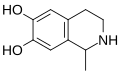
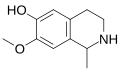
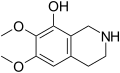
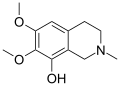
A substituted tetrahydroisoquinoline is a tetrahydroisoquinoline with one or more chemical substituents. [1] [2] Many simple tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids related to mescaline are known and occur naturally in cactus species such as peyote (Lophophora williamsii) and Pachycereus pringlei among many others. [1] [2] [3] [4] Simple tetrahydroisoquinolines may be thought of as cyclized phenethylamines. [1] [2] As an example, anhalinine may be thought of as a cyclized analogue of mescaline. [1] [2] The simple tetrahydroisoquinolines are analogous in concept to the β-carbolines and harmala alkaloids, which can be considered cyclized analogues of tryptamines. [5]
Contents
- List of simple tetrahydroisoquinolines
- Simple tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids
- Synthetic simple tetrahydroisoquinolines
- See also
- Notes
- References
- External links
Some of the simple tetrahydroisoquinolines, for instance pellotine, are known to be pharmacologically active, although none are known to have hallucinogenic activity. [1] [2] [4] Known activities of simple tetrahydroisoquinolines include sedative and hypnotic effects, monoamine oxidase inhibition, and convulsant effects, among various others. [4] [2] In the 2020s, various simple tetrahydroisoquinolines, like pellotine, were identified as serotonin 5-HT1D receptor ligands, serotonin 5-HT6 receptor partial agonists, and/or serotonin 5-HT7 receptor inverse agonists. [6] [7] These actions, such as the serotonin 5-HT6 and/or 5-HT7 receptor interactions, may be involved in the sedative and hypnotic effects of some of these compounds. [6] [7]
Synthetic tetrahydroisoquinoline analogues of phenethylamines, including AMPH-CR, METH-CR, PMMA-CR, DOM-CR, N-methyl-DOM-CR, DOB-CR, TDIQ (MDA-CR), and MDMTHIQ (MDMA-CR), have been developed and characterized. [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] In general, cyclization of stimulant, entactogen, and/or psychedelic phenethylamines into the corresponding tetrahydroisoquinolines results in abolition of the defining effects of these drugs as well as loss of their affinities for monoamine transporters and serotonin 5-HT2 receptors. [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] However, some of the tetrahydroisoquinoline forms, such as TDIQ, show selective affinity for α2-adrenergic receptors and associated effects. [12] [10]