The adrenergic receptors or adrenoceptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are targets of many catecholamines like norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) produced by the body, but also many medications like beta blockers, beta-2 (β2) agonists and alpha-2 (α2) agonists, which are used to treat high blood pressure and asthma, for example.
Alpha-1 blockers constitute a variety of drugs that block the effect of catecholamines on alpha-1-adrenergic receptors. They are mainly used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), hypertension and post-traumatic stress disorder. Alpha-1 adrenergic receptors are present in vascular smooth muscle, the central nervous system, and other tissues. When alpha blockers bind to these receptors in vascular smooth muscle, they cause vasodilation.
The alpha-2 (α2) adrenergic receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) associated with the Gi heterotrimeric G-protein. It consists of three highly homologous subtypes, including α2A-, α2B-, and α2C-adrenergic. Some species other than humans express a fourth α2D-adrenergic receptor as well. Catecholamines like norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) signal through the α2-adrenergic receptor in the central and peripheral nervous systems.

Alpha-adrenergic agonists are a class of sympathomimetic agents that selectively stimulates alpha adrenergic receptors. The alpha-adrenergic receptor has two subclasses α1 and α2. Alpha 2 receptors are associated with sympatholytic properties. Alpha-adrenergic agonists have the opposite function of alpha blockers. Alpha adrenoreceptor ligands mimic the action of epinephrine and norepinephrine signaling in the heart, smooth muscle and central nervous system, with norepinephrine being the highest affinity. The activation of α1 stimulates the membrane bound enzyme phospholipase C, and activation of α2 inhibits the enzyme adenylate cyclase. Inactivation of adenylate cyclase in turn leads to the inactivation of the secondary messenger cyclic adenosine monophosphate and induces smooth muscle and blood vessel constriction.

Cirazoline is a full agonist at the α1A adrenergic receptor, a partial agonist at both the α1B and α1D adrenergic receptors, and a nonselective antagonist to the α2 adrenergic receptor. It is believed that this combination of properties could make cirazoline an effective vasoconstricting agent.

The alpha-2C adrenergic receptor, also known as ADRA2C, is an alpha-2 adrenergic receptor, and also denotes the human gene encoding it.

The alpha-1D adrenergic receptor, also known as ADRA1D, is an alpha-1 adrenergic receptor, and also denotes the human gene encoding it.

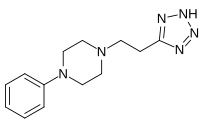
Idazoxan (INN) is a drug which is used in scientific research. It acts as both a selective α2 adrenergic receptor antagonist, and an antagonist for the imidazoline receptor. Idazoxan has been under investigation as an antidepressant, but it did not reach the market as such. More recently, it is under investigation as an adjunctive treatment in schizophrenia. Due to its alpha-2 receptor antagonism it is capable of enhancing therapeutic effects of antipsychotics, possibly by enhancing dopamine neurotransmission in the prefrontal cortex of the brain, a brain area thought to be involved in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia.

Abanoquil (INN) is an α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist.

Alpha-blockers, also known as α-blockers or α-adrenoreceptor antagonists, are a class of pharmacological agents that act as antagonists on α-adrenergic receptors (α-adrenoceptors).

Efaroxan is an α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist and antagonist of the imidazoline receptor.
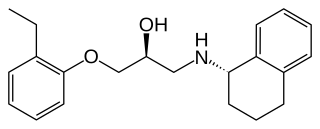
SR 59230A is a selective antagonist of the beta-3 adrenergic receptor, but was subsequently shown to also act at α1 adrenoceptors at high doses. It has been shown to block the hyperthermia produced by MDMA in animal studies.

Monatepil is a calcium channel blocker and α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist used as an antihypertensive.

Nantenine is an alkaloid found in the plant Nandina domestica as well as some Corydalis species. It is an antagonist of both the α1-adrenergic receptor and the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor, and blocks both the behavioral and physiological effects of MDMA in animals.

Imiloxan is a drug which is used in scientific research. It acts as a selective antagonist for the α2B adrenergic receptor, and has been useful for distinguishing the actions of the different α2 adrenergic subtypes.

L-765,314 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist of the α1-adrenergic receptor subtype α1B. It has mainly been used to investigate the role of α1B-adrenergic receptors in the regulation of blood pressure. The α1B receptor is also thought to have an important role in the brain; however, L-765,314 does not cross the blood–brain barrier.
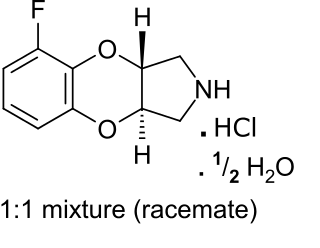
Fluparoxan is a potent α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist with excellent selectivity for this receptor over the α1-adrenergic receptor (2,630-fold), and is the only well-studied α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist in its structural family which does not antagonize any variant of the imidazoline receptor. It was shown to possess central α2-adrenoceptor antagonist activity after oral doses in man and was patented as an antidepressant by Glaxo in the early 1980s, but its development was discontinued when the compound failed to show a clear clinical advantage over existing therapies.

Domesticine is an α1D-adrenergic receptor antagonist.

Pelanserin (TR2515) is an antagonist of the 5-HT2 and α1-adrenergic receptors.

WB-4101 is a compound which acts as an antagonist at the α1B-adrenergic receptor. It was one of the first selective antagonists developed for this receptor and was invented in 1969, but is still commonly used in research into adrenergic receptors, especially as a lead compound from which to develop more selective drugs.