| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
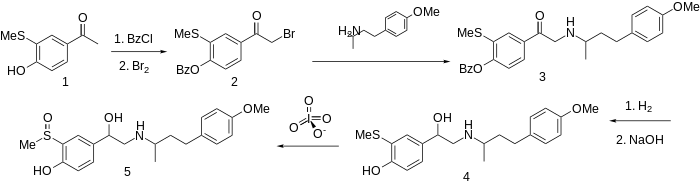
| IUPAC name 4-[1-Hydroxy-2-[4-(4-methoxyphenyl)butan-2-ylamino]ethyl]-2-methylsulfinylphenol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H27NO4S | |
| Molar mass | 377.50 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
This article needs additional citations for verification .(March 2021) |
Sulfinalol is a beta adrenergic receptor antagonist. [1]