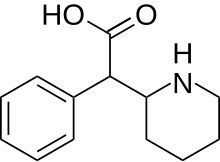
Methylphenidate, sold under the brand names Ritalin and Concerta among others, is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant used medically to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and, to a lesser extent, narcolepsy. It is a primary medication for ADHD ; it may be taken by mouth or applied to the skin, and different formulations have varying durations of effect, commonly ranging from 2–4 hours.

Cocaethylene (ethylbenzoylecgonine) is the ethyl ester of benzoylecgonine. It is structurally similar to cocaine, which is the methyl ester of benzoylecgonine. Cocaethylene is formed by the liver when cocaine and ethanol coexist in the blood. In 1885, cocaethylene was first synthesized, and in 1979, cocaethylene's side effects were discovered.

Valnoctamide has been used in France as a sedative-hypnotic since 1964. It is a structural isomer of valpromide, a valproic acid prodrug; unlike valpromide, however, valnoctamide is not transformed into its homologous acid, valnoctic acid, in vivo.

Iproniazid is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class. It is a xenobiotic that was originally designed to treat tuberculosis, but was later most prominently used as an antidepressant drug. However, it was withdrawn from the market because of its hepatotoxicity. The medical use of iproniazid was discontinued in most of the world in the 1960s, but remained in use in France until its discontinuation in 2015.

Hexobarbital or hexobarbitone, sold both in acid and sodium salt forms as Citopan, Evipan, and Tobinal, is a barbiturate derivative having hypnotic and sedative effects. It was used in the 1940s and 1950s as an agent for inducing anesthesia for surgery, as well as a rapid-acting, short-lasting hypnotic for general use, and has a relatively fast onset of effects and short duration of action. It was also used to murder women prisoners at Ravensbrück concentration camp. Modern barbiturates have largely supplanted the use of hexobarbital as an anesthetic, as they allow for better control of the depth of anesthesia. Hexobarbital is still used in some scientific research.

Ajulemic acid (1',1'-Dimethylheptyl-delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol-11-oic acid) (DMH-D8-THC-11-OIC) (AB-III-56, HU-239, IP-751, CPL 7075, CT-3, JBT-101, Anabasum, Resunab, Lenabasum) is a synthetic cannabinoid that shows anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory effects in pre-clinical studies without causing a subjective "high". Although its design was inspired by a metabolite of delta-9-THC known as delta-9-THC-11-oic acid, ajulemic acid is an analog of the delta-8-THC metabolite delta-8-THC-11-oic acid. It is being developed for the treatment of inflammatory and fibrotic conditions such as systemic sclerosis, dermatomyositis and cystic fibrosis. It does not share the anti-emetic effects of some other cannabinoids, but may be useful for treating chronic inflammatory conditions where inflammation fails to resolve. Side effects include dry mouth, tiredness, and dizziness. The mechanism of action is through activation of the CB2 receptor leading to production of specialized proresolving eicosanoids such as lipoxin A4 and Prostaglandin J2. Studies in animals at doses up to 40 mg/kg show minimal psychoactivity of ajulemic acid, compared to that produced by tetrahydrocannabinol. A composition of ajulemic acid named Lenabasum (formerly Anabasum, Resunab) is being developed by Corbus Pharmaceuticals (formerly JB Therapeutics) for the treatment of orphan chronic life-threatening inflammatory diseases.
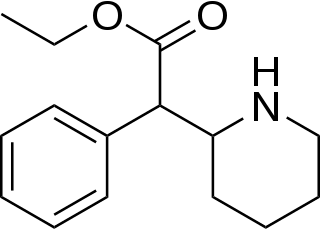
Ethylphenidate (EPH) is a psychostimulant and a close analog of methylphenidate.

Pethidinic acid is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative that is both a metabolite of and a precursor to pethidine (meperidine). It is scheduled by UN Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs. It is a Schedule II Narcotic controlled substance in the United States and has an ACSCN of 9234. The 2014 annual manufacturing quota was 6 grams.
Liver carboxylesterase 1 also known as carboxylesterase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CES1 gene. The protein is also historically known as serine esterase 1 (SES1), monocyte esterase and cholesterol ester hydrolase (CEH). Three transcript variants encoding three different isoforms have been found for this gene. The various protein products from isoform a, b and c range in size from 568, 567 and 566 amino acids long, respectively.

Carboxylesterase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CES2 gene. It is a member of the alpha/beta fold hydrolase family.

Carboxylesterase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CES3 gene.
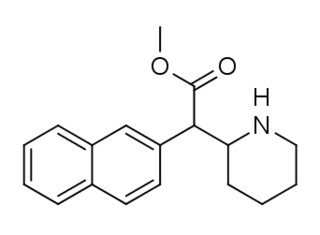
HDMP-28 or methylnaphthidate is a piperidine based stimulant drug, closely related to methylphenidate, but with the benzene ring replaced by naphthalene. It is a potent dopamine reuptake inhibitor, with several times the potency of methylphenidate and a short duration of action, and is a structural isomer of another potent dopamine reuptake inhibitor, N,O-Dimethyl-4-(2-naphthyl)piperidine-3-carboxylate.
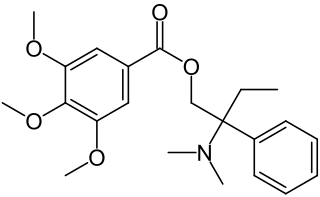
Trimebutine is a drug with antimuscarinic and weak mu opioid agonist effects. It is used for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome and other gastrointestinal disorders.
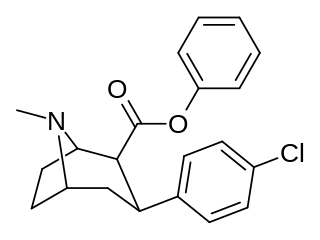
RTI(-4229)-113 is a stimulant drug which acts as a potent and fully selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI). It has been suggested as a possible substitute drug for the treatment of cocaine addiction. "RTI-113 has properties that make it an ideal medication for cocaine abusers, such as an equivalent efficacy, a higher potency, and a longer duration of action as compared to cocaine." Replacing the methyl ester in RTI-31 with a phenyl ester makes the resultant RTI-113 fully DAT specific. RTI-113 is a particularly relevant phenyltropane cocaine analog that has been tested on squirrel monkeys. RTI-113 has also been tested against cocaine in self-administration studies for DAT occupancy by PET on awake rhesus monkeys. The efficacy of cocaine analogs to elicit self-administration is closely related to the rate at which they are administered. Slower onset of action analogs are less likely to function as positive reinforcers than analogues that have a faster rate of onset.

meta-Methoxyamphetamine (MMA), also known as 3-methoxyamphetamine (3-MA), is a stimulant drug from the amphetamine family. It has similar effects in animal drug discrimination tests to the more widely known derivative 4-methoxyamphetamine (PMA), although with a slightly different ratio of monoamine release, being a combined serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine releasing agent rather than a fairly selective serotonin releaser like PMA. 3-Methoxyamphetamine has similarly appeared on the illicit market as a designer drug alternative to MDMA, although far more rarely than its infamous positional isomer. It produces gepefrine, a cardiac stimulant, as one of its major metabolites.
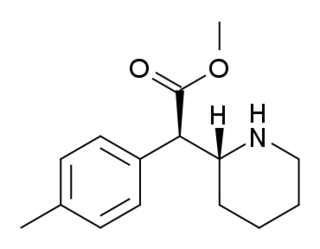
threo-4-Methylmethylphenidate (4-MeTMP) is a stimulant drug related to methylphenidate. It is slightly less potent than methylphenidate and has relatively low efficacy at blocking dopamine reuptake despite its high binding affinity, which led to its investigation as a possible substitute drug for treatment of stimulant abuse. On the other hand, several other simple ring-substituted derivatives of threo-methylphenidate such as the 4-fluoro and 3-chloro compounds are more potent than methylphenidate both in efficacy as dopamine reuptake inhibitors and in animal drug discrimination assays.

Hydroxybupropion, or 6-hydroxybupropion, is the major active metabolite of the antidepressant and smoking cessation drug bupropion. It is formed from bupropion by the liver enzyme CYP2B6 during first-pass metabolism. With oral bupropion treatment, hydroxybupropion is present in plasma at area under the curve concentrations that are as many as 16–20 times greater than those of bupropion itself, demonstrating extensive conversion of bupropion into hydroxybupropion in humans. As such, hydroxybupropion is likely to play a very important role in the effects of oral bupropion, which could accurately be thought of as functioning largely as a prodrug to hydroxybupropion. Other metabolites of bupropion besides hydroxybupropion include threohydrobupropion and erythrohydrobupropion.

HDEP-28 or ethylnaphthidate is a piperidine based stimulant drug, closely related to ethylphenidate, but with the benzene ring replaced by naphthalene. It is even more closely related to HDMP-28, which acts as a potent serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor with several times the potency of methylphenidate and a short duration of action.

Sergolexole (developmental code name LY-281,067) is an ergoline derivative which acts as a selective antagonist of the serotonin 5-HT2 receptors. It has been used for various research applications, but was never developed for medical use.