 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
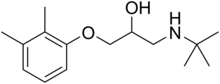
| Formula | C15H25NO2 |
| Molar mass | 251.370 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Xibenolol is a beta blocker. [1] [2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H25NO2 |
| Molar mass | 251.370 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Xibenolol is a beta blocker. [1] [2]

2,3-Xylenol [526-75-0] (1) And 1-Tert-Butyl-3-Azetidinol [13156-04-2] (2).
In the conventional way though, epichlorohydrin and tert-butylamine sequentially.

Sotalol, sold under the brand name Betapace among others, is a medication used to treat and prevent abnormal heart rhythms. It is only recommended in those with significant abnormal heart rhythms due to potentially serious side effects. Evidence does not support a decreased risk of death with long term use. It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein.

Rimantadine is an orally administered antiviral drug used to treat, and in rare cases prevent, influenzavirus A infection. When taken within one to two days of developing symptoms, rimantadine can shorten the duration and moderate the severity of influenza. Rimantadine can mitigate symptoms, including fever. Both rimantadine and the similar drug amantadine are derivates of adamantane. Rimantadine is found to be more effective than amantadine because when used the patient displays fewer symptoms. Rimantadine was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1994.

Tamsulosin, sold under the brand name Flomax among others, is a medication used to treat symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and chronic prostatitis and to help with the passage of kidney stones. The evidence for benefit with a kidney stone is better when the stone is larger. It is taken by mouth.
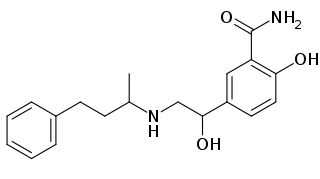
Labetalol is a medication used to treat high blood pressure and in long term management of angina. This includes essential hypertension, hypertensive emergencies, and hypertension of pregnancy. In essential hypertension it is generally less preferred than a number of other blood pressure medications. It can be given by mouth or by injection into a vein.

Nebivolol is a beta blocker used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure. As with other β-blockers, it is generally a less preferred treatment for high blood pressure. It may be used by itself or with other blood pressure medication. It is taken by mouth.
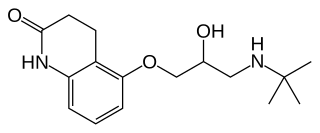
Carteolol is a non-selective beta blocker used to treat glaucoma.
Pramocaine is a topical anesthetic discovered at Abbott Laboratories in 1953 and used as an antipruritic. During research and development, pramocaine hydrochloride stood out among a series of alkoxy aryl alkamine ethers as an especially good topical local anesthetic agent. Pharmacologic study revealed it to be potent and of low acute and subacute toxicity, well tolerated by most mucous membranes and of a low sensitizing index in humans. Like other local anesthetics, pramocaine decreases the permeability of neuronal membranes to sodium ions, blocking both initiation and conduction of nerve impulses. Depolarization and repolarization of excitable neural membranes is thus inhibited, leading to numbness.
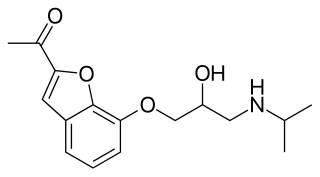
Befunolol (INN) is a beta blocker with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity used in the management of open-angle glaucoma. It also acts as a β adrenoreceptor partial agonist. Befunolol was introduced in Japan in 1983 by Kakenyaku Kako Co. under the trade name Bentos.

Idazoxan (INN) is a drug which is used in scientific research. It acts as both a selective α2 adrenergic receptor antagonist, and an antagonist for the imidazoline receptor. Idazoxan has been under investigation as an antidepressant, but it did not reach the market as such. More recently, it is under investigation as an adjunctive treatment in schizophrenia. Due to its alpha-2 receptor antagonism it is capable of enhancing therapeutic effects of antipsychotics, possibly by enhancing dopamine neurotransmission in the prefrontal cortex of the brain, a brain area thought to be involved in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia.

Moexipril an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor used for the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure. Moexipril can be administered alone or with other antihypertensives or diuretics.

Denopamine (INN) is a cardiotonic drug which acts as a β1 adrenergic receptor agonist. It is used in the treatment of angina and may also have potential uses in the treatment of congestive heart failure and for clearing pulmonary oedema. It is marketed in Japan under the brand name Kalgut (カルグート) and available as tablets of 5 and 10 mg, and 5% fine granules.
Arotinolol is a medication in the class of mixed alpha/beta blockers. It also acts as a β3 receptor agonist. A 1979 publication suggests arotinolol as having first been described in the scientific literature by Sumitomo Chemical as "β-adrenergic blocking, antiarrhythmic compound S-596".

Landiolol (INN) is an ultra short-acting, β1-superselective intravenous adrenergic antagonist, which decreases the heart rate effectively with less negative effect on blood pressure or myocardial contractility. In comparison to other beta blockers, landiolol has the shortest elimination half-life, ultra-rapid onset of effect, and predictable effectiveness with inactive metabolites. The pure S-enantiomer structure of landiolol is believed to develop less hypotensive side effects in comparison to other β-blockers. This has a positive impact on the treatment of patients when reduction of heart rate without decrease in arterial blood pressure is desired. Landiolol was developed by modifying the chemical structure of esmolol to produce a compound with a higher rate of cardioselectivity and a greater potency without increasing its duration of action. It is sold as landiolol hydrochloride. Based on its positive benefit risk profile, landiolol has been granted the marketing authorization and introduced to the European markets under the brand names Rapibloc, Raploc, Runrapiq, Landibloc mid 2016. Landiolol is available in Japan under the brand names Onoact (50 mg) and Corbeta.
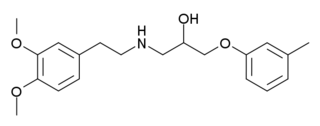
Bevantolol (INN) was a drug candidate for angina and hypertension that acted as both a beta blocker and a calcium channel blocker. It was discovered and developed by Warner-Lambert but in January 1989 the company announced that it had withdrawn the New Drug Application; the company's chairman said: "Who needs the 30th beta blocker?" As of 2016 it wasn't marketed in the US, UK, or Europe and the authors of a Cochrane review could find no product monograph for it.
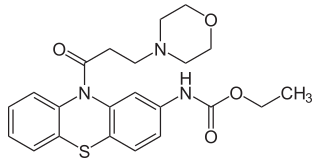
Moracizine or moricizine, sold under the trade name Ethmozine, is an antiarrhythmic of class IC. It was used for the prophylaxis and treatment of serious and life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias, but was withdrawn in 2007 for commercial reasons.

Ezlopitant (INN, code name CJ-11,974) is an NK1 receptor antagonist. It has antiemetic and antinociceptive effects. Pfizer was developing ezlopitant for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome but it appears to have been discontinued.

Alfurolol is a beta blocker.
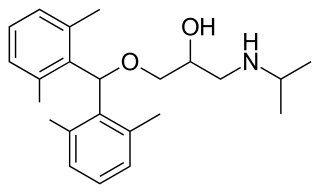
Xipranolol is a beta blocker.

Amixetrine (INN) is a drug that was formerly marketed in France but is now no longer sold. According to various sources it has been said to be an anti-inflammatory, antidepressant, antispasmodic, anticholinergic, antihistamine, and antiserotonergic, but its definitive indications and pharmacology are unclear. The drug was first synthesized in 1969 and was introduced in France in 1972.

Icotinib is a highly selective, first generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI). Icotinib is approved for use in China as first-line monotherapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer with somatic EGFR mutations.