 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H21NO4 |
| Molar mass | 279.336 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Alfurolol is a beta blocker. [1] [2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H21NO4 |
| Molar mass | 279.336 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Alfurolol is a beta blocker. [1] [2]
Monosaccharides, also called simple sugars, are the simplest form of sugar and the most basic units (monomers) of carbohydrates. The general formula is C
nH
2nO
n, albeit not all molecules fitting this formula are carbohydrates. They are usually colorless, water-soluble, and crystalline solids. Contrary to their name (sugars), only some monosaccharides have a sweet taste.

In chemistry, an enantiomer is one of two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other that are non-superposable, much as one's left and right hands are mirror images of each other that cannot appear identical simply by reorientation. A single chiral atom or similar structural feature in a compound causes that compound to have two possible structures which are non-superposable, each a mirror image of the other. Each member of the pair is termed an enantiomorph ; the structural property is termed enantiomerism. The presence of multiple chiral features in a given compound increases the number of geometric forms possible, though there may still be some perfect-mirror-image pairs.

A Zeppelin bend is an end-to-end joining knot formed by two symmetrically interlinked overhand knots. It is stable, secure, and highly resistant to jamming. It is also resistant to the effects of slack shaking and cyclic loading.
An international nonproprietary name (INN) is an official generic and non-proprietary name given to a pharmaceutical drug or an active ingredient. INNs are intended to make communication more precise by providing a unique standard name for each active ingredient, to avoid prescribing errors. The INN system has been coordinated by the World Health Organization (WHO) since 1953.

In geometry, a figure is chiral if it is not identical to its mirror image, or, more precisely, if it cannot be mapped to its mirror image by rotations and translations alone. An object that is not chiral is said to be achiral.

In chemistry, a molecule or ion is called chiral if it cannot be superposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotations and translations. This geometric property is called chirality. The terms are derived from Ancient Greek χείρ (cheir), meaning "hand"; which is the canonical example of an object with this property.
A chiral phenomenon is one that is not identical to its mirror image. The spin of a particle may be used to define a handedness, or helicity, for that particle, which, in the case of a massless particle, is the same as chirality. A symmetry transformation between the two is called parity transformation. Invariance under parity transformation by a Dirac fermion is called chiral symmetry.

Enantioselective synthesis, also called asymmetric synthesis, is a form of chemical synthesis. It is defined by IUPAC as: a chemical reaction in which one or more new elements of chirality are formed in a substrate molecule and which produces the stereoisomeric products in unequal amounts.
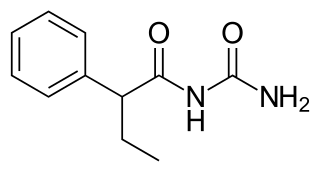
Pheneturide, also known as phenylethylacetylurea, is an anticonvulsant of the ureide class. Conceptually, it can be formed in the body as a metabolic degradation product from phenobarbital. It is considered to be obsolete and is now seldom used. It is marketed in Europe, including in Poland, Spain and the United Kingdom. Pheneturide has a similar profile of anticonvulsant activity and toxicity relative to phenacemide.

Racemoramide, or simply moramide, is an opioid analgesic and a racemic mixture of the substances dextromoramide and levomoramide, two enantiomers of a chiral molecule.
Adaprolol is a beta blocker.

Ancarolol is a beta blocker.
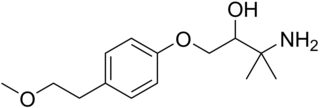
Arnolol is a beta blocker.
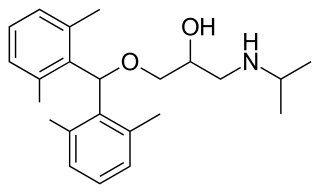
Xipranolol is a beta blocker.

Xibenolol is a beta blocker.

Chirality is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word chirality is derived from the Greek χειρ (kheir), "hand," a familiar chiral object.
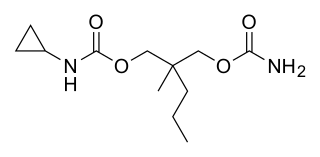
Lorbamate is a muscle relaxant and tranquilizer of the carbamate family which was never marketed.
Drug nomenclature is the systematic naming of drugs, especially pharmaceutical drugs. In the majority of circumstances, drugs have 3 types of names: chemical names, the most important of which is the IUPAC name; generic or nonproprietary names, the most important of which are the International Nonproprietary Names (INNs); and trade names, which are brand names. Under the INN system, generic names for drugs are constructed out of affixes and stems that classify the drugs into useful categories while keeping related names dinstinguishable. A marketed drug might also have a company code or compound code.
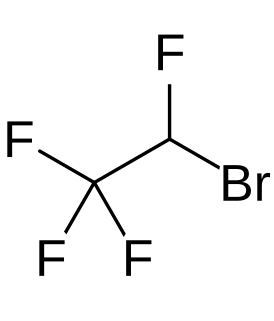
Teflurane is a halocarbon drug which was investigated as an inhalational anesthetic but was never marketed. Its clinical development was terminated due to a high incidence of cardiac arrhythmias in patients, similarly to the cases of halopropane and norflurane.

In nuclear physics, ab initio methods seek to describe the atomic nucleus from the bottom up by solving the non-relativistic Schrödinger equation for all constituent nucleons and the forces between them. This is done either exactly for very light nuclei or by employing certain well-controlled approximations for heavier nuclei. Ab initio methods constitute a more fundamental approach compared to e.g. the nuclear shell model. Recent progress has enabled ab initio treatment of heavier nuclei such as nickel.
| | This antihypertensive-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |