 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Urief, others |
| Other names | KAD-3213, KMD-3213 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a609002 |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | α1 blocker |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 32% |
| Protein binding | 96.6% |
| Metabolism | Liver glucuronidation (UGT2B7-mediated); also minor CYP3A4 involvement |
| Elimination half-life | 13±8 hours[ citation needed ] |
| Excretion | 33.5% Kidney, 54.9% fecal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.248.664 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
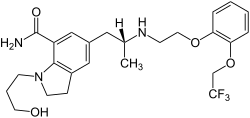
| Formula | C25H32F3N3O4 |
| Molar mass | 495.543 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Silodosin, sold under the brand name Urief among others, is a medication used for the symptomatic treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. [4] [5] It acts as an alpha-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist. [4] [5]
Contents
- Medical uses
- Contraindications
- Side effects
- Interactions
- Pharmacology
- Mechanism of action
- Pharmacokinetics
- History
- Society and culture
- Brand names
- Research
- References
- Further reading
The most common side effect is a reduction in the amount of semen released during ejaculation. [5]

