eye drops to manage ocular hypertension and open-angle glaucoma.

Bimatoprost, sold under the brand name Lumigan among others, is a medication used to treat high pressure inside the eye including glaucoma. Specifically it is used for open angle glaucoma when other agents are not sufficient. It may also be used to increase the size of the eyelashes. It is used as an eye drop and effects generally occur within four hours.

Travoprost, sold under the brand name Travatan among others, is a medication used to treat high pressure inside the eye including glaucoma. Specifically it is used for open angle glaucoma when other agents are not sufficient. It is used as an eye drop. Effects generally occur within two hours.

Alpha-adrenergic agonists are a class of sympathomimetic agents that selectively stimulates alpha adrenergic receptors. The alpha-adrenergic receptor has two subclasses α1 and α2. Alpha 2 receptors are associated with sympatholytic properties. Alpha-adrenergic agonists have the opposite function of alpha blockers. Alpha adrenoreceptor ligands mimic the action of epinephrine and norepinephrine signaling in the heart, smooth muscle and central nervous system, with norepinephrine being the highest affinity. The activation of α1 stimulates the membrane bound enzyme phospholipase C, and activation of α2 inhibits the enzyme adenylate cyclase. Inactivation of adenylate cyclase in turn leads to the inactivation of the secondary messenger cyclic adenosine monophosphate and induces smooth muscle and blood vessel constriction.
Brimonidine/timolol, sold under the brand name Combigan among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication eye drop used for the treatment of glaucoma. It is a combination of brimonidine and timolol.

Tafluprost is a prostaglandin analogue. It is used topically to control the progression of open-angle glaucoma and in the management of ocular hypertension, alone or in combination with other medication. It reduces intraocular pressure by increasing the outflow of aqueous fluid from the eyes.
Latanoprost/timolol, sold under the brand name Xalacom, is a combination drug used for the treatment of glaucoma, consisting of latanoprost and timolol.
Brinzolamide/brimonidine, sold under the brand name Simbrinza, is a fixed-dose combination medication used to reduce intra-ocular pressure in adults with ocular hypertension or in those with an eye condition known as open-angle glaucoma. It contains brinzolamide and brimonidine tartrate. It is used as an eye drop.
Posner–Schlossman syndrome (PSS) also known as glaucomatocyclitic crisis (GCC) is a rare acute ocular condition with unilateral attacks of mild granulomatous anterior uveitis and elevated intraocular pressure. It is sometimes considered as a secondary inflammatory glaucoma.