| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
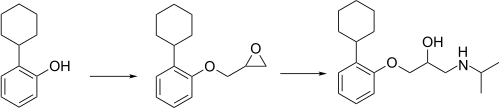
| IUPAC name 1-(2-Cyclohexylphenoxy)-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propan-2-ol | |
| Other names Esprolol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H29NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 291.435 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Exaprolol is a beta-adrenoceptor antagonist. [1]